Opiates are powerful medications that can be used to treat a variety of ailments, including pain relief and addiction. However, it is important to understand the differences between opiates and other drugs, and to know the proper use and potential side effects of these medications. In this article, we will explore what medications are opiates, the types of opiates, and their potential uses and risks.
Contents
What are Opiate Medications?
Opiate medications are drugs derived from the opium poppy plant, and are used to treat a variety of medical conditions. Opiates are among the oldest and most powerful medications used to treat pain, and have been used for centuries to treat a wide range of medical conditions. As a result, opiate medications are commonly prescribed for chronic pain, acute pain, and even for the management of opioid addiction. In recent years, however, the misuse of opiates has led to an epidemic of opioid misuse and abuse in the United States.
Opiate medications include a wide range of drugs, including natural opioids such as morphine and codeine, as well as synthetic opioids such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, and fentanyl. These medications are generally prescribed to treat pain, but they can also be used to treat other medical conditions such as diarrhea, coughing, and shortness of breath.
How Do Opiate Medications Work?
Opiate medications work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and other parts of the body. When these receptors are activated, they produce feelings of pleasure, relaxation, and pain relief. Opiates also increase levels of dopamine in the brain, which is responsible for the feeling of euphoria associated with opiate use.
The short-term effects of opiate use can include feelings of pleasure and relaxation, as well as a decrease in pain. However, long-term use of opiate medications can lead to a number of negative effects, including addiction, tolerance, and physical and psychological dependence.
Side Effects of Opiate Medications
The long-term use of opiate medications can lead to a number of side effects, including nausea, constipation, drowsiness, confusion, and respiratory depression. These side effects can worsen with long-term use and can be dangerous if not properly managed.
In addition, opiate use can lead to dependence and addiction. Dependence occurs when the body becomes physically dependent on the drug and requires increasing doses to achieve the same effect. Addiction occurs when the person begins to use the drug for non-medical reasons and is unable to control their use of the drug.
Risks of Opiate Use
The misuse and abuse of opiate medications can have serious consequences, including overdose, organ damage, and death. Opiates can also be dangerous when combined with other substances, such as alcohol or other drugs. This can increase the risk of overdose, as well as other serious health complications.
Treatment for Opiate Use
If you or someone you know is struggling with opiate use, it is important to seek help as soon as possible. Treatment for opiate addiction typically involves a combination of medications and counseling. Medications such as methadone and buprenorphine can help to reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings, while counseling can help a person to develop healthy coping skills and address underlying issues related to their opiate use.
Prevention of Opiate Use
The best way to prevent opiate use is to avoid taking opiate medications unless they are absolutely necessary. If you are prescribed an opiate medication, it is important to take it exactly as prescribed and to never share or sell your medication.
Opiate Use and Mental Health
It is important to note that opiate use can have serious consequences for mental health. Long-term use of opiates can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. If you or someone you know is struggling with opiate use, it is important to seek help from a mental health professional.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Opiates?
Opiates are drugs derived from the opium poppy, a flowering plant native to Central and Southwestern Asia. They are the most powerful pain-relieving drugs available, and are often prescribed for severe pain, such as that associated with cancer, surgery, or injury. Opiates work by attaching to opioid receptors in the brain, which then reduce the perception of pain. Common opiates include morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone.
What Are the Side Effects of Opiates?
The most common side effects of opiates include nausea, vomiting, constipation, drowsiness, itching, and slowed breathing. Long-term use can lead to tolerance, physical dependence, and addiction. Opiates can also cause respiratory depression, which can be deadly.
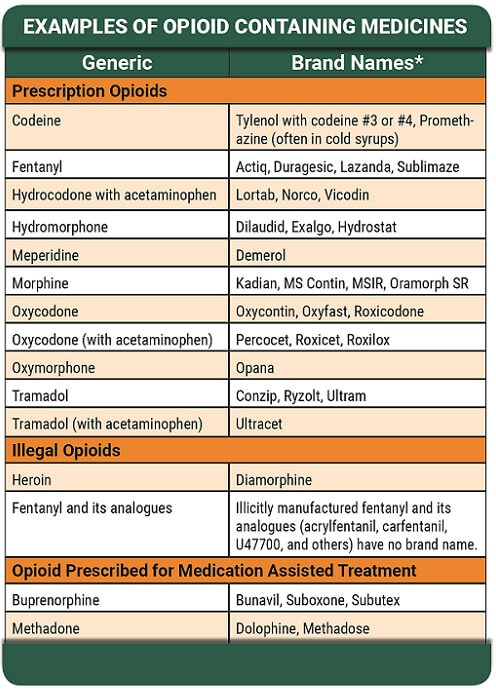
What Medications Contain Opiates?
Many prescription medications contain opiates as the active ingredient. Examples of commonly prescribed opiate-containing medications include oxycodone (OxyContin, Percocet), hydrocodone (Vicodin, Norco), morphine (MS Contin, Kadian), codeine (Tylenol with Codeine), and fentanyl (Duragesic).
Are Opiates Addictive?
Yes, opiates are highly addictive. They create a physical dependence, which means that users must take increasing amounts of the drug to achieve the same effects. This can lead to addiction, which is characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use.
What Are the Risks of Taking Opiates?
The risks of taking opiates include respiratory depression, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and addiction. Long-term use can also lead to tolerance, physical dependence, and overdose.
Are There Non-Opiate Medications for Pain?
Yes, there are several non-opiate medications available for the treatment of pain. These include over-the-counter (OTC) medications such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen, as well as prescription medications such as pregabalin (Lyrica), duloxetine (Cymbalta), and gabapentin (Neurontin).
The best opioid addiction treatment is more opioids
In conclusion, opiates are a powerful class of medications that can be used to treat severe pain, but must be taken with caution. When used responsibly, they can provide relief to those suffering from severe pain, but when abused, they can cause serious and even life-threatening consequences. It is important to be aware of the potential risks and dangers of opiate medications and always follow a doctor’s instructions when taking them.

