Nicotine is one of the most common and widely used drugs in the world today. It is found in cigarettes, e-cigarettes, smokeless tobacco, and other nicotine products. But is nicotine addictive? In this article, we’ll explore the science behind nicotine addiction, its effects on the body, and the impact it has on health. We’ll also look at various treatments available to help people quit nicotine and break free from addiction.
How to Quit Nicotine Addiction:
- Make a plan to quit. Talk to your doctor about quitting strategies.
- Remove all nicotine sources from your home and car.
- Replace your smoking habit with a new, healthier habit like exercising or going for a walk.
- Avoid places, people, and activities that make you want to smoke.
- Seek support from family, friends, and support groups.
Nicotine vs. Tobacco:
| Nicotine | Tobacco |
|---|---|
| A colorless liquid alkaloid that is the active agent in tobacco. | A plant that grows in warm climates and is used to make cigarettes and other tobacco products. |
| Highly addictive. | Not addictive. |
| Can be found in cigarettes, e-cigarettes, and chewing tobacco. | Can be found in cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and smokeless tobacco. |
| Can cause cancer, heart disease, and respiratory diseases. | Can cause cancer, heart disease, and respiratory diseases. |
Contents
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is a natural stimulant found in tobacco plants. It is the main component that makes tobacco products such as cigarettes and cigars so addictive. Nicotine acts on the brain and central nervous system to produce a feeling of pleasure and relaxation. It also increases alertness and can improve concentration.
When people smoke cigarettes, nicotine is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream through the lungs. This causes a rapid increase in blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration. The effects of nicotine can last for several hours and can be very powerful. The body quickly builds up a tolerance to nicotine, meaning that more and more of it is needed to get the same effect.
How Addiction to Nicotine Develops
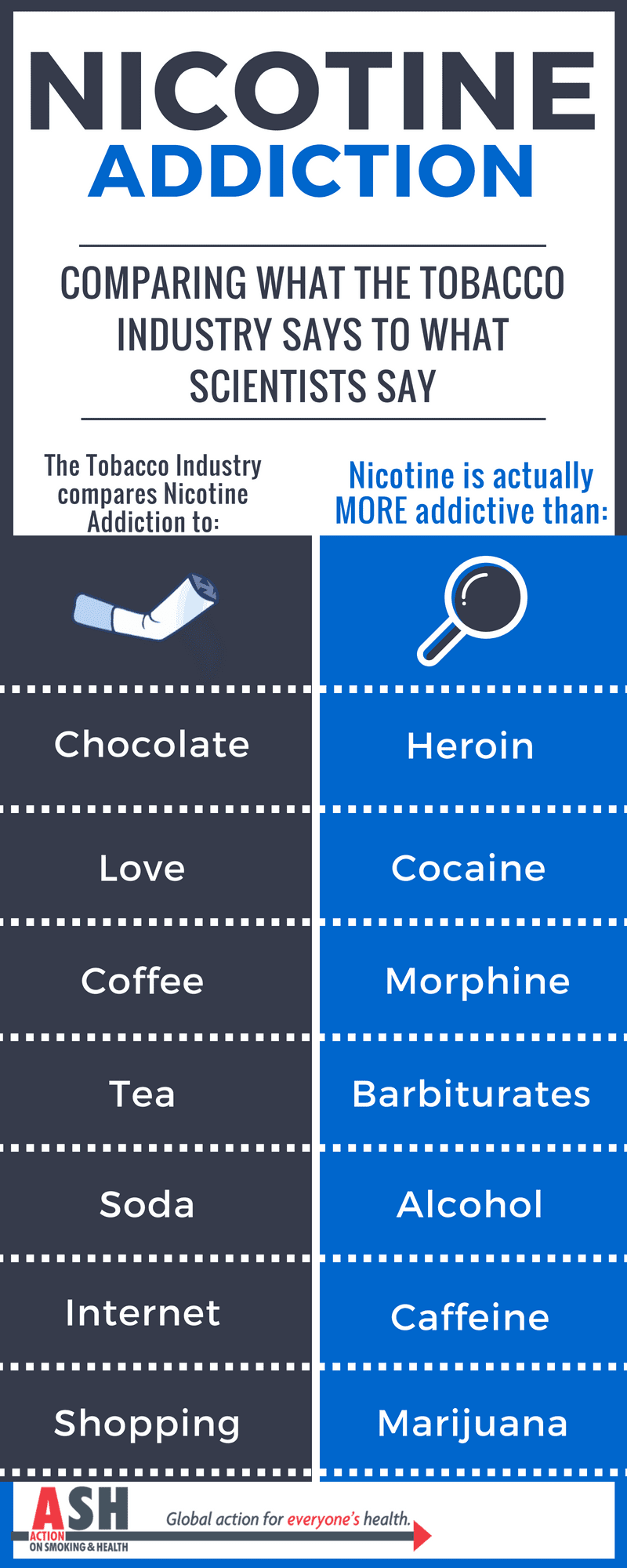
When a person smokes a cigarette, nicotine passes quickly to the brain where it binds to receptors that control feelings of pleasure and reward. This mechanism is the same as with other drugs of abuse, such as heroin and cocaine. As the person smokes more, the brain becomes accustomed to the nicotine and begins to crave it.
