Addiction can be a devastating experience for both the individual and their family. It can have a profound effect on all aspects of life, from physical health to financial stability. But what causes an addiction? Is it simply a lack of willpower or are there deeper issues that lead to a dependency? In this article, we will look at the various factors that can lead to an addiction—from biological influences to environmental influences—so that we can better understand why addiction happens and how we can help those affected.
If the keyword starts with the “How To” word, Then,
- Understand your triggers – Identify the situations and emotions that trigger cravings for drugs or alcohol.
- Develop healthier coping skills – Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and talking to supportive people.
- Avoid high-risk situations – Stay away from places and people who may encourage you to use drugs or alcohol.
- Remove drugs and alcohol from your environment – Get rid of any substances you have at home, as this will make it easier to resist temptation.
- Seek professional help – Talk to a doctor or therapist about addiction treatment options.
If the keyword includes the “vs” word, Then,
| Drugs vs Alcohol | Drugs | Alcohol |
|---|---|---|
| Physiological Effects | Slowed breathing, increased heart rate, confusion, impaired coordination | Slurred speech, loss of coordination, poor judgment, slowed reaction time |
| Long-Term Effects | Organ damage, memory problems, mood swings, social isolation | Liver damage, weakened immune system, high blood pressure, memory loss |
| Addiction Potential | High | High |
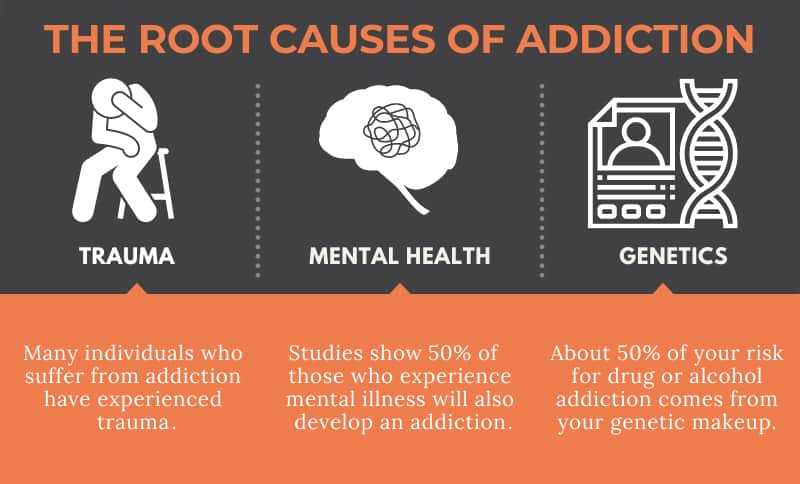
What are the Main Causes of Addiction?
Addiction is a complex disorder that can affect many aspects of an individual’s life. It is characterized by a compulsive need to use a substance or engage in an activity despite the negative consequences it causes. The causes of addiction are varied and can include biological, psychological, and social factors. While the exact cause of addiction is not known, research has identified several key contributors.
The biological factors that can lead to addiction include genetic influences, the presence of certain hormones or brain chemistry, and physical changes in the brain. People with certain genetic factors may be more likely to become addicted to substances or activities. Certain hormones, such as dopamine, can increase the pleasure associated with certain activities, making them more rewarding and reinforcing the behavior. Additionally, physical changes in the brain can increase an individual’s susceptibility to addiction.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors are thought to play a role in the development of addiction. Certain mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), can make an individual more vulnerable to addiction. Additionally, people who have experienced trauma or have a history of substance abuse may be more likely to develop an addiction. Stress can also be a trigger for addiction.
People who have difficulty managing their emotions or lack the necessary coping skills to manage stress may turn to substances or activities to self-medicate. Additionally, individuals who have difficulty forming meaningful relationships or feel isolated may be more likely to become addicted to drugs or activities.
Social Factors
Social factors can also play a role in the development of addiction. People who are exposed to drugs or alcohol at an early age may be more likely to develop an addiction later in life. Additionally, people who come from families where addiction is normalized may be more likely to use drugs or alcohol. Additionally, people who have few social supports or lack positive relationships may be more likely to turn to drugs or activities as a way to cope with stress.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also influence an individual’s likelihood of developing an addiction. People who are exposed to drugs or alcohol at an early age may be more likely to become addicted later in life. Additionally, people who come from families where addiction is normalized may be more likely to use drugs or alcohol. Additionally, people who live in areas where drugs or alcohol are readily available may be more likely to become addicted.
Brain Chemistry
Brain chemistry can also be a contributing factor in the development of addiction. Certain drugs or activities can cause changes in the brain that can lead to addiction. These changes can include an increase in the reward pathways in the brain, which can reinforce certain behaviors. Additionally, certain drugs or activities can increase dopamine levels, which can create a feeling of pleasure and reward.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors can also contribute to the development of addiction. People who have certain genetic factors may be more likely to become addicted to substances or activities. Additionally, family history of addiction can increase an individual’s risk of developing an addiction. Additionally, certain genetic factors can make an individual more vulnerable to environmental influences.
Conclusion
Addiction is a complex disorder that can have many causes. Biological, psychological, social, environmental, and genetic factors can all contribute to the development of addiction. While the exact cause of addiction is not known, research has identified several key contributors. Understanding the causes of addiction can help individuals develop effective strategies to prevent or manage addiction.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Addiction?
Addiction is a chronic disorder characterized by an inability to abstain from a habit-forming substance or behavior. Addiction can include anything from alcohol, drugs, gambling, shopping, sex, and even food. People who have an addiction often have an intense focus on the object of their addiction and can develop physical and psychological dependence.
What Causes an Addiction?
Addictions are caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, social and cultural influences, and psychological factors. Genetics are thought to be a major factor in addiction, as certain genetic variations can increase the risk of developing an addiction. Environmental and social factors, such as poverty, trauma, or exposure to addiction in the home, can also lead to addiction. Psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, or depression, can also lead to an addiction.
What Are the Signs of Addiction?
The signs of addiction vary, but generally include an inability to stop or cut back on the object of addiction, intense cravings, withdrawal symptoms when trying to abstain, and changes in behavior, such as lying or aggression. Other signs of addiction can include obsessively thinking about the object of addiction, isolation, neglecting responsibilities, and financial problems.
What Are the Risks of Addiction?
The risks of addiction are numerous, and can include physical and psychological health problems, financial difficulties, relationship problems, and even legal issues. Addiction can also lead to an increased risk of overdose, as well as an increased risk of death due to the use of substances or behaviors.
What Are the Treatments for Addiction?
Treatment for addiction typically involves both medical and psychological approaches. Medication can be used to address physical issues, such as withdrawal symptoms, and psychological approaches can help with addressing issues related to thoughts and behaviors. Additionally, therapy, support groups, and lifestyle changes can help to manage addiction.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Addiction?
The long-term effects of addiction can vary, but can include physical health issues, psychological issues, relationship problems, and financial difficulties. Additionally, addiction can lead to an increased risk of relapse and can cause a person to lose control over their life. Long-term effects of addiction can also include an increased risk of overdose or death due to the use of substances or behaviors.
What causes addiction?
Addiction is a complex problem with an equally complex set of underlying causes. From environmental factors to genetic predispositions, it is clear that addiction is a multifaceted issue. It is also clear that addiction has a range of negative consequences, from financial strain to social isolation and beyond. Therefore, it is important for individuals to recognize the potential signs of addiction, seek help from a mental health professional, and take the necessary steps to reduce their risk of developing an addiction.

