Have you ever been asked to take a drug test as part of an application process for a job or for some other reason? If so, you may have wondered what exactly a drug test is looking for and what is being detected by the test. In this article, we will explore what a drug test can detect and provide some insight into why they are so commonly used. Read on to learn more about drug testing and how it works.
Contents
What Does a Drug Test Detect?
What is a Drug Test?
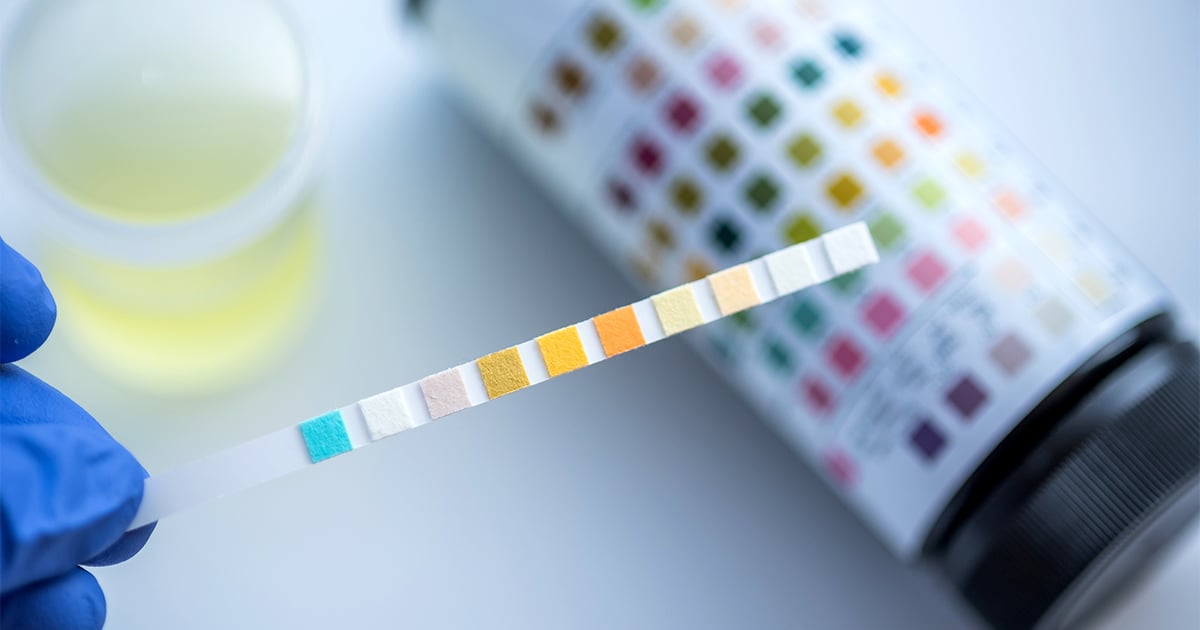
A drug test is a technical analysis of a biological sample, such as urine, hair, blood, sweat, or oral fluid/saliva — to determine the presence or absence of specified parent drugs or their metabolites. Major applications of drug testing include detection of the presence of performance enhancing steroids in sport, employers and parole/probation officers screening for drugs prohibited by law (such as cannabis, cocaine, methamphetamine, and heroin) and police officers testing for the presence and concentration of alcohol (ethanol) in the blood commonly referred to as BAC (blood alcohol content).
Types of Drug Tests
The most common drug tests are urine tests, hair tests, sweat tests, saliva tests, and blood tests. Urine tests are the most common type of drug test used. They can detect a range of substances, including alcohol, cocaine, marijuana, and amphetamines. Hair tests are used to detect the presence of drugs for up to 90 days. Sweat tests are used to detect the presence of drugs for up to 14 days. Saliva tests are used to detect the presence of drugs for up to 72 hours. Blood tests are the most accurate type of drug test, but they can only detect the presence of drugs for up to 24 hours.
What Drugs Are Tested?
