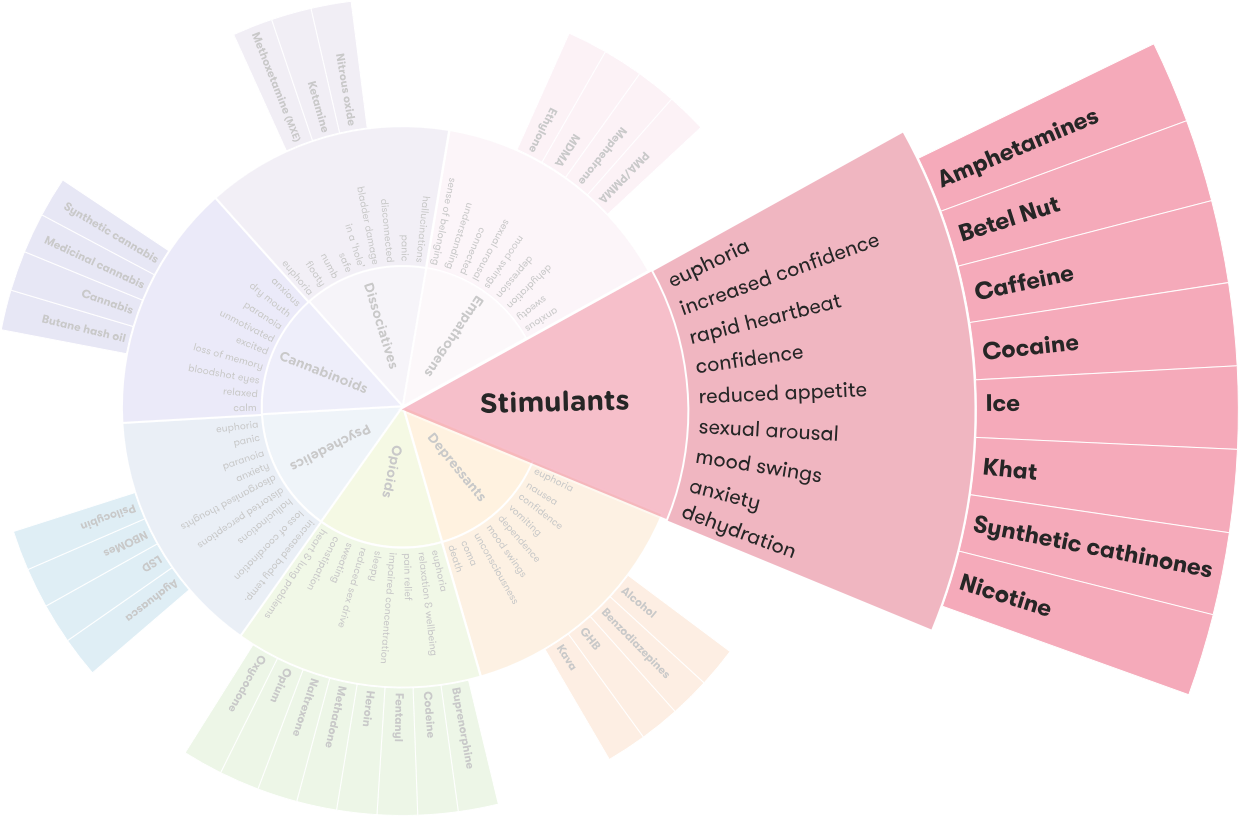
Ice, also known as crystal methamphetamine, is a powerful drug that has caused a great deal of suffering in communities across the globe. It is a potent stimulant that has been linked to a wide range of physical and psychological issues, including addiction. But what kind of drug is it? Is ice a stimulant depressant or hallucinogen? This article will explore the properties of ice, its effects, and the potential risks associated with using it.
Ice is not a stimulant, depressant, or hallucinogen. Ice is the street name for crystal methamphetamine, a powerful and highly addictive stimulant drug that affects the central nervous system. Ice is an illegal drug that is often abused for its euphoric and energizing effects, but it can also have dangerous side effects and long-term consequences. Ice is a white, odorless, bitter-tasting crystalline powder that easily dissolves in water or alcohol.
Contents
Ice is Not a Stimulant, Depressant or Hallucinogen
Ice, also known as methamphetamine, is a powerful and highly addictive stimulant drug. While it is often referred to as a stimulant, depressant or hallucinogen, ice is actually none of these. It is classified as a psychostimulant, meaning it alters brain chemistry to produce a sense of increased alertness, energy and pleasure.
