Benzodiazepines are a type of medication commonly prescribed to treat anxiety, insomnia, and other psychological conditions. They have been around for decades, and are some of the most commonly prescribed medications in the world. In this article, we’ll explore what benzodiazepines do, how they work, and why they are so widely used. We’ll also discuss the potential side effects and risks associated with taking benzodiazepines, so you can make an informed decision about whether or not these medications are right for you.
Benzodiazepines are a class of psychoactive drugs that can reduce anxiety, muscle spasms and seizures, and help with insomnia. They work by binding to receptors in the brain and central nervous system, causing a calming effect. Common benzodiazepines include alprazolam (Xanax), clonazepam (Klonopin), diazepam (Valium), and lorazepam (Ativan).
Contents
What are Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines are a type of drug used to treat anxiety, panic attacks, insomnia, and seizures. They work by calming the central nervous system. Benzodiazepines are also known as tranquilizers, sedatives, and hypnotics. They are one of the most commonly prescribed medications in the United States.
Benzodiazepines are classified as central nervous system (CNS) depressants. This means they slow down certain functions in the body, such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. Benzodiazepines can be taken orally, injected, or inhaled.
How do Benzodiazepines Work?
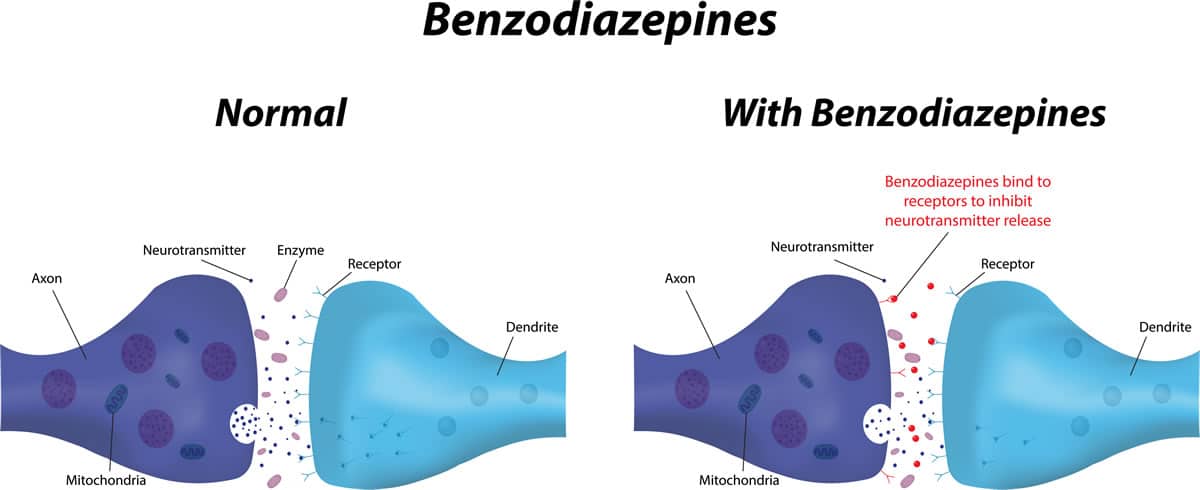
Benzodiazepines work by increasing the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter in the brain. GABA is responsible for regulating muscle tension, and when it is increased, muscles relax and anxiety is reduced.
Benzodiazepines can also reduce the symptoms of insomnia by helping the brain to relax. This can help people to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Side Effects of Benzodiazepines
The most common side effects of benzodiazepines are drowsiness, confusion, and dizziness. Other side effects include headaches, blurred vision, depression, and irritability.
Long-term use of benzodiazepines can lead to physical and psychological dependence. This means that when someone stops taking the drug, they may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and seizures.
Who Should Not Take Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines are not recommended for people with certain medical conditions, such as:
Liver Disease
People with liver disease should not take benzodiazepines because these drugs can accumulate in the body and cause an overdose.
Respiratory Disease
Benzodiazepines can also worsen respiratory conditions such as asthma or COPD.
Pregnancy
Benzodiazepines can cause birth defects and should not be taken by pregnant women.
Alcoholism
Benzodiazepines can be dangerous for people with alcohol use disorders. They can increase the risk of overdose and death.
Uses of Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are most commonly used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. They can also be used to treat certain types of pain, muscle spasms, and alcohol withdrawal.
Anxiety
Benzodiazepines can help reduce the symptoms of anxiety, such as racing thoughts, restlessness, and difficulty focusing. They can also help with panic attacks and phobias.
Insomnia
Benzodiazepines can help people with insomnia fall asleep and stay asleep. They can be used for short-term treatment or long-term treatment, depending on the severity of the insomnia.
Risks of Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines can be addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence. They can also lead to tolerance, meaning that the effects of the drug will lessen over time and higher doses will be needed to achieve the same effect.
People who take benzodiazepines for a long period of time may experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking the drug. These symptoms can include anxiety, insomnia, and seizures.
Drug Interactions
Benzodiazepines can interact with other medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and narcotic pain relievers. This can lead to increased side effects or an increased risk of overdose.
Overdose
Taking too much of a benzodiazepine can lead to an overdose. Symptoms of an overdose include confusion, slurred speech, drowsiness, shallow breathing, and loss of consciousness. An overdose can be fatal and medical help should be sought immediately.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What are Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that act on the brain and central nervous system to produce a calming effect. They are commonly used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and seizures, but can also be used to relieve muscle spasms and alcohol withdrawal. Benzodiazepines work by enhancing the activity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps to reduce the activity of the nerve cells and produce a calming effect.
How Do Benzodiazepines Work?
Benzodiazepines work by increasing the activity of the neurotransmitter GABA, which helps reduce the activity of nerve cells and has a calming effect. The drugs bind to GABA receptors in the brain, which then triggers a cascade of events that leads to the inhibition of the nerve cells. This inhibition causes a decrease in the communication between nerve cells, leading to a decrease in the activity of the cells and a feeling of relaxation.
What Are Some Common Side Effects of Benzodiazepines?
Common side effects of benzodiazepines include drowsiness, confusion, dizziness, impaired coordination, and slurred speech. Other side effects can include increased appetite, nausea, constipation, headache, blurred vision, and dry mouth. Long-term use of benzodiazepines can lead to physical and psychological dependence and can even worsen existing mental health problems.
What Are the Risks of Taking Benzodiazepines?
The use of benzodiazepines can lead to physical and psychological dependence, and long-term use can worsen existing mental health problems. Benzodiazepines can also interact with other drugs, such as alcohol, and can cause dangerous side effects. Taking benzodiazepines with alcohol can lead to slowed breathing and even death.
How Long Do the Effects of Benzodiazepines Last?
The effects of benzodiazepines can last anywhere from a few hours to several days, depending on the dosage and the individual. Short-acting benzodiazepines typically have effects that last up to 4 hours, while longer-acting benzodiazepines can have effects that last up to 24 hours.
Are Benzodiazepines Addictive?
Yes, benzodiazepines can be addictive and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. When taken for long periods of time, benzodiazepines can cause tolerance, which means that the same dose will no longer produce the same effects. Taking higher doses or taking the drug more often can lead to addiction and withdrawal symptoms if the drug is stopped abruptly.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are powerful medications that have a wide range of therapeutic uses, from treating anxiety to seizures. They are highly effective and have a low risk of addiction when taken as prescribed. However, when taken in large amounts or for a long time, benzodiazepines can be dangerous, so it is important to be aware of the risks and only take them as prescribed by a doctor. With careful use and monitoring, benzodiazepines can be an effective and safe treatment option.

