Drugs have become increasingly prevalent in our society, and it can be difficult to understand how they can affect the way our brains work. While some drugs are used for medicinal purposes, others are used for recreational purposes, and both types of drugs can have a significant impact on the way our brains operate. In this article, we will explore what drugs do to your brain and why it is important to understand the effects of drugs on the brain. We will look at how different drugs interact with the brain, what the short-term and long-term effects of drug use can be, and how to reduce the risks associated with using drugs.
Drugs can affect the brain in various ways, from disrupting normal chemical processes to causing irreversible damage. Long-term drug use can lead to changes in the brain’s structure and functioning, making it difficult to think clearly, exercise good judgment, and feel normal without the drug.
Short-term effects can include confusion, impaired judgment, and problems with coordination, while long-term effects can include memory problems, depression and anxiety, and even psychotic symptoms. Drugs can also cause changes in the brain’s reward system, which can lead to addiction.
How Drugs Affect the Brain
Drugs are substances that can alter the way our brain functions and can have a variety of cognitive and physical effects. Drugs can be abused and lead to addiction, a condition that is characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use. Drugs can also have long-term effects on the brain, such as changes in brain structure and function.
The effects of drugs on the brain can vary depending on the type of drug used. Some drugs can cause changes in the brain that may be permanent and can lead to long-term problems with memory, mood, decision-making, and behavior. Other drugs may cause temporary changes in the brain, such as changes in alertness or concentration.
How Drugs Affect Brain Chemistry
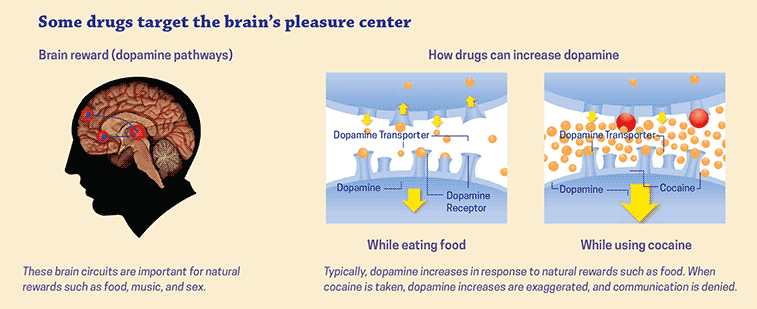
Drugs affect the brain by altering levels of neurotransmitters, the chemicals that carry signals between nerve cells. Drugs can increase or decrease the levels of certain neurotransmitters, which can affect mood and behavior. For example, drugs such as cocaine and methamphetamine can increase the level of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which can lead to feelings of euphoria.
Drugs can also affect the way the brain responds to neurotransmitters. For example, drugs such as opioids can interfere with the brain’s ability to recognize pleasure. This can lead to drug cravings and make it difficult for a person to stop using drugs.
How Drugs Affect Brain Structure
Drugs can also have long-term effects on the brain’s structure. For example, long-term use of drugs such as cocaine and methamphetamine can lead to changes in the brain’s reward system. This can make it difficult for a person to experience pleasure without using drugs.
Drugs can also cause changes in the brain’s structure that are permanent. These changes can lead to a variety of cognitive and physical problems. For example, long-term use of drugs such as alcohol and methamphetamine can cause changes in the brain’s white matter, which can lead to problems with memory and concentration.
How Drugs Affect Brain Function
Drugs can also affect the way the brain functions. For example, long-term use of drugs such as alcohol and benzodiazepines can lead to changes in the brain’s prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for planning and decision-making. This can lead to problems with impulse control and decision-making.
Drugs can also interfere with the brain’s ability to learn and remember. For example, long-term use of drugs such as cocaine and methamphetamine can lead to changes in the brain’s hippocampus, which is responsible for memory. This can lead to problems with memory and learning.
How Drugs Affect Cognitive Performance
Drugs can also affect cognitive performance. For example, long-term use of drugs such as alcohol and marijuana can lead to problems with memory and concentration. This can make it difficult for a person to focus, remember information, and make decisions.
How Drugs Affect Physical Performance
Drugs can also affect physical performance. For example, long-term use of drugs such as opioids can lead to problems with coordination, balance, and strength. This can make it difficult for a person to perform physical activities.
How Drugs Affect Mental Health
Drugs can also affect mental health. For example, long-term use of drugs such as alcohol and marijuana can lead to depression and anxiety. This can lead to problems with mood regulation, making it difficult for a person to cope with stress or anxiety.
How Drugs Affect Behavior
Drugs can also affect behavior. For example, long-term use of drugs such as alcohol and cocaine can lead to problems with aggression and impulsivity. This can lead to risky behavior and make it difficult for a person to control their emotions.
How Drugs Affect Social Life
Drugs can also affect a person’s social life. For example, long-term use of drugs such as alcohol and marijuana can lead to problems with relationships and social interactions. This can make it difficult for a person to maintain relationships and form new ones.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Drug?
A drug is any substance that changes the way the brain and body work. This includes both legal and illegal substances. Common drugs that can be found in the United States include alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, cocaine, prescription medications, and other drugs of abuse.
How Do Drugs Affect the Brain?
Drugs can cause changes in the way the brain functions. They can affect the way we think, feel, and behave. Drugs can also cause changes in the brain’s chemistry, affecting our moods and emotions. Some drugs can even damage the brain and its ability to think, remember, and learn.
What are the Short-Term Effects of Drug Use?
The short-term effects of drug use vary depending on the type of drug and the amount used. Some drugs can cause a person to feel relaxed, energized, or euphoric. Other drugs can cause feelings of confusion, paranoia, and aggression. In addition, drugs can cause physical effects such as changes in heart rate, breathing rate, and body temperature.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Drug Use?
Long-term drug use can lead to a variety of problems. It can affect the brain’s ability to think, remember, and learn. It can also lead to physical health problems, such as an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. Additionally, long-term drug use can lead to social problems, such as an increased risk of homelessness, unemployment, and criminal activity.
What are the Consequences of Drug Use?
The consequences of drug use vary depending on the type of drug and the amount used. Drug use can lead to health problems, social problems, and legal problems. It can also lead to addiction, which can cause a person to lose control of their life. Drug use can also lead to death in some cases.
How Can Drug Use be Prevented?
Drug use can be prevented by educating people about the harms of drug use and the risks of addiction. Additionally, people should be aware of the warning signs of drug use and addiction, and be able to recognize them in themselves and in others. Additionally, people should be encouraged to seek help if they or someone they know is struggling with drug use.
How do drugs affect the brain? – Sara Garofalo
Drugs have a powerful and often damaging effect on the brain. They can cause irreparable damage to the brain, lead to addiction, and even death. It is important to recognize the dangers of drug use and the serious consequences that can arise from it. If you or someone you know is struggling with a drug addiction, it is essential to seek professional help. With the right support, individuals can begin to make healthier choices and take back control of their lives. Drug use can be a destructive force, but it does not have to be. With the right guidance and support, anyone can overcome the challenges of addiction and reclaim their life.

