If you’re like many people, you’ve probably heard about nicotine and its effects on the body, but do you really know what it does to you? From its effects on your heart rate and blood pressure to how it affects your brain chemistry and appetite, nicotine is a powerful substance that can have a major impact on your health. In this article, we’ll explore what nicotine does to you and how it can be dangerous if used in high doses. So read on to learn more about the effects of nicotine and why it’s important to understand them.
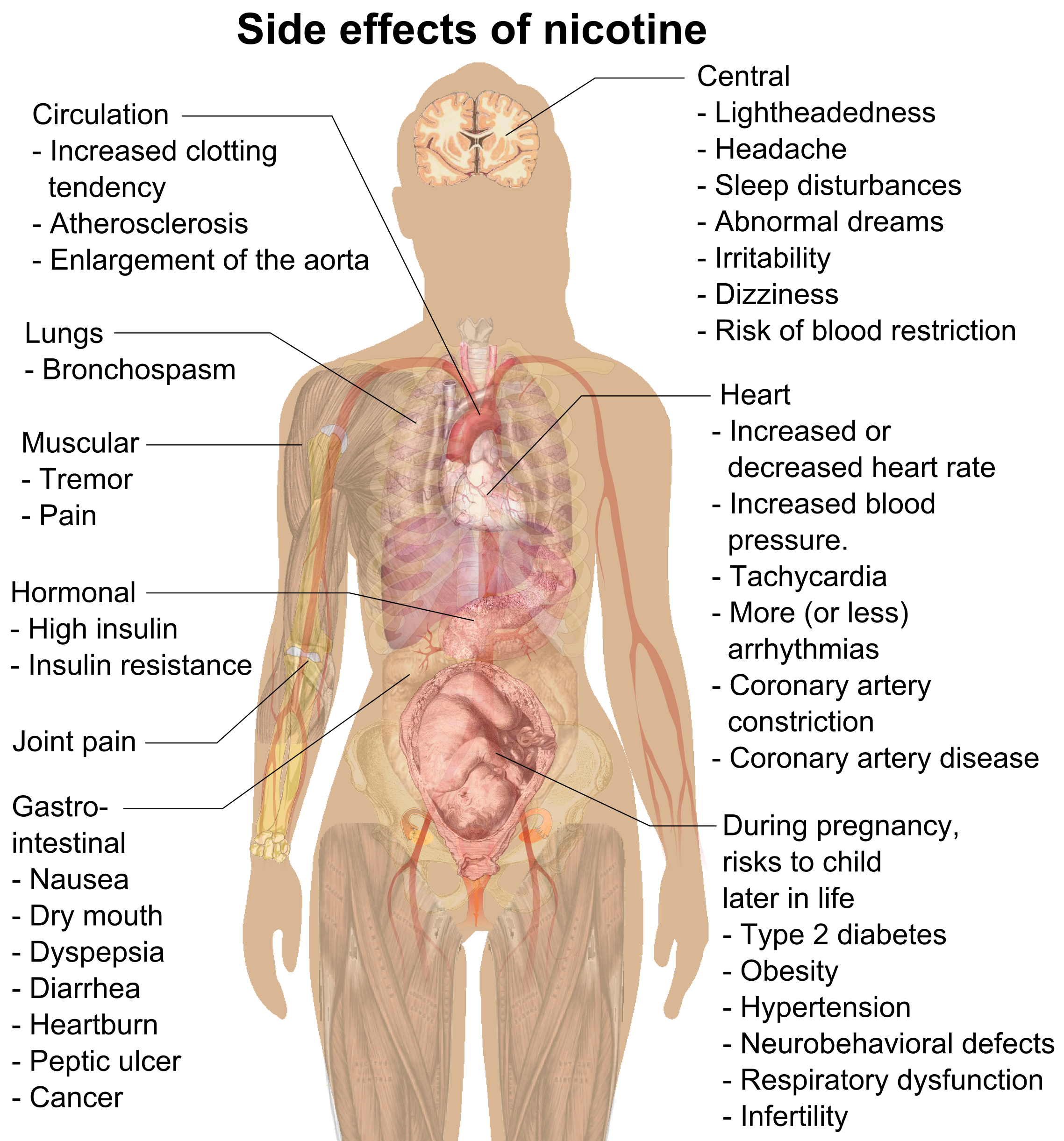
Nicotine is a highly addictive stimulant found in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. It increases alertness and can cause a feeling of euphoria. Long-term effects of nicotine use include increased risk of heart disease and cancer, as well as lung, mouth, and throat problems. Nicotine also affects cognitive performance and can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
Contents
What Does Nicotine Do to You?
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is an addictive alkaloid found in tobacco and certain other plants. It is a stimulant that can produce a variety of effects, both physical and psychological, in humans and other animals. Nicotine is the primary component of cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products, and is what makes them so addictive. The effects of nicotine can be both beneficial and harmful, depending on the dosage and how it is used.
