Cocaine is one of the most dangerous and widely abused drugs in the world. Its effects on the body and mind are varied and complex, and can range from stimulating to depressant and even hallucinogenic. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what cocaine is, how it affects the body, and whether it can be classified as a stimulant, depressant, or hallucinogen. We’ll also discuss the potential risks associated with using cocaine and the consequences of long-term abuse.
Contents
- What is Cocaine?
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- Is Cocaine a Stimulant, Depressant, or Hallucinogen?
- What Are the Short- and Long-Term Effects of Cocaine Use?
- How Is Cocaine Used?
- What Are the Signs of Cocaine Addiction?
- What Are the Risks of Using Cocaine?
- What Are the Treatments for Cocaine Addiction?
- Drug Awareness: Depressants, Hallucinogens And Stimulants
What is Cocaine?
Cocaine is a powerful drug that is derived from coca plant, which is native to South America. It is one of the most commonly abused illicit drugs in the world and is highly addictive. Cocaine is a central nervous system stimulant, meaning it increases the activity of certain chemicals in the brain that produce feelings of pleasure and euphoria. It also speeds up the body’s processes, including heart rate and respiration, and can lead to dangerous side effects.
Cocaine can be taken through injection, snorting, smoking, or ingestion. It is also commonly mixed with other drugs or alcohol to produce a more intense experience, which can be dangerous and potentially deadly. Cocaine use can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as a variety of serious health issues.
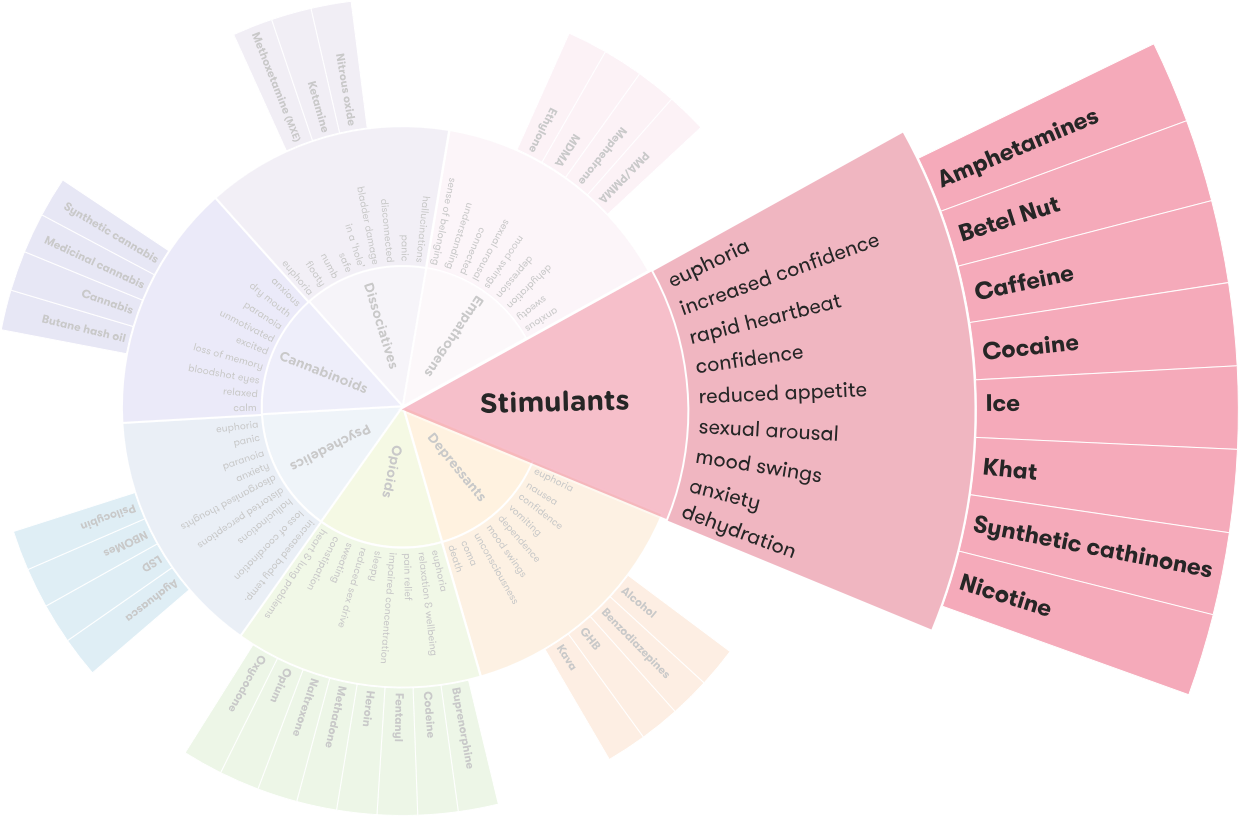
Is Cocaine a Stimulant?
