Drugs that dilate pupils are often used to treat certain medical conditions, but they can also have serious side effects. This article will explore what drugs dilate pupils, how they work, and the associated risks. From prescription medications to illicit substances, we’ll cover it all and explain the science behind how these drugs affect the pupils of the eye. So, buckle up and get ready to learn about the drugs that can make your pupils larger!
Drugs that dilate pupils include mydriatics, such as cyclopentolate, tropicamide, and phenylephrine. These drugs are used to treat a variety of eye conditions, such as narrowing of the pupil due to injury or infection, as well as glaucoma and cataracts. Mydriatics work by blocking the action of the muscles that control the size of the pupil.
Contents
What Drugs Cause Pupil Dilation?
Pupil dilation, or mydriasis, is a common side effect of many drugs. When pupils enlarge, they can be more sensitive to light and distracting. Understanding the different substances that can lead to pupil dilation can help people to make informed decisions about their drug use. This article covers the drugs that can cause pupil dilation, how they work, and the potential effects of pupil dilation.
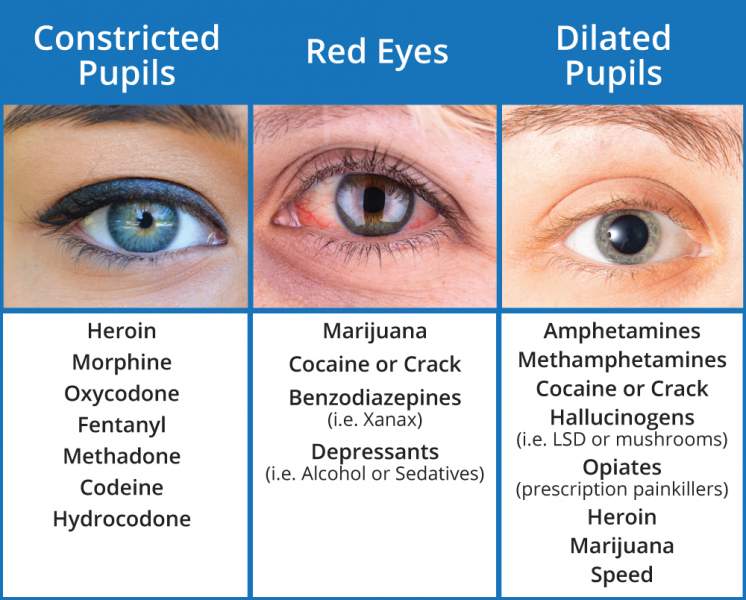
The most common drugs that cause pupil dilation are those that affect the nervous system. Many of these drugs are used to treat medical conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and insomnia. These drugs include benzodiazepines, such as Valium and Xanax; tricyclic antidepressants, such as Elavil and Tofranil; and monoamine oxidase inhibitors, such as Parnate and Nardil. Other drugs that cause pupil dilation are hallucinogens, such as LSD and psilocybin, and stimulants, such as cocaine and methamphetamine.
How do these Drugs Work?
The drugs that cause pupil dilation work by altering the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. Neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, are chemicals that allow nerve cells to communicate with each other. When these neurotransmitters are disrupted, it can lead to changes in behavior, mood, and physiological processes, such as pupil dilation.
The exact mechanism by which certain drugs cause pupil dilation is not fully understood. However, it is believed that the drugs affect the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for controlling the pupil’s size. When this system is stimulated, the pupils can become wider and more sensitive to light.
The Effects of Pupil Dilation
The effects of pupil dilation can vary depending on the drug and the individual. In general, people who have dilated pupils may experience light sensitivity, blurred vision, and difficulty focusing. These effects can be uncomfortable and distracting, and may last for several hours after the drug has worn off.
People who take drugs that cause pupil dilation may also experience other side effects, such as dizziness, nausea, and confusion. In some cases, these side effects can be dangerous and should be monitored by a medical professional. It is important to speak to a doctor before taking any drug that can cause pupil dilation.
Drugs That Cause Pupil Constriction
In addition to drugs that cause pupil dilation, there are also drugs that can cause pupil constriction, or miosis. These drugs are often used to treat glaucoma, an eye condition that can cause permanent vision loss. Some of the most common drugs that can cause pupil constriction are beta blockers, such as Timolol and Propranolol; carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, such as Dorzolamide and Brinzolamide; and cholinergic agonists, such as Pilocarpine and Carbachol.
How do these Drugs Work?
Similar to drugs that cause pupil dilation, drugs that cause pupil constriction work by affecting the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. These drugs act on the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for controlling the pupil’s size. When this system is stimulated, the pupils can become narrower and less sensitive to light.
The Effects of Pupil Constriction
The effects of pupil constriction can vary depending on the drug and the individual. In general, people who have constricted pupils may experience difficulty seeing in dim light, blurred vision, and increased sensitivity to bright light. These effects can be uncomfortable and distracting, and may last for several hours after the drug has worn off.
People who take drugs that cause pupil constriction may also experience other side effects, such as dry mouth, headache, and dizziness. In some cases, these side effects can be dangerous and should be monitored by a medical professional. It is important to speak to a doctor before taking any drug that can cause pupil constriction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Drugs Dilate Pupils?
Answer: Drugs that can dilate pupils include psychedelics, such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), mescaline, and psilocybin; stimulants, such as amphetamines, cocaine, and methylphenidate; and certain opioids, such as meperidine, morphine, and oxycodone. Other drugs that can cause pupil dilation include anticholinergics, antispasmodics, and certain types of antidepressants.
How Do Drugs Dilate the Pupils?
Answer: Drugs that dilate the pupils do so by blocking the effect of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals the muscles in the iris of the eye to constrict, or shrink, the pupils. When the pupils are blocked from receiving this message, they dilate, or widen, instead.
What Are the Effects of Pupil Dilation?
Answer: The effects of pupil dilation can vary depending on the type of drug used. For example, psychedelics can cause visual distortions and an altered sense of time, while stimulants can cause increased energy and alertness. Opioids can cause a feeling of euphoria, while anticholinergics can cause dry mouth, blurred vision, and urinary retention.
Are There Any Potential Side Effects of Pupil Dilation?
Answer: Yes, there can be potential side effects of pupil dilation, depending on the type and strength of the drug used. Common side effects can include dizziness, headaches, nausea, and confusion. In rare cases, pupil dilation can also lead to an increase in blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature.
Can Pupil Dilation Be Reversed?
Answer: Yes, pupil dilation can be reversed. This can be accomplished by administering medications known as “anticholinergics” which can block the action of acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter responsible for pupil constriction. In most cases, the effects of pupil dilation can be reversed within a few minutes after the administration of anticholinergics.
Is Pupil Dilation Dangerous?
Answer: While pupil dilation itself is not necessarily dangerous, it can be a sign of potentially dangerous drug use. For example, pupil dilation can be a sign of excessive alcohol or drug use, or of mixing different drugs together. In addition, pupil dilation can be dangerous if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as confusion, nausea, or dizziness. It is important to seek medical attention if these symptoms are present.
What Drugs Can Cause Pupil Dilation? | More Than Rehab
When it comes to drugs that dilate pupils, it is important to understand the potential risks and benefits associated with each one. While these drugs can provide relief from certain medical conditions, they also come with potential risks such as an increased risk of seizures, blurred vision, and other adverse effects. As such, it is important to consult with a medical professional prior to taking any drug that could potentially dilate pupils.