At the same time, the body builds up a tolerance to nicotine. This means that more and more nicotine is needed to get the same effect. This leads to increased cravings, which can be hard to resist. As the cravings become stronger, the person is more likely to keep smoking even if they know it’s bad for them.
The physical and psychological dependence on nicotine can be very strong. Smokers may not be aware of how much they rely on nicotine until they try to quit. The withdrawal symptoms that occur when a smoker stops can be very uncomfortable and can make it hard to stay off cigarettes.
Treatment for Nicotine Addiction
There are a number of treatments available for nicotine addiction. Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is one of the most popular. This involves using nicotine patches, gum, or lozenges to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Other treatments include medications, such as bupropion and varenicline, which can reduce cravings and make it easier to quit. Counseling and support groups can also be helpful. These provide a way to talk about smoking and share tips and strategies for quitting.
The Long-Term Effects of Nicotine Addiction
Nicotine addiction can have serious long-term effects. Smoking increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, cancer, and other serious health problems. It can also have a negative impact on fertility and increase the risk of birth defects.
Smokers are also more likely to suffer from depression and anxiety. This is because nicotine affects the brain’s reward system, which can lead to changes in mood.
Preventing Nicotine Addiction
The best way to prevent nicotine addiction is to avoid smoking or using tobacco products. There are also a number of strategies that can help smokers quit. These include setting a quit date, creating a plan, and getting support.
Nicotine replacement therapy and medications can also be helpful. These can make it easier to resist cravings and stay away from cigarettes.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is an alkaloid chemical compound found in the nightshade family of plants, primarily in tobacco. It is the primary psychoactive constituent of cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products, and is responsible for their addictive properties. Nicotine is also found in lower concentrations in other plants, including eggplants, potatoes, and tomatoes.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Brain?
Nicotine activates the reward pathways of the brain, releasing dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is associated with pleasure. This reinforces the habit of smoking and increases the likelihood of addiction. Over time, the brain becomes tolerant to nicotine, requiring more and more of it to achieve the same effect. Withdrawal symptoms can occur when the nicotine levels in the brain drop, such as irritability, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating.
Is Nicotine Addictive?
Yes, nicotine is highly addictive. It is estimated that up to 70% of smokers are dependent on nicotine. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, nicotine is just as addictive as heroin, cocaine, and alcohol.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Nicotine Addiction?
Long-term nicotine addiction can lead to an increased risk of developing many serious health conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, and lung disease. Additionally, nicotine addiction can cause social and psychological issues, such as relationship problems, financial difficulties, and decreased productivity.
What Are Some Treatment Options for Nicotine Addiction?
Treatment options for nicotine addiction include nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), medications, counseling, and support groups. NRT involves using products such as patches, gum, or inhalers to reduce the cravings for nicotine. Medications, such as bupropion or varenicline, can also be used to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Counseling and support groups can help people to recognize triggers for smoking and develop strategies for coping with them.
Can Nicotine Addiction Be Cured?
While nicotine addiction can be managed and treated, it is not considered to be curable. Quitting smoking is difficult and can take multiple attempts before it is successful. It is important to have a plan in place to help with the quitting process, such as medications, counseling, and support groups. With the right resources and support, quitting smoking can be successful.
It is clear that nicotine is a highly addictive substance. It can create strong physical and psychological dependence in those who use it, leading to a range of adverse health effects. Nicotine significantly increases the risk of developing serious medical conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and cancer. For this reason, it is essential to be aware of the risks associated with nicotine and to seek help if you or a loved one is struggling with nicotine addiction.

