Nsaids (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are commonly used to relieve pain, inflammation, and fever. They are the most prescribed drugs worldwide and are used to treat a wide variety of ailments, from minor aches and pains to serious illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis and cancer. In this article, we’ll explore what Nsaids are, how they work, and the side effects associated with them. Stay tuned to learn more about these powerful drugs!
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are medications used to reduce pain, inflammation, and fever. They can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including headache, muscle aches, arthritis, back pain, tendinitis, and menstrual cramps. NSAIDs are available over-the-counter and in prescription form. These drugs work by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation. Common side effects of NSAIDs include stomach upset, dizziness, and nausea.
Contents
What are Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a group of medications that are used to reduce inflammation, pain, and fever. These drugs are commonly used to treat a variety of conditions, such as pain, arthritis, and fever. They are available both over-the-counter (OTC) and by prescription. NSAIDs work by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation and pain.
NSAIDs are generally considered safe when taken as directed. However, they can have serious side effects, including bleeding, ulcers, and kidney damage. It is important to talk to your doctor before taking any NSAID to make sure it is safe for you.
Types of NSAIDs
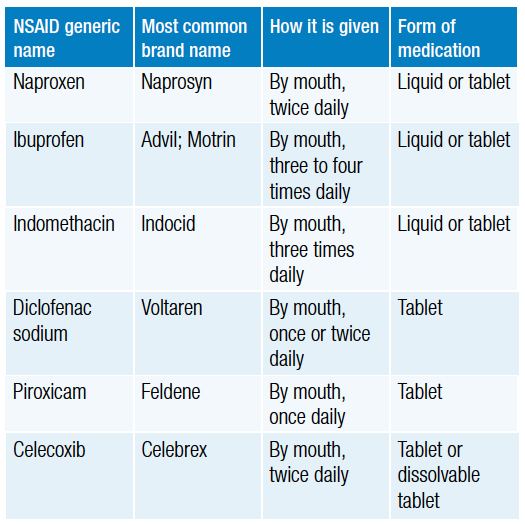
There are several different types of NSAIDs available. The most commonly used are ibuprofen, naproxen sodium, and aspirin. These three medications are available both over-the-counter and by prescription. There are also other types of NSAIDs, such as celecoxib, meloxicam, and diclofenac, which are only available by prescription.
Each type of NSAID works differently, so it is important to talk to your doctor to determine which one is best for you. Some NSAIDs, such as aspirin, may interact with other medications, so it is important to tell your doctor about all medications you are taking.
Risks and Side Effects of NSAIDs
NSAIDs can cause serious side effects if taken in large doses or for long periods of time. People who are at risk for these side effects include those with kidney or liver disease, high blood pressure, or a history of stomach ulcers.
The most common side effects of NSAIDs include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Other side effects may include headache, rash, dizziness, and drowsiness. In some people, NSAIDs may also cause liver or kidney damage.
GI Bleeding
NSAIDs can also increase the risk of bleeding in the stomach or intestines. This is known as gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. Symptoms of GI bleeding include black or bloody stools, vomiting blood, or stomach pain.
If you experience any of these symptoms, stop taking the NSAID and call your doctor right away. Long-term use of NSAIDs can also increase the risk of developing ulcers in the stomach or small intestine.
Kidney Damage
Long-term use of NSAIDs can also increase the risk of kidney damage. Symptoms of kidney damage include swelling of the feet and ankles, fatigue, and an increase in urine output. If you experience any of these symptoms, stop taking the NSAID and call your doctor right away.
Conclusion
NSAIDs can be effective for reducing inflammation and pain, but they can also have serious side effects. It is important to talk to your doctor before taking any NSAID to make sure it is safe for you. Be sure to tell your doctor about any other medications you are taking, as some NSAIDs can interact with other medications.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What are NSAIDs?
NSAIDs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are a class of medications used to reduce inflammation and pain. They are commonly used to treat conditions such as arthritis, headaches, muscle pain, and menstrual cramps. NSAIDs work by blocking enzymes in the body that produce substances that cause inflammation.
What are the side effects of NSAIDs?
Common side effects of NSAIDs include stomach pain, nausea, heartburn, and indigestion. They can also increase the risk of certain types of stroke and heart attack, as well as other cardiovascular events. Other side effects can include kidney or liver damage, and an increased risk of bleeding.
Are NSAIDs safe?
NSAIDs can be generally safe when taken as prescribed. However, it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects and risks, especially when taking them for a long period of time. It’s important to talk to your doctor about any potential risks associated with taking NSAIDs.
Who should not take NSAIDs?
People with certain medical conditions, such as asthma, high blood pressure, heart disease, kidney disease, and liver disease, should not take NSAIDs. People who are taking blood thinners, such as warfarin, or who have a history of stomach ulcers should also avoid taking NSAIDs.
Are there any other types of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs?
Yes, there are other types of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that are not as commonly used. These include cox-2 inhibitors, such as celecoxib, and topical NSAIDs, such as ketoprofen. These drugs are used to treat more specific conditions, such as osteoarthritis.
What is the difference between NSAIDs and other types of pain relief medications?
NSAIDs work to reduce inflammation and pain by blocking the production of certain substances in the body. Other types of pain relief medications, such as acetaminophen, work by blocking the transmission of pain signals in the brain. NSAIDs can also be used to reduce fever, while acetaminophen cannot.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | NSAIDs
In conclusion, NSAIDs, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are a class of pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications that are used to treat a variety of conditions. Although they are generally safe and effective, NSAIDs can have serious side-effects and should always be taken as directed by your doctor. They are an important tool in managing pain and inflammation, and should be used cautiously and under medical supervision.