Drug tests typically detect the presence of the following drugs: Amphetamines (such as methamphetamine, MDMA, and ecstasy), Barbiturates, Benzodiazepines (such as Valium and Xanax), Cocaine (including crack cocaine), Marijuana (including THC), Opiates (such as heroin, morphine, and codeine), Phencyclidine (PCP), and Propoxyphene.
How Does a Drug Test Work?
A drug test works by detecting the presence of drugs or their metabolites in the sample being tested. Depending on the type of drug test being conducted, the sample may be a urine, saliva, blood, sweat, or hair sample. The sample is then analyzed using a variety of methods, such as immunoassay, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, or high-performance liquid chromatography.
Urine Tests
Urine tests are the most common type of drug test and are used to detect the presence of drugs or their metabolites. Urine samples are collected in a clean and secure environment and tested for the presence of drugs. Urine tests are relatively easy to administer and can detect the presence of drugs for up to a few days after use.
Saliva Tests
Saliva tests are used to detect the presence of drugs or their metabolites in a person’s saliva. Saliva tests are less invasive than urine tests and can detect the presence of drugs for up to 72 hours after use. However, they are not as reliable as urine tests and can be prone to false positives.
What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Drug Tests?
Advantages
Drug tests can detect the presence of drugs or their metabolites in the body, allowing for early detection of drug use and allowing for appropriate intervention. Drug tests can also be used to detect drug abuse, allowing for early treatment and prevention of further drug use.
Disadvantages
Drug tests can be expensive and time-consuming to administer and analyze. They can also be prone to false positives and false negatives, resulting in inaccurate results. Additionally, drug tests can be invasive and may not be able to detect the presence of all drugs.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Drug Test?
A drug test is a technical analysis of a biological sample, such as urine, hair, saliva, sweat, or blood, to determine the presence or absence of specified drugs or their metabolites. Drug tests are used to detect recreational drugs such as marijuana, cocaine, heroin, and amphetamines. They can also be used to detect prescription drugs, such as barbiturates and tranquilizers.
Who May be Subject to Drug Testing?
Drug testing is commonly used in the workplace and in the criminal justice system. In the workplace, drug testing is used to detect drug use by employees. It is also used to help determine if a person has a drug problem and to help employers comply with safety regulations. In the criminal justice system, drug testing is used to identify drug use by individuals who are on probation or parole.
What Types of Tests are Available?
There are several types of drug tests available, including urine, saliva, hair, and blood tests. Urine tests are the most common type of drug tests and are the least expensive and easiest to administer. Saliva tests are typically less expensive than urine tests, but may not detect drugs as quickly. Hair tests can detect drugs for a longer period of time, but are more expensive than urine or saliva tests. Blood tests are the most expensive type of drug test and are typically used for legal purposes.
What Substances Can be Detected?
Drug tests can detect a variety of substances, including marijuana, cocaine, heroin, and amphetamines. In addition, many drug tests can also detect prescription drugs, such as barbiturates and tranquilizers. Some drug tests can also detect synthetic marijuana, known as K2 or Spice.
What is the Detection Period?
The detection period for a drug test depends on the type of drug test and the type of substance being tested. Urine tests are typically the most common type of drug test and can detect drugs for up to 3 days after drug use. Saliva tests can detect drugs for up to 24 hours after drug use. Hair tests can detect drugs for up to 90 days after drug use. Blood tests are typically used for legal purposes and can detect drugs for up to 24 hours after drug use.
What are the Consequences of a Failed Drug Test?
The consequences of a failed drug test depend on the type of test and the individual’s circumstances. In the workplace, a failed drug test may result in disciplinary action or termination of employment. In the criminal justice system, a failed drug test may result in a longer sentence or a revocation of probation or parole. Additionally, a failed drug test may lead to increased scrutiny by law enforcement or the court system.
How Accurate Are Drug Tests?
Drug tests are an important tool to help employers, health care professionals and others detect the presence of drugs in someone’s system. Through the use of urine, hair, saliva or blood samples, drug tests can detect the presence of drugs like marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines, opioids and more. By providing employers, health care professionals and others with a reliable and accurate way to detect the presence of drugs, drug tests are an important and valuable tool to help ensure safety and sobriety for the community.

