The highly addictive prescription drug OxyContin has been a source of debate for many years. It has been heavily linked with the opioid crisis and has been the subject of much scrutiny. In this article, we will explore the effects of OxyContin and whether it is classified as a depressant or stimulant. We will look at the science behind the drug and discuss the implications of its use in today’s society.
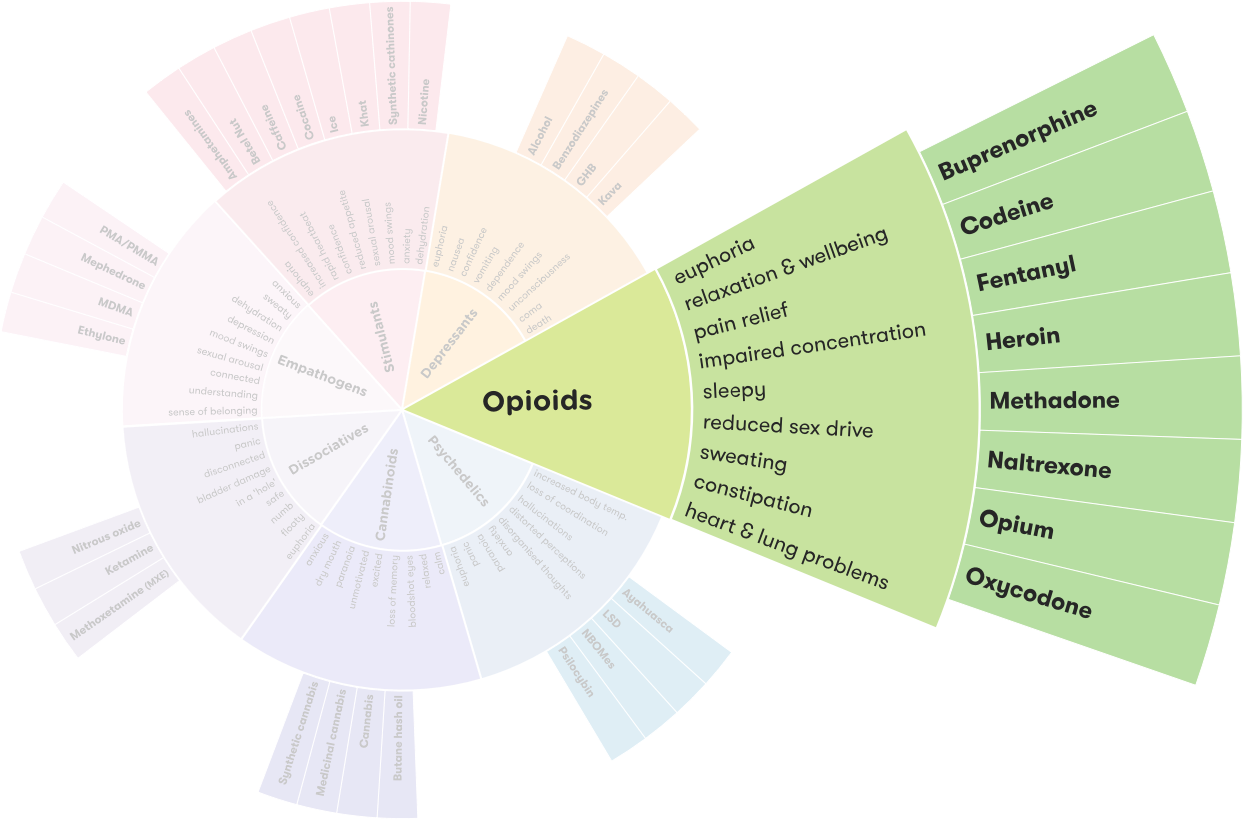
Oxycontin is a depressant. It works by slowing down the activity of the central nervous system, reducing pain and producing a calming, relaxed feeling. It is an opioid, meaning it binds to opioid receptors in the brain, leading to pain relief and relaxation. Oxycontin is used to treat moderate to severe pain and is available in both immediate-release and extended-release forms. Common side effects include nausea, constipation, drowsiness, and headaches.
Contents
- What is OxyContin?
- Is OxyContin a Depressant or Stimulant?
- Conclusion
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: Is Oxycontin a Depressant or Stimulant?
- Q2: What are the Side Effects of Oxycontin?
- Q3: How Dangerous is Oxycontin?
- Q4: What is the Difference Between Oxycontin and Oxycodone?
- Q5: What is the Proper Way to Take Oxycontin?
- Q6: What Should I Do if I Miss a Dose of Oxycontin?
- Neurobiological Impact of Stimulants Depressants and Hallucinogens
What is OxyContin?
OxyContin is a brand name for the drug oxycodone, which is a prescription pain reliever. It is an opioid medication that is used to relieve moderate to severe pain. OxyContin is an extended-release form of oxycodone that is taken orally and is available in tablet, capsule, and liquid form. It works by changing the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain.
