Lorazepam is a commonly prescribed benzodiazepine medication used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and other mental health conditions. But is Lorazepam an opiate? This question has been asked by many people and is the focus of this article. We’ll explore the facts and answer this question, looking at the evidence to determine if Lorazepam is an opiate. So, let’s find out if Lorazepam is an opiate or not.
No, Lorazepam is not an opiate. It is a benzodiazepine, which is a type of sedative that produces a calming effect. Unlike opiates, which bind to opioid receptors in the brain, benzodiazepines bind to GABA receptors, which produce a sedative effect. Lorazepam is often used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and other mental health disorders. It is not used to treat pain and is not considered an opioid.
Contents
Is Lorazepam a Narcotic?
Lorazepam is a prescription drug that is commonly used to treat anxiety and seizures. It is also sometimes used to help people with insomnia get to sleep. Although it is a common medication, many people wonder whether Lorazepam is a narcotic. The answer is no, Lorazepam is not a narcotic.
Lorazepam is classified as a benzodiazepine, a type of drug used to treat anxiety and other mental disorders. Benzodiazepines work by suppressing the central nervous system and have a calming effect on the body. Unlike narcotics, which are derived from the opium poppy plant, benzodiazepines are synthetic drugs created in a laboratory.
Lorazepam has many uses, from treating anxiety and insomnia to preventing seizures and treating alcohol withdrawal symptoms. It is also sometimes used to treat muscle spasms and mania. However, it is important to note that because of its sedative effects, Lorazepam is only meant to be used for short-term use. Long-term use can lead to dependence and addiction.
What is the Difference Between Opiates and Narcotics?
Many people confuse the terms “opiates” and “narcotics,” but they are not the same thing. Opiates are drugs derived from the opium poppy plant, while narcotics are a broader classification that includes synthetic drugs and opiates.
The most common opiate is morphine, which is used to treat pain. Opiates can also be used to treat a variety of other conditions, such as diarrhea and coughing. Other opiates include codeine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone.
Narcotics are a broader classification of drugs that includes both opiates and synthetic drugs. The most common narcotics are opioids, which are synthetic drugs used to treat pain. Other narcotics include benzodiazepines, such as Lorazepam, barbiturates, and amphetamines.
What are the Side Effects of Lorazepam?
Lorazepam is a powerful drug and can cause a variety of side effects. The most common side effects include drowsiness, confusion, impaired coordination, and dizziness. Other side effects include nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, dry mouth, and constipation.
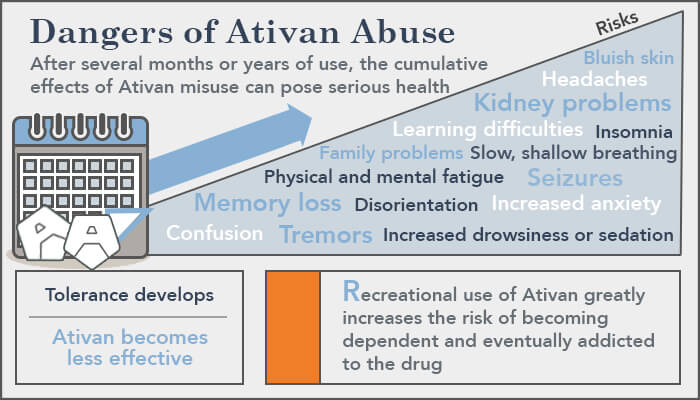
Lorazepam can also cause more serious side effects, including breathing problems, liver damage, and depression. It is important to note that Lorazepam can be habit-forming and can lead to addiction if it is not used as prescribed.
What are the Risks of Taking Lorazepam?
Like any medication, Lorazepam carries a risk of side effects. It is important to understand the potential risks before taking the medication. People with a history of drug or alcohol abuse, mental illness, or liver or kidney disease should be especially cautious when taking Lorazepam.
Lorazepam can also interact with other medications, such as certain antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and antihistamines. It is important to always tell your doctor about any medications you are taking before taking Lorazepam.
What are the Alternatives to Lorazepam?
If you are concerned about the risks of taking Lorazepam, there are a number of alternatives you can consider. Exercise, meditation, and cognitive behavioral therapy are all effective methods of managing anxiety and insomnia.
If you are looking for a medication to treat anxiety or insomnia, there are a number of other medications available. Buspirone, hydroxyzine, and trazodone are all commonly used to treat anxiety. Zolpidem and eszopiclone are commonly used to treat insomnia.
It is important to talk to your doctor before taking any medications. Your doctor can help you decide which medication is right for you and which one is safest for you to take.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Lorazepam?
Lorazepam is a prescription medication used to treat anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and other conditions. It is a benzodiazepine, which is a type of medication that works by calming the brain and nerves. Lorazepam is sometimes used as a sedative before medical procedures. It can also be used to treat alcohol withdrawal. Lorazepam works by increasing the amount of GABA, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate nerve activity in the brain.
2. Is Lorazepam an Opiate?
No, Lorazepam is not an opiate. Opiates are a type of narcotic drug derived from the opium poppy plant. They act on the brain to produce feelings of pain relief and euphoria. Lorazepam is a benzodiazepine, which is a type of medication that acts on the brain to produce a calming effect.
3. What are the Side Effects of Lorazepam?
Common side effects of Lorazepam include drowsiness, confusion, memory problems, coordination problems, slurred speech, constipation, and dry mouth. Less common side effects include nausea, headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, and difficulty urinating. If you experience any of these side effects, contact your doctor right away.
4. How Should Lorazepam be Taken?
Lorazepam should be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor. It is usually taken orally, but it can also be given intravenously or intramuscularly. It is important to follow your doctor’s directions carefully and not to take more or less than prescribed. Do not stop taking Lorazepam without talking to your doctor first.
5. What are the Potential Drug Interactions of Lorazepam?
Lorazepam can interact with certain medications, including certain antibiotics, antifungals, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants. It can also interact with alcohol, which can increase the risk of side effects. Always tell your doctor and pharmacist about any medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
6. Is Lorazepam Addictive?
Yes, Lorazepam can be addictive if it is used for a long period of time or in high doses. People who take Lorazepam may develop a physical and psychological dependence on the drug. If you are taking Lorazepam, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and to never take more or less than prescribed. Do not stop taking Lorazepam without talking to your doctor first.
The Effects of Mixing Benzos and Opiates
Ultimately, Lorazepam is not an opiate, but it is still a powerful drug that should be taken with caution. While it may have some of the same effects as an opiate, its chemical structure and the way it works in the body are vastly different. Lorazepam can be a beneficial medication when monitored and administered properly, however, it should never be used without consulting a medical professional.