Ice can be taken in many forms, including snorting, smoking and injecting. The drug produces powerful and long-lasting effects, including increased energy and alertness, a greater sense of confidence and improved concentration. It can also lead to paranoia, aggression and violent behavior. The drug can cause physical and psychological dependence and can lead to addiction if used for an extended period of time.
The Effects of Ice on the Brain and Body
Ice causes a significant increase in the levels of dopamine in the brain, which is responsible for feelings of pleasure. This increase in dopamine causes intense feelings of pleasure, but can also lead to a rapid psychological dependence on the drug.
The drug also affects the body in a number of ways. It can lead to an increased heart rate, heightened blood pressure and increased respiration. It can also cause insomnia, anxiety and agitation. Long-term use of the drug can lead to cardiac arrhythmia, stroke and even death.
The Dangers of Ice Addiction
Ice addiction is a serious concern for individuals who use the drug for extended periods of time. The drug can cause a range of physical and psychological health problems, including depression, anxiety and aggression. It can also lead to serious financial problems, as users may become increasingly desperate to obtain the drug.
Ice addiction is also associated with an increased risk of contracting HIV and other blood-borne diseases due to the sharing of needles. The drug can also cause a range of social problems, such as relationship breakdowns and job loss.
Treatment for Ice Addiction
Treatment for ice addiction typically involves a combination of medication, counseling and support. Treatment should be tailored to the individual, and should focus on helping the person to develop healthier coping strategies and to identify and address any underlying issues that may have led to their addiction.
Medication such as antidepressants and mood stabilizers may be prescribed to help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. In some cases, medications such as naltrexone may be prescribed to reduce the effects of the drug and help the person to remain abstinent.
Counseling and Support
Counseling is an important part of treatment for ice addiction. Counseling can help the person to understand their addiction, identify and address any underlying issues that may have contributed to their addiction and develop healthier coping strategies.
Support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous, can also be beneficial for those in recovery from ice addiction. These groups provide a safe and supportive environment in which to share experiences and offer encouragement to others in recovery.
Prevention of Ice Addiction
The best way to prevent ice addiction is to avoid using the drug altogether. If someone is already using the drug, they should seek professional help as soon as possible. Education and awareness of the dangers of ice addiction can also help to prevent the problem from becoming more widespread.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is ice a stimulant, depressant, or hallucinogen?
A1: Ice is a stimulant. Ice is a form of methamphetamine which is a stimulant drug that increases activity in the body by affecting the central nervous system. It increases alertness, attention, and energy, as well as elevating mood. It can lead to increased physical activity, faster breathing, and increased heart rate. It is highly addictive and has been linked with serious physical and psychological health problems.
Q2: What are the effects of using ice?
A2: The effects of using ice vary depending on the amount taken and the individual’s physical and psychological health. Common physical effects include increased heart rate, dilated pupils, and increased blood pressure. Psychological effects can include irritability, anxiety, and paranoia. Long-term use of ice can lead to serious health problems including addiction, mental health issues, and organ damage.
Q3: How is ice used?
A3: Ice is typically taken orally, smoked, or injected. Oral forms of the drug are swallowed, whereas smoking involves inhaling the vaporized drug. Injecting ice is the most dangerous method of use as it increases the risk of overdose, HIV, and hepatitis C.
Q4: Are there any long-term effects of using ice?
A4: Yes, there are a number of long-term effects associated with the use of ice. These can include physical and psychological dependence, memory and cognitive problems, changes in behavior, paranoia, and depression. Long-term use can also lead to organ damage, including damage to the heart, lungs, and kidneys.
Q5: Is ice addictive?
A5: Yes, ice is highly addictive. Over time, users develop a tolerance to the drug, meaning they need to use more and more to achieve the same effects. People who use ice can quickly become dependent on the drug, and may experience withdrawal symptoms when they try to quit.
Q6: What are the risks of using ice?
A6: The risks associated with using ice are numerous. Short-term risks include overdose, mental health problems, and impaired judgment. Long-term risks include addiction, organ damage, and difficulty concentrating. Other risks include social problems, financial difficulties, and legal consequences.
Neurobiological Impact of Stimulants Depressants and Hallucinogens
Ice is a powerful stimulant drug that has the potential to be highly addictive and extremely damaging to the user’s health. It can cause severe physical and mental health problems and can even result in death. It is important to be aware of the dangers of taking ice and to seek help if a person is struggling with addiction. Ice is not a hallucinogen and should not be used as a recreational drug. By understanding the dangers of ice, people can make the right decisions and protect their health.

