Drugs can have a powerful and dangerous effect on your mental health and your brain. From mood swings to permanent brain damage, the consequences of drug abuse can be life-altering and devastating. In this article, we’ll explore the various effects that drugs have on the brain, including how they can impact your memory, emotions, concentration, and mental health. We’ll also cover some of the most harmful drugs and the dangers associated with them. By understanding the effects of drugs on your brain, you’ll be better equipped to make informed choices about your health and wellbeing.
Contents
The Direct Effects of Drugs on the Brain
Drugs can have a direct and immediate effect on the brain. By altering the brain’s chemical balance and interfering with its neurotransmitters, drugs can cause changes in mood, behavior, and thinking. Many drugs, such as cocaine, heroin, and marijuana, can be addictive, meaning that users become dependent on the drug and crave it even when it is harmful to them.
Drugs can also have long-term effects on the brain, such as impairing cognitive function, affecting memory and concentration, and even causing permanent brain damage. Depending on the drug, long-term use can also lead to physical and psychological dependence, which can make it difficult to quit.
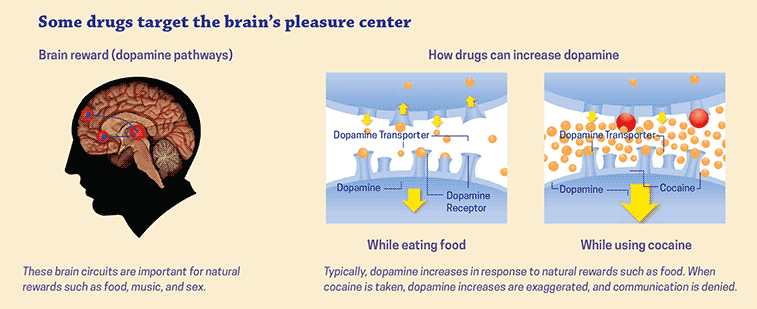
The Effects of Stimulants on the Brain
Stimulants, such as cocaine and amphetamines, can cause an immediate increase in alertness and energy, as well as euphoria. This is because stimulants increase the levels of the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can create a feeling of pleasure.
However, these effects can be short-lived, and long-term use of stimulants can lead to addiction, aggression, and paranoia. Stimulants can also cause changes in brain structure and chemistry, leading to impaired cognitive function and memory.
The Effects of Depressants on the Brain
Depressants, such as alcohol and barbiturates, have the opposite effect of stimulants. They slow down the brain’s activity, leading to feelings of relaxation and sedation. Depressants also increase the levels of the neurotransmitter GABA, which can further reduce anxiety and produce a sense of calm.
However, long-term use of depressants can lead to tolerance and physical dependence, as well as depression, memory problems, and impaired thinking. Depressants can also increase the risk of suicide and accidental death.
The Effects of Hallucinogens on the Brain
Hallucinogens, such as LSD and psilocybin, act on the brain’s serotonin system, leading to changes in mood, perception, and behavior. Many hallucinogens produce a feeling of euphoria, as well as altered sense of time, visual and auditory hallucinations, and impaired judgment.
However, long-term use of hallucinogens can lead to persistent psychosis, flashbacks, and persistent changes in personality and behavior. Hallucinogens can also cause anxiety and paranoia, as well as physical problems such as nausea, vomiting, and tremors.
The Effects of Inhalants on the Brain
Inhalants, such as solvents and aerosol sprays, act on the brain’s dopamine system, leading to feelings of euphoria and changes in behavior. Inhalants can also cause dizziness, confusion, and impaired judgment.
However, long-term use of inhalants can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as impaired cognitive function and memory. Inhalants can also increase the risk of heart and lung damage, as well as sudden death.
The Effects of Opioids on the Brain
Opioids, such as heroin and prescription painkillers, act on the brain’s opioid receptors, leading to feelings of euphoria and pain relief. Opioids also increase the levels of dopamine in the brain, leading to increased pleasure and reward.
However, long-term use of opioids can lead to tolerance, physical dependence, and addiction. Opioids can also cause breathing problems, impaired cognitive function, and memory problems.
The Effects of Over-the-Counter Drugs on the Brain
Over-the-counter drugs, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, act on the brain’s chemical balance, leading to pain relief and fever reduction. Some over-the-counter drugs can also cause drowsiness and dizziness.
However, long-term use of over-the-counter drugs can lead to liver damage, kidney damage, and stomach ulcers. Over-the-counter drugs can also increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
The Effects of Synthetic Drugs on the Brain
Synthetic drugs, such as K2 and Spice, act on the brain’s cannabinoid receptors, leading to feelings of euphoria and relaxation. Synthetic drugs can also cause changes in perception, mood, and behavior.
However, long-term use of synthetic drugs can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as impaired cognitive function and memory. Synthetic drugs can also increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and seizures.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What are drugs?
Drugs are substances that can be taken by humans or animals to alter the way they think, feel, and behave. They can be illegal, like cocaine, heroin, or marijuana; they can be legal, like prescription medications; or they can be over-the-counter medicines, like cold and cough medicines. All drugs have the potential to affect the brain and body in different ways.
How do drugs affect the brain?
When drugs enter the body, they travel through the bloodstream and eventually reach the brain. Once in the brain, drugs can interfere with normal communication between brain cells by affecting the way neurons send, receive, and process signals. Drugs can also cause the release of excessive amounts of natural neurotransmitters, or they can mimic the action of neurotransmitters and bind to the receptors. This can have effects on both the structure and function of the brain, leading to changes in behavior, cognition, and emotion.
What are some short-term effects of drug use?
The short-term effects of drug use can vary depending on the type of drug taken and the amount taken. Generally, drugs cause an increase in energy, alertness, and relaxation, as well as changes in mood, perception, and behavior. These effects can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours or even days.
What are some long-term effects of drug use?
Long-term drug use can lead to serious physical and mental health problems, including addiction, memory loss, and changes in behavior. It can also lead to impaired judgment, increased risk of heart disease and stroke, and damage to vital organs. Additionally, long-term drug use can lead to social and financial problems, such as relationship problems, unemployment, and financial difficulties.
What are the risks of taking drugs?
The risks of taking drugs vary depending on the type and amount of drug taken. Generally, the risks include addiction, overdose, physical and psychological dependence, and death. Additionally, long-term use of drugs can lead to physical and mental health problems, such as memory loss, impaired judgment, and changes in behavior and emotion.
What can be done to reduce the risks associated with drug use?
There are several things that can be done to reduce the risks associated with drug use. These include avoiding drugs altogether, seeking help from a doctor or counselor if you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, and talking to friends and family about the risks associated with drug use. Additionally, it is important to be aware of the signs of drug overdose and to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing any of these signs.
How do drugs affect the brain? – Sara Garofalo
Drugs have a powerful and dangerous effect on the brain. They can disrupt the balance of hormones, increase the risk of physical and emotional problems, and cause serious long-term damage. Drug use can cause impaired judgment, memory loss, and an inability to learn new information. It can also lead to addiction and a range of mental health issues. It is important to understand the risks associated with drug use and to seek help if a problem arises. Drug use can have serious, life-altering consequences, so it is important to stay informed and make healthy choices.