OxyContin is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance, meaning it is a drug with a high potential for abuse and addiction. It is only available with a prescription and is often used to treat chronic pain. Common side effects of OxyContin include constipation, nausea, drowsiness, and headache.
Is OxyContin a Depressant or Stimulant?
OxyContin is an opioid depressant, meaning it slows down brain activity and the central nervous system. It binds to opioid receptors in the brain and blocks the transmission of pain signals to the body. As a result, the user feels less pain and experiences a sense of calm and relaxation. OxyContin can also cause a decrease in respiration, which can lead to a decrease in blood pressure and heart rate.
The effects of OxyContin can vary depending on the person, dosage, and duration of use. In general, OxyContin can cause sedation, drowsiness, and euphoria. It can also cause slowed movement, slowed breathing, constipation, and confusion. Long-term use of OxyContin can lead to tolerance, dependence, and addiction.
The Effects of OxyContin Abuse
OxyContin is a powerful and potentially dangerous drug. When abused or taken in large doses, it can cause a number of serious side effects. These include extreme drowsiness, slowed or shallow breathing, confusion, nausea, and constipation. Overdose is also a risk, as OxyContin can slow breathing to the point of death.
OxyContin abuse can also lead to dependence and addiction. People who become dependent on OxyContin may experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking the drug. These symptoms can include anxiety, sweating, nausea, and insomnia. It is important to note that OxyContin should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
The Dangers of Mixing OxyContin with Other Drugs
Mixing OxyContin with alcohol or other drugs can be especially dangerous. Alcohol can increase the sedative effects of OxyContin, making users more likely to overdose. Mixing OxyContin with other depressants, such as benzodiazepines or barbiturates, can also be deadly.
It is also important to note that some over-the-counter medications, such as cold and allergy medicines, can interact with OxyContin and cause dangerous side effects. It is important to talk to a doctor or pharmacist before taking any medications while taking OxyContin.
Conclusion
OxyContin is an opioid depressant used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance and is only available with a prescription. Common side effects of OxyContin include constipation, nausea, drowsiness, and headache. OxyContin abuse can lead to dependence and addiction and can be especially dangerous when mixed with alcohol or other drugs. It is important to take OxyContin only as prescribed by a doctor and to talk to a doctor or pharmacist before taking any other medications while taking OxyContin.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is Oxycontin a Depressant or Stimulant?
A1: Oxycontin is a depressant. Oxycontin is an opioid pain reliever that is used to manage moderate-to-severe pain. It is a Schedule II drug, which means that it has a high potential for abuse and addiction. Oxycontin works by slowing down the central nervous system, which causes a feeling of relaxation, sedation, and euphoria. It can also be used to treat anxiety and depression, but it is not typically recommended because of its high risk of addiction.
Q2: What are the Side Effects of Oxycontin?
A2: The side effects of Oxycontin can include nausea, constipation, drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, and headache. More serious side effects can include breathing difficulties, confusion, seizures, and even coma. Long-term use of Oxycontin can lead to tolerance, dependence, and addiction. It is important to only take Oxycontin as prescribed and to speak to a doctor if any side effects occur.
Q3: How Dangerous is Oxycontin?
A3: Oxycontin can be very dangerous, especially if it is not taken as prescribed. It has a high potential for abuse and addiction, so it is important to only take it as directed. Overdose can occur if too much is taken, and can lead to difficulty breathing, coma, and even death. If you or someone you know is abusing Oxycontin, seek help right away.
Q4: What is the Difference Between Oxycontin and Oxycodone?
A4: Oxycontin and oxycodone are both opioid pain relievers. Oxycontin is an extended-release form of oxycodone, meaning that the effects of the drug can last up to 12 hours. Oxycodone is a short-acting opioid, and its effects last for about 4-6 hours. Oxycontin is usually prescribed for around-the-clock pain management, while oxycodone is usually prescribed for more mild pain.
Q5: What is the Proper Way to Take Oxycontin?
A5: Oxycontin should be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor. It should not be taken more often or in larger doses than directed. It is important to take Oxycontin with food, as it can help reduce the risk of stomach upset. Do not crush, break, or chew the tablets, as this can lead to a dangerous overdose.
Q6: What Should I Do if I Miss a Dose of Oxycontin?
A6: If you miss a dose of Oxycontin, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take the next one as scheduled. Do not take two doses at once, as this can lead to an overdose. It is important to take Oxycontin as prescribed and to speak to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns.
Neurobiological Impact of Stimulants Depressants and Hallucinogens
In conclusion, Oxycontin is an opioid drug that can have a range of effects on the human body. While it can act as a stimulant, it is most often used to treat chronic pain and is classified as a depressant. It can be an effective treatment for chronic pain, but it is important to use it responsibly and as prescribed, as it is highly addictive and carries a risk of abuse and overdose.

