Alcoholism is a serious disorder that has far-reaching implications for the health and well-being of those who suffer from it. While most of us are familiar with the physical and social consequences of alcoholism, the psychological aspects of this disorder are often overlooked or misunderstood. In this article, we will explore the psychological aspects of alcoholism, and how they can contribute to this serious disorder. We will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatments for alcoholism, as well as ways to support those who are suffering from it. By understanding the psychological components of alcoholism, we can better understand how to help those who are affected by it.
Yes, alcoholism is a psychological disorder. It is a chronic, progressive, and potentially fatal disease that can have serious physical, mental, and social repercussions. Alcoholism involves a strong physical and psychological dependence on alcohol, and it can cause severe withdrawal symptoms, such as anxiety, tremors, and hallucinations, if not treated properly. People with alcoholism may also experience changes in their personality and behavior, such as depression, mood swings, and poor impulse control. Treatment for alcoholism typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
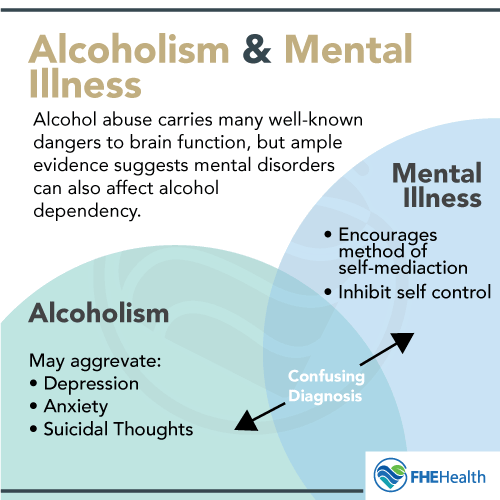
For example:
Contents
What is Alcoholism?
Alcoholism is a chronic and progressive brain disorder characterized by an uncontrollable craving for alcohol. It is a form of substance-related disorder that can lead to physical, psychological, and social problems. It can affect individuals of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. It is estimated that 3.3 million people in the United States are affected by alcoholism.
Alcoholism is a complex condition with many contributing factors. It is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and psychological issues. Alcoholism is also linked to mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
The signs and symptoms of alcoholism vary depending on the individual. Common signs and symptoms include an increased tolerance for alcohol, an inability to stop drinking despite negative consequences, cravings for alcohol, and physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms when not consuming alcohol.
What Causes Alcoholism?
Alcoholism is a complex disorder with many contributing factors. While the exact cause of alcoholism is unknown, researchers believe it is caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
Genetics: Research suggests that certain genes may predispose an individual to alcoholism. For example, some people may have a higher risk of developing alcoholism due to their genetic makeup.
Environment: Environmental factors such as stress, peer pressure, and access to alcohol can also contribute to the development of alcoholism.
Psychology: Psychological issues such as depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders can also increase an individual’s risk of developing alcoholism.
Treatment of Alcoholism
The treatment of alcoholism depends on the individual’s needs and the severity of the addiction. Treatment typically includes a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Medication: Medication can be used to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Commonly used medications include disulfiram, naltrexone, and acamprosate.
Therapy: Therapy can be used to help individuals identify the underlying causes of their addiction and develop coping skills to prevent relapse. Common types of therapy used to treat alcoholism include cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and dialectical behavior therapy.
Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle changes such as avoiding triggers, eating a healthy diet, and increasing physical activity can also be beneficial in treating alcoholism.
Complications of Alcoholism
Alcoholism can lead to a number of physical, psychological, and social complications. It is important to seek treatment for alcoholism as soon as possible to reduce the risk of developing complications.
Physical Complications
Alcoholism can lead to a number of physical health problems such as liver damage, cardiovascular disease, and pancreatitis. It can also increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Psychological Complications
Alcoholism can lead to psychological issues such as depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. It can also lead to an increased risk of suicide.
Social Complications
Alcoholism can lead to social problems such as strained relationships with family and friends, financial difficulties, and job loss. It can also lead to legal problems such as DUIs.
Related Faq
1. What is Alcoholism?
Alcoholism, also known as alcohol use disorder (AUD), is a chronic and progressive mental health disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to drink alcohol, regardless of the consequences. It is a medical condition that can cause physical, psychological, and social problems. Alcoholism can affect any gender, race, or age group, and can range from mild to severe.
2. What are the Symptoms of Alcoholism?
The symptoms of alcoholism can vary from person to person, but generally include a strong craving for alcohol, a loss of control over drinking, physical and psychological dependence on alcohol, and an inability to stop drinking even when it is causing physical and emotional harm. Other signs include drinking more than intended, drinking to cope with difficult emotions, feeling guilty or ashamed about drinking, and neglecting responsibilities due to drinking.
3. What Causes Alcoholism?
The exact cause of alcoholism is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, psychological, and environmental factors. Genetics can play a role in a person’s predisposition to alcoholism, as can psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. Environmental factors such as peer pressure, a family history of alcoholism, or a culture that encourages drinking can also contribute.
4. What are the Treatments for Alcoholism?
Treatment for alcoholism typically consists of a combination of psychotherapy and medication. Psychotherapy can help individuals develop healthier coping skills and make healthier lifestyle choices, while medications such as naltrexone and acamprosate can reduce cravings and help individuals manage their drinking. Inpatient and outpatient treatment programs are also available to provide support and guidance.
5. Is Alcoholism a Psychological Disorder?
Yes, alcoholism is considered a psychological disorder. It is classified as a mental health disorder in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). As with other psychological disorders, alcoholism is characterized by a pattern of behaviors that cause significant impairment or distress.
6. What are the Long-Term Effects of Alcoholism?
The long-term effects of alcoholism can be serious and potentially life-threatening. Long-term health risks include liver disease, pancreatitis, heart disease, cancer, and brain damage. Alcoholism can also lead to cognitive problems, difficulty with relationships, financial troubles, and an increased risk of suicide.
Is Alcoholism a Mental Illness? A Psychologist’s Opinion!
In conclusion, alcoholism is a serious psychological disorder that can have long-term effects on an individual’s mental health. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of alcoholism in order to seek help for oneself or for a loved one. With proper treatment and support, individuals can learn to manage their alcohol use and lead healthier, happier lives.

