Addictive drugs are substances that can alter the way one thinks, feels, and behaves. They can be extremely dangerous and lead to a wide range of physical and mental health problems, including addiction. These drugs are often abused due to their ability to produce feelings of pleasure and relaxation, but their use can quickly become compulsive and lead to devastating consequences. In this article, we will explore what addictive drugs are, the effects they can have on the body and mind, and how to identify and address an addiction.
Addictive drugs are substances that cause physical or psychological dependence. Examples of addictive drugs are heroin, cocaine, prescription painkillers, marijuana, and nicotine. Long-term use of these drugs can lead to physical and psychological dependence, and can have serious health risks, including overdose and death.
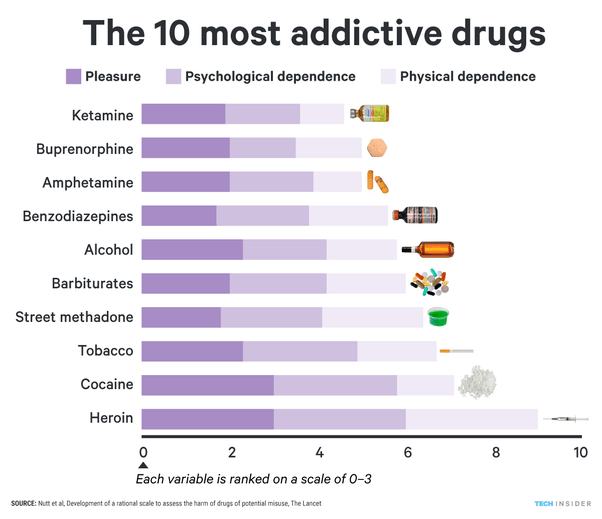
What are Addictive Drugs?
Addiction to drugs is a serious and chronic problem in the United States. Drugs are substances that can cause physical and psychological dependence. Some drugs are more addictive than others, and some people are more susceptible to addiction than others. Addictive drugs can have devastating physical, mental, and social effects on the user and those around them.
Addictive drugs are typically divided into two categories: depressants and stimulants. Depressants slow down the body’s functions and can lead to feelings of relaxation and sedation. Stimulants speed up the body’s functions and can lead to feelings of alertness and energy. These two categories of drugs can be further divided into various sub-categories.
Types of Depressants
Depressants are drugs that slow down the body’s functions, resulting in feelings of relaxation and sedation. Examples of depressants include alcohol, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and opiates. These drugs can be abused and can lead to physical and psychological dependence if used in large doses or over a prolonged period of time.
Alcohol is one of the most commonly abused depressants. It is a depressant that affects the brain in a number of ways, including reducing inhibitions, impairing judgment, and increasing the risk of accidents and injuries. Long-term use of alcohol can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as a range of other health problems.
Benzodiazepines are a class of depressants that act on the body’s central nervous system. They are prescribed to treat anxiety and insomnia, but they can be abused and lead to physical and psychological dependence. Long-term use of benzodiazepines can also lead to memory problems and cognitive deficits.
Types of Stimulants
Stimulants are drugs that speed up the body’s functions and can lead to feelings of alertness and energy. Examples of stimulants include cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamine, and prescription stimulants. These drugs can be abused and can lead to physical and psychological dependence if used in large doses or over a prolonged period of time.
Cocaine is one of the most commonly abused stimulants. It is a powerful stimulant that increases alertness, energy, and euphoria. Long-term use of cocaine can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as a range of other health problems.
Amphetamines and methamphetamine are stimulants that act on the central nervous system. They are typically prescribed to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy, but they can be abused and lead to physical and psychological dependence. Long-term use of amphetamines and methamphetamine can also lead to memory problems and cognitive deficits.
Prescription stimulants are drugs that are prescribed to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). These drugs can be abused and lead to physical and psychological dependence if used in large doses or over a prolonged period of time. Long-term use of prescription stimulants can also lead to memory problems and cognitive deficits.
Signs and Symptoms of Addiction
Addiction to drugs can have a range of physical, mental, and social effects. Some of the most common signs and symptoms of addiction include:
Physical Signs: Nausea, vomiting, fatigue, sweating, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, changes in weight, and tremors.
