Addiction psychology is an important field of study for understanding and treating the complex psychological and behavioral issues associated with substance abuse and other forms of addiction. It is a rapidly growing field of study that focuses on understanding the underlying causes of addictive behavior, developing effective interventions and treatments, and finding ways to prevent or reduce the harmful effects of addiction. This article will explore the fundamentals of addiction psychology, discussing the various facets of this field and its importance in today’s world.
Addiction psychology is a specialty field that focuses on the study of addiction, substance use, and related mental health issues. It combines aspects of psychology, neuroscience, and medicine to understand the underlying causes and effects of addiction. Addiction psychologists take a holistic approach to treatment, focusing on the whole person instead of just the addiction itself.
Contents
- Introduction to Addiction Psychology
- Types of Addiction
- Theories of Addiction
- Treatment of Addiction
- Conclusion
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What Is Addiction Psychology?
- What Kind of Training Does an Addiction Psychologist Have?
- What Are the Goals of Addiction Psychology?
- What Are the Common Treatments Used in Addiction Psychology?
- How Do Addiction Psychologists Work with Other Professionals?
- What Are the Benefits of Working with an Addiction Psychologist?
- The Science of Addiction and The Brain
Introduction to Addiction Psychology
Addiction psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on the study of addiction and its effects on individuals, families, and society. It is a multidisciplinary field that includes aspects of psychology, social work, psychiatry, and addiction medicine. Addiction psychology combines research and clinical practice to provide a comprehensive approach to understanding and treating addiction. It seeks to understand the underlying causes of addiction, and to develop effective interventions to help individuals recover and maintain sobriety.
Types of Addiction
Addiction psychology deals with a wide range of addictions, including substance use disorders, gambling addiction, and sex addiction. Substance use disorders include alcohol and drug abuse and dependence, while gambling addiction is characterized by persistent gambling despite negative consequences. Sex addiction is typically associated with compulsive sexual behavior, such as excessive masturbation or engaging in high-risk sexual activities.
Substance Use Disorders
Substance use disorders are characterized by an uncontrollable pattern of substance use despite negative consequences. Substance use disorders can range from mild to severe, depending on the type of substance being abused and the amount of use. Addiction psychologists work with individuals to help them identify their substance use patterns and develop strategies to reduce or eliminate their substance use.
Gambling Addiction
Gambling addiction is characterized by persistent gambling despite negative consequences. Gambling addiction can take many forms, including sports betting, lotteries, and playing slots or video poker. Addiction psychologists work with individuals to help them identify the underlying causes of their gambling behavior and develop strategies to reduce or eliminate their gambling.
Theories of Addiction
Addiction psychology uses a variety of theoretical frameworks to understand and explain addiction. These include biopsychosocial, cognitive-behavioral, and psychodynamic theories. Biopsychosocial theories view addiction as a complex interaction between biological, psychological, and social factors. Cognitive-behavioral theories focus on the individual’s thoughts and behaviors, and how they contribute to addiction. Psychodynamic theories emphasize the unconscious motivations and conflicts underlying addiction.
Biopsychosocial theories view addiction as a complex interaction between biological, psychological, and social factors. Biological factors include genetics, neurotransmitter abnormalities, and drug-induced changes in the brain. Psychological factors include issues such as stress, anxiety, depression, and trauma. Social factors include family dynamics, poverty, social isolation, and cultural issues.
Cognitive-Behavioral Theories
Cognitive-behavioral theories focus on the individual’s thoughts and behaviors, and how they contribute to addiction. This approach emphasizes the role of individual beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors in the development and maintenance of addiction. Cognitive-behavioral interventions involve identifying and changing maladaptive thoughts and behaviors, and developing new coping strategies.
Treatment of Addiction
Addiction psychologists use a variety of evidence-based treatments to help individuals recover from addiction. These treatments include cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, relapse prevention, and 12-step programs. Cognitive-behavioral therapy helps individuals identify and change maladaptive thoughts and behaviors, while motivational interviewing helps individuals develop their own motivation to change. Relapse prevention helps individuals anticipate and manage relapse situations, and 12-step programs provide a supportive environment for recovery.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based treatment that helps individuals identify and change maladaptive thoughts and behaviors. CBT helps individuals become aware of their thoughts and behaviors, and learn to recognize and modify unhealthy patterns. Therapists also help individuals develop new coping strategies and learn to manage their emotions.
Motivational Interviewing
Motivational interviewing is a counseling technique that helps individuals develop their own motivation to change. This approach focuses on exploring and resolving the ambivalence individuals may have about changing their behavior. Therapists help individuals identify their own reasons for wanting to change and develop a plan for making changes.
Conclusion
Addiction psychology is a multidisciplinary field that seeks to understand the underlying causes of addiction and develop effective interventions to help individuals recover and maintain sobriety. Addiction psychologists use a variety of evidence-based treatments to help individuals recover from addiction, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, relapse prevention, and 12-step programs.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Addiction Psychology?
Answer: Addiction psychology is a specialization in clinical psychology that focuses on the study of how individuals become addicted to substances, activities, and behaviors. It seeks to understand the underlying causes and contributing factors of an individual’s addiction, as well as the psychological, social, and physiological effects of addiction. Addiction psychologists work with individuals, families, and communities to develop evidence-based treatments that help people overcome their addictions and lead healthier lives.
What Kind of Training Does an Addiction Psychologist Have?
