Opium is one of the oldest drugs known to mankind, and has had a long and controversial history. It has been used both medicinally and recreationally, but is often associated with addiction and negative health implications. But is opium an opiate? In this article we will explore the history and chemistry of opium, and discuss its classification as an opiate. We will also delve into the potential health risks and benefits of opium use.
Yes, Opium is an opiate. Opiates are substances that are derived from the poppy plant and are used to produce drugs like morphine and codeine. Opium is the name for the sap that is extracted from the seedpod of the opium poppy. It can be eaten, smoked, or taken as a tea. Opium is a highly addictive drug and can be used for both medicinal and recreational purposes.
What is Opium?
Opium is a drug derived from the poppy plant. It contains various alkaloids, the most notable of which are morphine and codeine. It has been used for centuries as a pain reliever, sedative, and recreational drug. The effects of opium depend on the amount taken and the frequency of use. In high doses, it can cause a feeling of euphoria, but in lower doses, it can lead to feelings of relaxation and sleepiness.
Opium has been used medicinally for centuries, but it is now illegal in most countries due to its high potential for abuse and addiction. In the United States, opium is a Schedule II drug, meaning it has a high potential for abuse and dependence.
The Difference Between Opium and Opiates
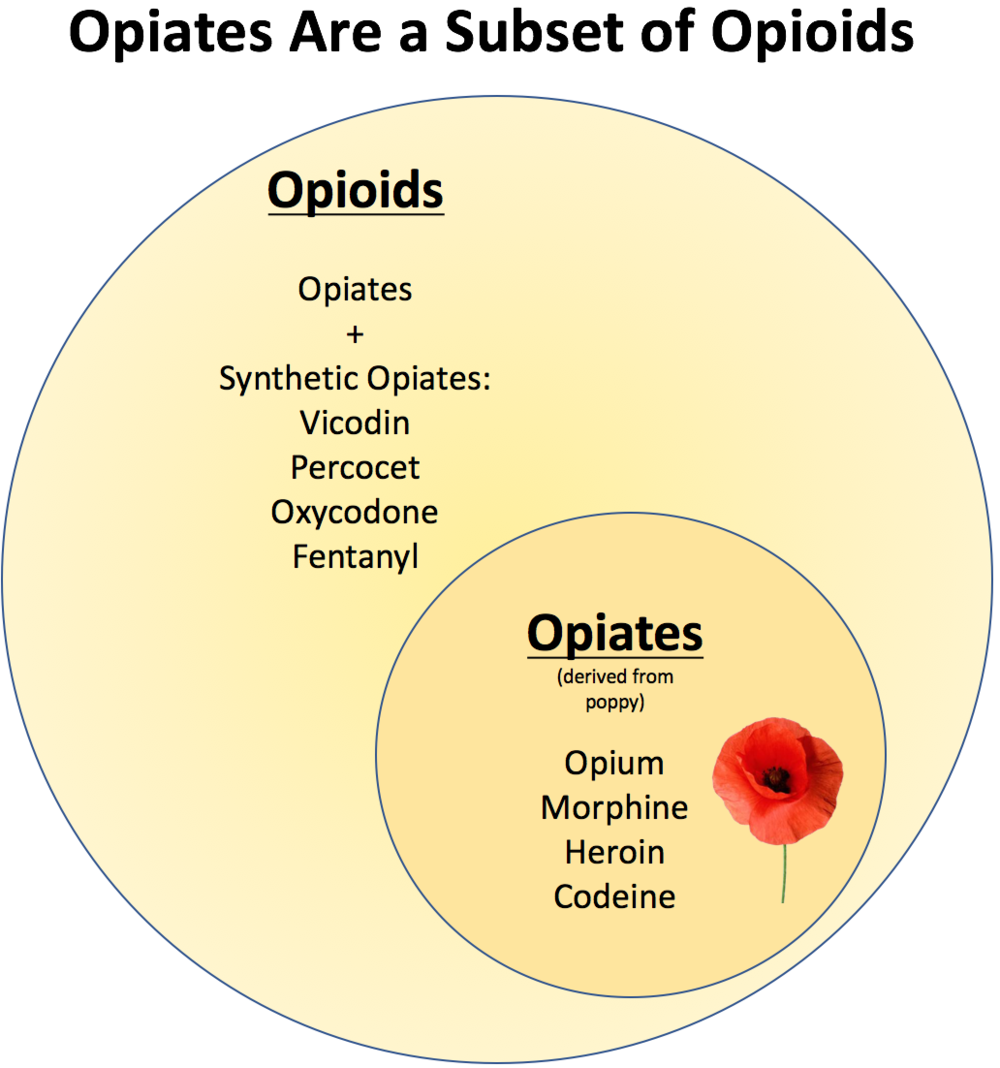
Opium and opiates are two different substances, although they are often confused. Opium is the raw form of the drug, while opiates are derivatives of opium. Opiates are drugs that are chemically altered from opium and include drugs such as heroin, oxycodone, and hydrocodone. All opiates are derived from opium, but not all opiates are derived from opium.