Mental Signs: Poor concentration, poor memory, irritability, agitation, mood swings, and impaired judgment.
Social Signs: Isolation from friends and family, changes in behavior, changes in interests, and financial difficulties.
Treatment Options
Addiction to drugs is a serious condition that can have devastating effects on the user and those around them. Fortunately, there are a variety of treatment options available to help those suffering from addiction. Treatment typically involves a combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychotherapy, medications, and lifestyle changes.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is a type of psychotherapy that helps the user to identify and modify their thoughts and behaviors associated with drug use. This type of therapy can help the user to develop healthier coping strategies and reduce their risk of relapse.
Medications can also be used to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. This can help to make the recovery process more manageable and reduce the risk of relapse.
Finally, lifestyle changes can also be helpful in recovery. These include getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and engaging in meaningful activities.
Risk Factors for Addiction
Although anyone can become addicted to drugs, there are certain factors that can increase the risk. These risk factors include:
Genetic Factors: A person’s genetic makeup can influence their risk of addiction. Those with a family history of addiction are more likely to develop an addiction themselves.
Psychological Factors: Mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, or trauma can increase the risk of addiction.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environments can increase the risk of addiction. These include environments in which drug use is tolerated or encouraged.
The Dangers of Addiction
Addiction to drugs can have a range of physical, mental, and social effects. These can include:
Physical Dangers: These include an increased risk of accidents and injuries, organ damage, and an increased risk of infectious diseases such as HIV and hepatitis.
Mental Dangers: These include memory problems, impaired judgment, and an increased risk of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
Social Dangers: These include financial problems, relationship problems, and an increased risk of legal problems.
Preventing Addiction
The best way to prevent addiction is to avoid drug use altogether. This can be done by educating yourself about the risks of drug use and avoiding environments in which drug use is tolerated or encouraged. If you or someone you know is struggling with addiction, it is important to seek professional help as soon as possible.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Addictive Drugs?
Answer: Addictive drugs are any substances that cause physical and psychological dependence and can lead to compulsive drug-seeking behavior. These drugs can be legal, such as alcohol and nicotine, or illicit, such as heroin and cocaine. Some drugs can be both legal and illicit, such as prescription opioids.
What Are the Effects of Addictive Drugs?
Answer: The effects of addictive drugs vary depending on the type and amount of drug taken, as well as the user’s tolerance and genetic makeup. Generally, people experience a rush of pleasure and a feeling of euphoria that can be followed by a crash and feelings of lethargy and depression. Repeated use of addictive drugs can lead to tolerance and physical dependence, which can cause unpleasant withdrawal symptoms when the user attempts to stop taking the drug.
How Are People Diagnosed With an Addiction?
Answer: People who are suspected of having an addiction to an addictive drug can be diagnosed by a medical professional. The doctor will typically ask questions about the patient’s history of drug use, their behavior, and any other relevant factors. The doctor may also order tests to check for physical signs of addiction, such as changes in brain chemistry or organ function.
What Are the Treatments for Addiction?
Answer: Treatment for addiction to an addictive drug typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, counseling, and medications. Cognitive-behavioral therapy is often used to help people understand and change their behavior related to drug use. Medications may also be prescribed to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. In some cases, detoxification and residential treatment may be necessary to help the person stop using the drug.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Addictive Drugs?
Answer: The long-term effects of using addictive drugs can vary depending on the type and amount of drug used, as well as the user’s individual health. Generally, long-term use of addictive substances can lead to an increased risk of organ damage, cognitive impairment, and mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. In some cases, long-term use can also lead to an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Can Addictive Drugs Be Used Safely?
Answer: Generally, it is not recommended to use addictive drugs, even if they are prescribed by a doctor. If a person is prescribed an addictive drug, they should only use it as directed and should never increase the dosage without consulting their doctor. It is also important to be aware of the potential risks associated with using the drug, and to avoid using it in combination with other drugs or alcohol.
Ask Dr. Nandi: The five most addictive substances in the world
Addictive drugs are a serious problem in our society, and the consequences of their use can be devastating. While there is no single solution to the problem, it is important to understand the risks and be aware of the available resources for those who are struggling. By understanding the dangers of addictive drugs and seeking help when needed, we can reduce their devastating effects and promote a healthier, happier society.