Answer: An addiction psychologist typically holds a doctoral degree in psychology, such as a Psy.D. or Ph.D., and has specialized training in working with clients with substance use and behavioral addictions. Additionally, addiction psychologists must hold a license in the state in which they practice. To obtain a license, psychologists must complete graduate-level courses and supervised clinical experience, pass a national exam, and meet other state-specific requirements.
What Are the Goals of Addiction Psychology?
Answer: The primary goal of addiction psychology is to help individuals and families affected by addiction to identify and address underlying causes and risk factors for their addiction. Addiction psychologists may also provide evidence-based treatments, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, to help individuals modify their behaviors, cope with emotional and environmental triggers, and develop healthier lifestyle habits. Additionally, addiction psychologists can provide support and guidance to families and friends of those with an addiction to help them better understand and support their loved ones.
What Are the Common Treatments Used in Addiction Psychology?
Answer: Common treatments used in addiction psychology include cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and family therapy. Cognitive-behavioral therapy helps individuals identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors that are associated with their addiction. Motivational interviewing is a client-centered approach that helps individuals explore their ambivalence about their addiction and helps them to find the motivation to make positive changes. Family therapy helps family members understand the addiction and provides them with the tools and support necessary to help their loved one through the recovery process.
How Do Addiction Psychologists Work with Other Professionals?
Answer: Addiction psychologists often work as part of a larger team of health care professionals to provide comprehensive treatment for individuals with addictions. The team may include medical doctors, psychiatrists, counselors, nurses, and social workers. The addiction psychologist may provide assessments and treatment plans, coordinate care with other members of the team, and provide individual and group therapy. The team provides a holistic approach to treatment that is tailored to meet the individual needs of the client.
What Are the Benefits of Working with an Addiction Psychologist?
Answer: Working with an addiction psychologist can provide numerous benefits for individuals with addictions. An addiction psychologist can provide a safe and non-judgmental environment for individuals to gain insight into their addiction, identify underlying causes and contributing factors, and develop evidence-based strategies to overcome their addiction. Additionally, an addiction psychologist can provide ongoing support and guidance to help individuals maintain their sobriety and adopt healthier lifestyle habits.
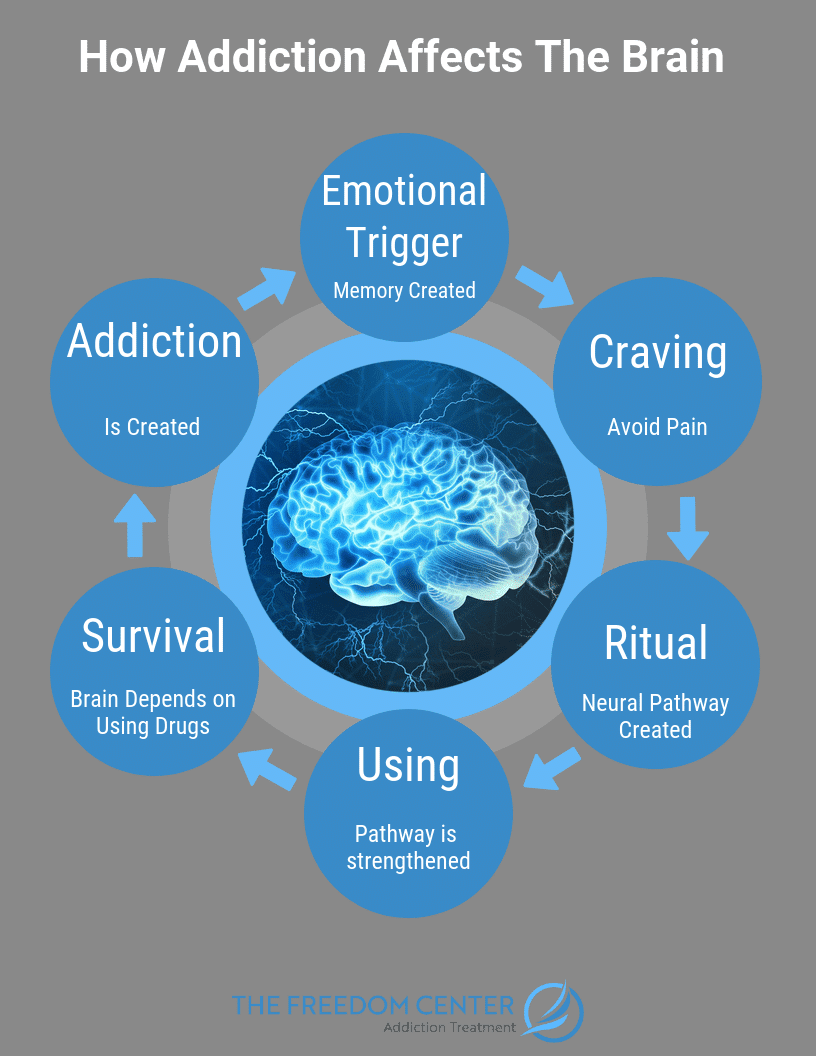
The Science of Addiction and The Brain
Addiction Psychology is a field of study that focuses on understanding the psychological, behavioral, and physiological aspects of addiction. It looks at the underlying factors that contribute to addiction, such as mental health issues, trauma, and environmental factors, and seeks to develop effective strategies for prevention, treatment, and recovery. By understanding the psychological aspects of addiction, psychologists can help individuals with addiction to gain control of their lives and make positive changes. Addiction Psychology has become an integral part of the treatment of addictions, and is an important part of the healing process for those affected by addiction.