Short-Term Effects of Nicotine
Nicotine has a number of short-term effects on the body, including increased alertness and concentration, improved mood, reduced appetite, and increased heart rate and blood pressure. These effects can last for several hours and are usually felt within minutes of inhalation. Nicotine can also increase the risk of heart attack and stroke, as well as cause insomnia and irritability.
Long-Term Effects of Nicotine
Long-term use of nicotine can lead to an increased risk of some serious health conditions, such as cancer, lung and heart disease, and stroke. Nicotine can also interfere with the body’s ability to absorb certain vitamins and minerals, which can lead to an increased risk of developing other health problems. In addition, long-term nicotine use can lead to an increased risk of addiction and dependence.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Brain?
Nicotine has a direct effect on the brain, affecting both its chemical and electrical activity. When nicotine is inhaled, it quickly reaches the brain and binds to nicotine receptors, which results in a release of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin. This release is what gives users the feeling of pleasure and satisfaction. Over time, the brain becomes accustomed to the presence of nicotine, leading to addiction and dependence.
Nicotine and Cognitive Function
Nicotine has been found to have both positive and negative effects on cognitive function. In the short-term, nicotine has been found to improve focus, concentration, and memory. However, long-term use of nicotine has been associated with a decrease in cognitive function, including memory and concentration.
Nicotine and Mental Health
Nicotine has also been linked to an increase in certain mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. Studies have found that nicotine can increase the risk of developing these conditions, as well as worsen existing mental health conditions.
What Other Effects Does Nicotine Have?
Nicotine and Weight Gain
Nicotine has been linked to weight gain in both short-term and long-term use. In the short-term, nicotine increases the body’s metabolism, leading to an increase in energy expenditure. Over time, however, nicotine can cause the body to become dependent on it for energy, leading to an increase in appetite and, ultimately, weight gain.
Nicotine and Fertility
Nicotine has also been linked to fertility issues in both men and women. Studies have found that nicotine can reduce sperm count and motility in men, as well as increase the risk of miscarriage and birth defects in pregnant women. In addition, nicotine has been linked to an increased risk of infertility in both men and women.
Final Thoughts
Nicotine is an addictive stimulant found in tobacco and certain other plants. Its effects can be both beneficial and harmful, depending on the dosage and how it is used. In the short-term, nicotine can increase alertness and concentration, improve mood, and reduce appetite. In the long-term, however, nicotine can increase the risk of serious health conditions, such as cancer, lung and heart disease, and stroke, as well as interfere with the body’s ability to absorb certain vitamins and minerals. Nicotine can also affect cognitive function and mental health, as well as lead to weight gain and fertility issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine is an addictive chemical found in cigarettes and other tobacco products. It is a stimulant, meaning it increases alertness and energy levels. Nicotine is absorbed through the mouth and lungs when smoking, and it can also be absorbed through the skin when used in patches or gums. Nicotine acts on the brain and nervous system, causing a rush of adrenaline and a release of dopamine, which is a feel-good chemical. Nicotine has been linked to various health risks, including increased risk of stroke, heart attack, cancer, and other health problems.
What are the effects of nicotine on the body?
Answer: Nicotine has a number of short-term effects on the body. These include increased heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration rate, as well as increased alertness and wakefulness. Long-term effects of nicotine can include an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and some types of cancer, as well as an increased risk of addiction. Nicotine can also increase the risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
What are the risks of using nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine is a highly addictive substance and its use can lead to addiction. As nicotine is a stimulant, it can cause a range of physical and psychological side effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate, increased alertness and wakefulness, and increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and some types of cancer. Additionally, nicotine can increase the risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
Is nicotine considered a drug?
Answer: Yes, nicotine is considered a drug. While it is not classified as an illegal drug, it is a highly addictive substance and its use can lead to addiction. Nicotine acts on the brain and nervous system, causing a rush of adrenaline and a release of dopamine, which is a feel-good chemical.
How does nicotine affect the brain?
Answer: Nicotine affects the brain by increasing the release of dopamine, which is a feel-good chemical. It also increases alertness and energy levels and can cause a range of physical and psychological side effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Over time, nicotine can increase the risk of addiction and can have long-term effects on the brain, including an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
What are the long-term effects of nicotine?
Answer: The long-term effects of nicotine include an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and some types of cancer, as well as an increased risk of addiction. Additionally, nicotine can increase the risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems. Additionally, nicotine use can lead to increased tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect, and withdrawal symptoms when quitting.
In conclusion, nicotine is a powerful drug that can have both short-term and long-term effects on your body. It can cause an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, as well as increase your risk for chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Additionally, nicotine can be addictive and lead to serious health consequences if used in large doses over a long period of time. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the potential harms of nicotine and to take steps to protect your health.