Opioids, on the other hand, are synthetic drugs that are chemically similar to opiates, but are not derived from opium. Examples of opioids include fentanyl, methadone, and buprenorphine.
The Dangers of Opium
Opium is a highly addictive drug, and it can cause a number of serious health problems. In addition to the risk of addiction, long-term use of opium can lead to liver damage, respiratory depression, and an increased risk of overdose.
Opium can also lead to psychological dependence. People who are dependent on opium may experience intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms when they attempt to quit. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and even dangerous, and they may require professional help to manage.
Is Opium an Opiate?
The short answer is yes. Opium is the raw form of the drug, while opiates are derivatives of opium. Opiates are drugs that are chemically altered from opium, and they include drugs such as heroin, oxycodone, and hydrocodone.
Opium and opiates have similar effects and carry the same risks, but there are some important differences. Opium is illegal in most countries and is classified as a Schedule II drug in the United States, while opiates are regulated by prescription and are only available with a doctor’s authorization.
The Effects of Opium
Opium is a powerful drug that can have a variety of effects on the body and mind. In low doses, it can produce feelings of relaxation and sedation. In higher doses, it can cause a feeling of euphoria as well as slowed breathing and heart rate.
Opium can also be addictive, and long-term use can lead to tolerance, meaning that more of the drug is needed to achieve the desired effects. People who are addicted to opium may experience withdrawal symptoms when they attempt to quit, and these symptoms can be uncomfortable and even dangerous.
The Dangers of Opium Abuse
Opium abuse can lead to a number of dangerous health consequences, including liver damage, respiratory depression, and an increased risk of overdose. It can also lead to psychological dependence, and people who are addicted to opium may experience intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms when they attempt to quit.
In addition, long-term use of opium can lead to tolerance, meaning that more of the drug is needed to achieve the desired effects. This can lead to an increased risk of overdose and other dangerous health consequences.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Opium?
Opium is a resin obtained from the seedpod of the opium poppy (Papaver somniferum). It is a naturally occurring substance that contains a number of alkaloids, including morphine and codeine. Opium is used in the form of an extract, tincture, or as a powder. It has a long history of medicinal and recreational use, and is still used in some countries as an analgesic and anesthetic.
What are Opiates?
Opiates are drugs derived from opium that act on the central nervous system to produce a range of effects, including pain relief, sedation, and euphoria. Opiates include natural opium alkaloids such as morphine and codeine, as well as synthetic compounds such as oxycodone and hydrocodone. Opiates are commonly used for pain management and can be highly addictive.
Is Opium an Opiate?
Yes, opium is an opiate. Opium contains a range of naturally occurring alkaloids, including morphine and codeine, which are also found in synthetic opiates. Therefore, opium can be classified as an opiate.
What are the Effects of Opiates?
The effects of opiates vary depending on the type and dosage of the drug. Common effects of opiates include pain relief, sedation, and euphoria. Opiates can also cause drowsiness, nausea, constipation, slowed breathing, and dependence. High doses of opiates can cause life-threatening respiratory depression.
What are the Risks of Using Opiates?
The risks of using opiates include addiction, overdose, and death. Opiates can be habit-forming and long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Overdose can occur due to the drug’s sedative effects, which can cause breathing to slow or stop. In addition, opiates can interact with other drugs, leading to increased risks of overdose.
How Can Opiate Addiction Be Treated?
Opiate addiction can be treated with a combination of medication and behavioral therapies. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is often used to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Behavioral therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and motivational interviewing can help individuals develop strategies to cope with triggers and cravings, and to learn new behaviors. Other treatments such as group therapy, individual counseling, and support groups can also be helpful.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, it is clear that opium is an opiate. Opium is derived from the poppy plant and contains the alkaloids morphine and codeine, which are both opiates. While opium has been used for thousands of years for its medicinal and recreational properties, it is important to note that it can be highly addictive and should be used with extreme caution. As always, it is best to consult a medical professional before using any type of drug.