Yes, cocaine is classified as a stimulant drug. Stimulants are substances that increase activity in the body and brain, resulting in increased alertness, energy, and concentration. Cocaine acts on the brain’s reward system to produce feelings of pleasure and euphoria. It also increases the levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, which can cause an intense feeling of pleasure.
However, cocaine’s effects on the brain can be very dangerous. The drug can cause increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and risk of stroke or heart attack. It can also induce feelings of paranoia, aggression, and restlessness. Long-term use of cocaine can lead to serious health problems, such as depression, anxiety, and addiction.
Is Cocaine a Depressant?
No, cocaine is not classified as a depressant drug. Depressants are substances that slow down the body and brain, resulting in decreased alertness, energy, and concentration. Common depressants include alcohol, opioids, and benzodiazepines.
Although cocaine does not have the same effects as depressants, it can still have a depressant-like effect on the brain. Long-term use of cocaine can lead to depression, as well as a number of other physical and psychological health issues.
Is Cocaine a Hallucinogen?
No, cocaine is not classified as a hallucinogen. Hallucinogens are substances that cause distortions in perception, thoughts, and feelings. Common hallucinogens include LSD, mushrooms, and ketamine.
Cocaine does not cause distortions in perception, thoughts, or feelings in the same way as hallucinogens. However, the drug can cause a person to have hallucinations, which are false sensory perceptions that can be visual, auditory, or tactile in nature. Hallucinations can be a side effect of cocaine use, and can be a sign of an overdose.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
Is Cocaine a Stimulant, Depressant, or Hallucinogen?
Answer: Cocaine is a stimulant. Stimulants are drugs that increase alertness, concentration, focus, and energy levels, while also increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. Cocaine is one of the most potent and widely used stimulants, and it can be found in a variety of forms, including powder, paste, and crack.
What Are the Short- and Long-Term Effects of Cocaine Use?
Answer: The short-term effects of cocaine use include increased alertness and energy, increased heart rate and blood pressure, and increased respiration. In the long-term, cocaine use can cause damage to the cardiovascular system, damage to the brain and central nervous system, and even death due to overdose. Additionally, cocaine use can lead to addiction and dependence, as well as mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
How Is Cocaine Used?
Answer: Cocaine is typically administered through the nose, where it is snorted, or through injection. However, it can also be smoked, swallowed, or applied to the gums. Smoking and injecting cocaine provide a more intense and rapid high, but these methods also carry a greater risk of addiction and overdose.
What Are the Signs of Cocaine Addiction?
Answer: The signs of cocaine addiction can vary from person to person, but some of the most common signs include an intense craving for cocaine, a loss of control over cocaine use, and a strong desire to continue using cocaine despite negative consequences. Other signs of cocaine addiction can include changes in behavior, such as taking risks or engaging in risky behavior, as well as changes in sleep patterns, appetite, and mood.
What Are the Risks of Using Cocaine?
Answer: The risks of using cocaine include physical and psychological health problems, such as cardiovascular damage, brain damage, and respiratory damage. Additionally, cocaine use can lead to addiction, overdose, and death. Other risks include an increased risk of violence and accidents, as well as financial problems due to the expense of purchasing cocaine.
What Are the Treatments for Cocaine Addiction?
Answer: The primary treatments for cocaine addiction are cognitive-behavioral therapy, medications, and support groups. Cognitive-behavioral therapy helps individuals identify and change their thoughts and behaviors related to cocaine use. Medications can help reduce cravings, reduce withdrawal symptoms, and reduce the risk of relapse. Support groups such as Narcotics Anonymous can provide individuals with a safe space to talk about their experiences, as well as provide support and guidance.
Drug Awareness: Depressants, Hallucinogens And Stimulants
In conclusion, cocaine is a stimulant drug that can cause a wide range of effects on a person’s physical and mental health. It can have both short-term and long-term effects such as increased energy, euphoria, and feelings of invincibility; however, long-term use of cocaine can lead to depression, psychosis, and even death. For these reasons, it is important to understand the risks associated with using cocaine and to seek help if you or someone you know is struggling with addiction.

