Nicotine is one of the most widely used, and most dangerous, drugs in the world. It’s found in cigarettes, e-cigarettes, chewing tobacco, and other smoking products, and its effects on your body can be devastating. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what nicotine does to your body and why it’s so important to avoid it. We’ll explore the short-term and long-term effects of nicotine, the risks associated with its use, and what you can do to protect yourself. So if you’re curious to learn more about nicotine and how it affects your health, keep reading!
Nicotine is a stimulant drug found in tobacco products. It can have both positive and negative effects on the body. Nicotine stimulates the central nervous system, which can increase alertness, concentration and reaction time. It also raises blood pressure and heart rate, and can act as a mild sedative. However, prolonged nicotine use can lead to addiction, increased risk of stroke and heart attack, and potentially cancer.
Contents
What Is Nicotine and What Does It Do to Your Body?
Nicotine is an addictive stimulant found in tobacco products. It is the main component in cigarettes and other forms of tobacco, such as cigars and chewing tobacco. Nicotine acts on the central nervous system, stimulating the release of adrenaline and increasing heart rate and blood pressure. It can also cause a person to feel relaxed and content, as well as give them a physical and mental rush.
When nicotine enters the body, it quickly reaches the brain and binds to certain receptors in the brain. This triggers the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure. This dopamine rush is what gives people the feeling of satisfaction and pleasure when they smoke. However, the effects of nicotine are short-lived and can cause physical and mental addiction.
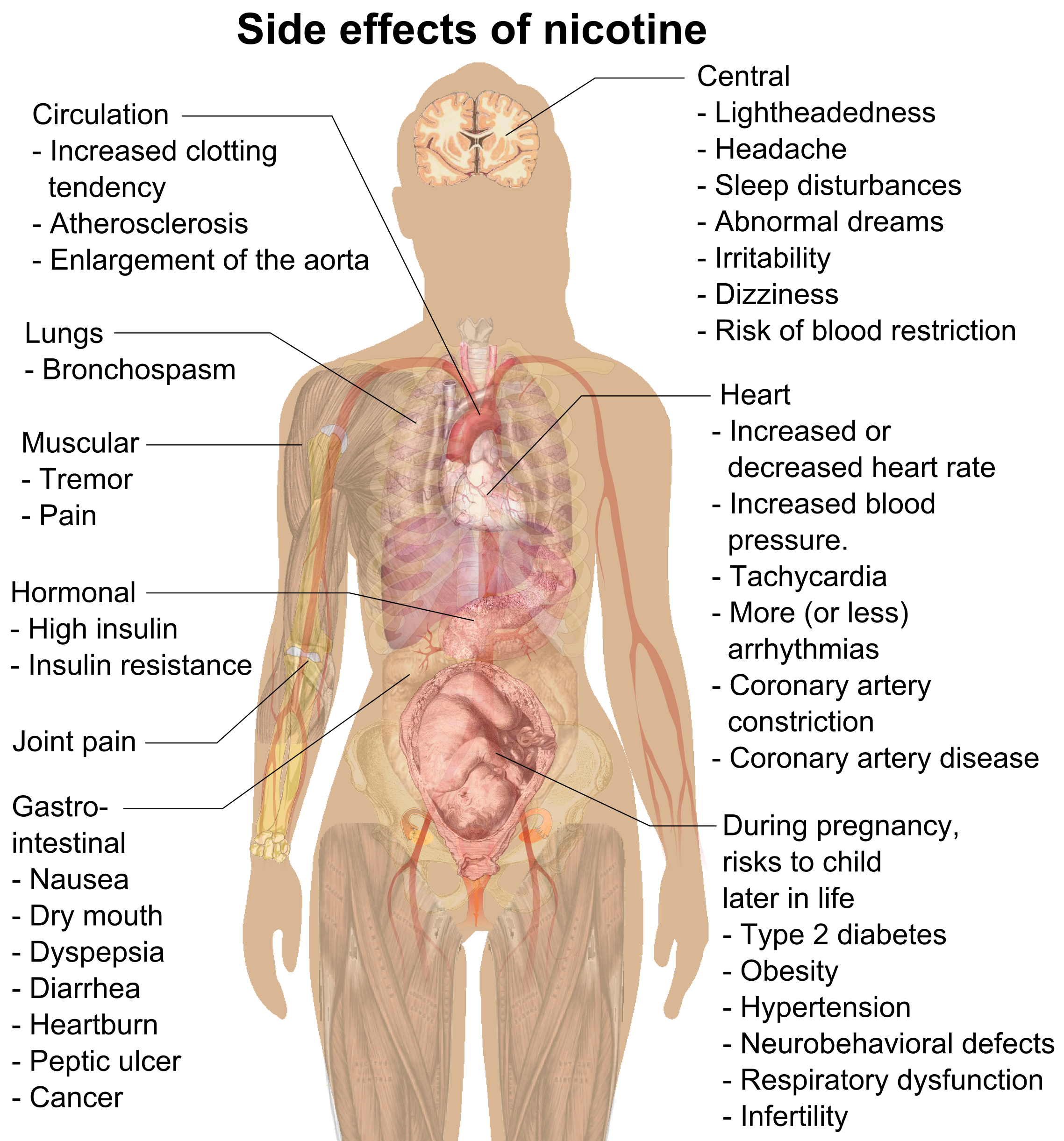
The long-term effects of nicotine are serious and can affect the body in many ways. It can increase the risk of cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other respiratory illnesses. It can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as well as contribute to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
What Are the Short-Term Effects of Nicotine?
The short-term effects of nicotine can be felt almost immediately. It can cause an increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased breathing rate. It can also cause dizziness, nausea, and headaches.
Nicotine can also affect the brain in various ways. It can cause mental alertness and improved concentration. It can also lead to mood swings and irritability. In addition, it can increase the risk of developing anxiety and depression.
Physical Effects
Nicotine has many physical effects on the body. It can increase blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing rate. It can also cause a dry mouth and throat irritation. In addition, it can cause constipation and stomach cramps.
Psychological Effects
Nicotine can also cause psychological effects on the brain. It can lead to increased alertness and improved concentration. However, it can also cause mood swings and irritability. In addition, it can lead to increased anxiety and depression.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Nicotine?
The long-term effects of nicotine can be even more serious than the short-term effects. It can increase the risk of developing cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other respiratory illnesses. It can also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Physical Effects
The long-term effects of nicotine can include an increased risk of developing cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other respiratory illnesses. It can also cause permanent damage to the lungs and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Psychological Effects
The long-term effects of nicotine can also include an increased risk of developing mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. It can also lead to increased irritability and mood swings. In addition, it can lead to decreased concentration and memory problems.
Related Faq
What is Nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine is a stimulant drug present in tobacco and many other plants. It is a highly addictive drug, and is responsible for the feeling of pleasure and relaxation that smokers experience. Nicotine is absorbed through the lungs and enters the bloodstream, where it is carried to the brain and other organs. It affects the brain by activating the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, which is associated with pleasure.
What Are the Short-Term Effects of Nicotine?
Answer: The short-term effects of nicotine include a temporary feeling of pleasure and relaxation, increased alertness and concentration, and improved reaction time. Nicotine also affects the body’s cardiovascular system, increasing heart rate and blood pressure. It can cause nausea, dizziness, and headaches. Nicotine also affects the respiratory system, making it harder to take deep breaths.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Nicotine?
Answer: Over time, regular use of nicotine can lead to a number of long-term effects on the body. These include an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Nicotine can also damage the lungs and respiratory system, leading to a decrease in lung function. It can also cause an increase in cholesterol levels and an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes. In addition, nicotine can affect mental health, leading to an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Brain?
Answer: Nicotine affects the brain by activating the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, which are associated with feelings of pleasure and relaxation. Nicotine also increases the levels of epinephrine, which is a hormone associated with alertness. Over time, nicotine can cause changes in the brain’s structure and function, leading to an increased risk of addiction and other mental health issues.
Can Nicotine Have Beneficial Effects?
Answer: There is some evidence that nicotine can have beneficial effects, including improved cognitive performance, increased alertness, and improved reaction time. However, these benefits must be weighed against the potential risks of nicotine use, which include an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
Can Nicotine Be Addictive?
Answer: Yes, nicotine is highly addictive. Regular use of nicotine can lead to physical and psychological dependence, which can be difficult to overcome. People who are addicted to nicotine may experience withdrawal symptoms when they try to quit, such as irritability, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating.
In conclusion, nicotine has been proven to have serious consequences on your health and well-being. From increased heart rate and blood pressure to increased risk of cancer, nicotine can cause a wide range of negative effects on your body. It is important to be aware of the dangers of nicotine and to make informed decisions about its use. By avoiding nicotine altogether, you can protect yourself from its harmful effects and live a healthier, longer life.

