Addiction is a complex issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be difficult to understand, but it is important to recognize that it is a real problem that needs to be addressed. The scientific community has recognized addiction as a brain disease for more than two decades, and this has opened the door to more research and understanding of how addiction works. In this article, we will look at the science behind addiction, the brain changes associated with it, and the potential treatments available. We will also discuss why addiction is considered a brain disease and how this understanding can help those struggling with addiction.
Yes, addiction is a brain disease. Addiction is a complex condition, a brain disease that is manifested by compulsive substance use despite harmful consequences. It is considered a brain disease because drugs change the brain—they change its structure and how it works. These brain changes can be long lasting and can lead to the harmful behaviors seen in people who abuse drugs.
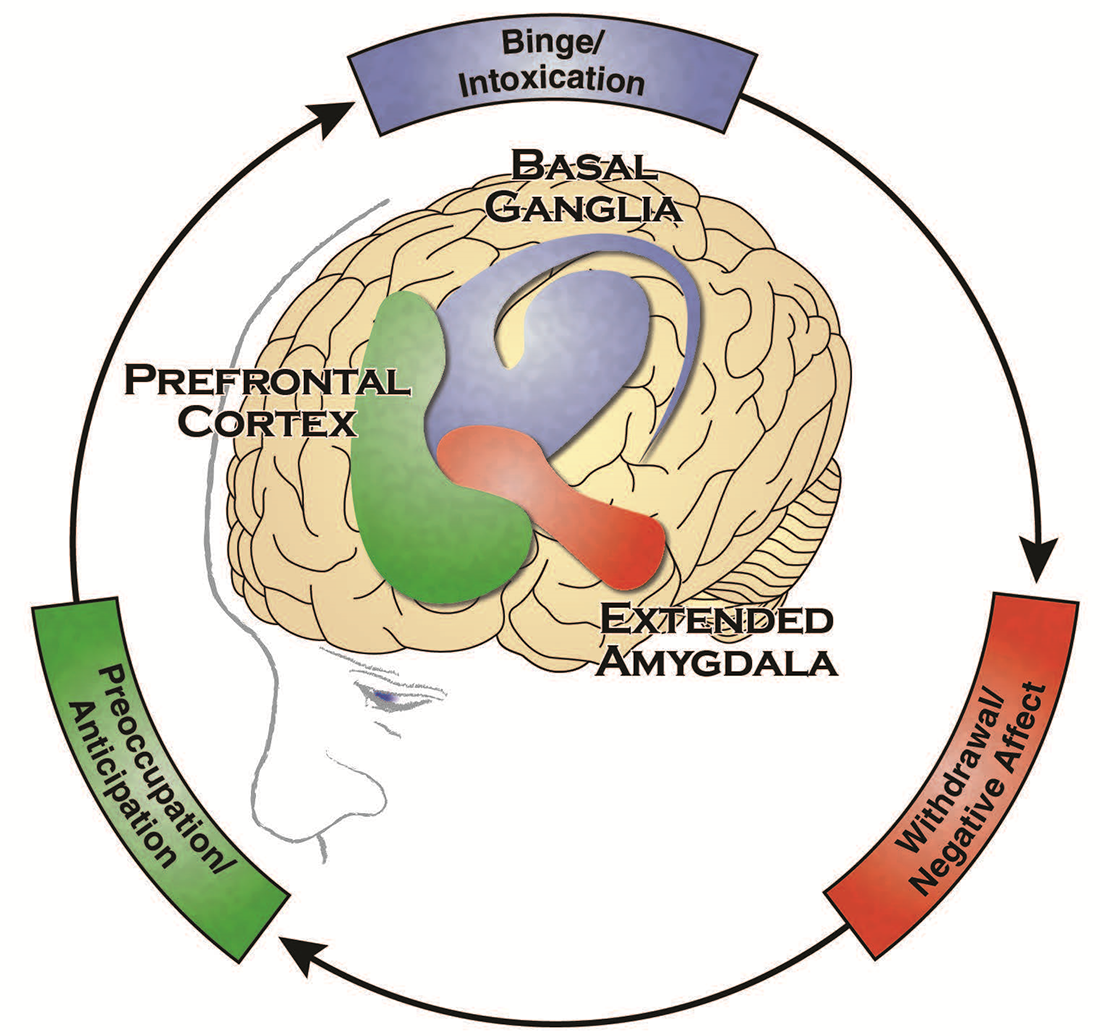
What Is Addiction?
Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder that affects the brain’s reward system. It is characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences. People who are addicted may not be able to control their drug use and may continue using drugs despite the harm it causes. Addiction is a complex and chronic brain disease that can cause the person to continue using drugs despite the harm it causes.
Addiction is a brain disorder that is caused by changes in the brain’s structure and chemistry. It is a chronic illness, meaning it lasts a lifetime. People with addiction may not be able to stop using drugs, even when they want to. They may try to quit, but find it difficult or impossible to do so.
What Causes Addiction?
Addiction is caused by a combination of biological, environmental, and psychological factors. These factors can include genetics, brain chemistry, and external influences such as peer pressure and stress.
Genetics can play a role in addiction. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to addiction, meaning they are more likely to develop an addiction than others. Brain chemistry also plays a role in addiction. When certain drugs are used, they can cause changes in the brain’s chemistry, which can lead to addiction.
External factors can also contribute to addiction. These can include peer pressure, stress, and environmental factors such as poverty and lack of access to drug treatment.
What Are the Signs of Addiction?
Addiction can manifest in different ways in different people. However, some common signs of addiction include:
• Compulsive use of drugs or alcohol, even when it is causing harm.
• A strong desire to use drugs or alcohol, even when it is causing harm.
• A lack of control over drug or alcohol use, even when it is causing harm.
• A persistent craving for drugs or alcohol.
• A feeling of being powerless to stop using drugs or alcohol.
• A preoccupation with obtaining and using drugs or alcohol.
• A decrease in other activities, such as work or hobbies, due to drug or alcohol use.
How Is Addiction Treated?
Addiction is a complex disorder that requires comprehensive treatment. Treatment for addiction typically involves a combination of medication, behavioral therapy, and support groups.
Medication
Medication can be used to help manage cravings, reduce the risk of relapse, and treat any underlying mental health conditions. Examples of medications used to treat addiction include:
• Antidepressants.
• Antipsychotics.
• Opioid agonists.
• Naltrexone.
• Disulfiram.
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy is an important part of addiction treatment. It helps the person learn healthy coping skills and identify the situations that may trigger their drug use. Examples of behavioral therapies include:
• Cognitive-behavioral therapy.
• Dialectical behavior therapy.
• Motivational interviewing.
• Contingency management.
Conclusion
Addiction is a chronic, relapsing brain disease that affects the brain’s reward system. It is caused by a combination of biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Treatment for addiction typically involves a combination of medication, behavioral therapy, and support groups.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Addiction?
Addiction is a chronic disorder characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, despite adverse consequences. It is defined by an inability to consistently abstain, impairment in behavioral control, craving, diminished recognition of significant problems with one’s behaviors and interpersonal relationships, and a dysfunctional emotional response. People struggling with addiction often continue using the substance of choice despite serious consequences and may even require medical or psychological intervention to stop.
Is Addiction a Brain Disease?
Yes, addiction is considered a brain disease because it is caused by changes in the structure and function of the brain. Drug abuse and addiction lead to changes in the brain’s reward system, which is an area of the brain that controls our natural response to pleasure and reward. These changes can lead to compulsive drug seeking and use, even in the face of negative consequences.
What Causes Addiction?
Addiction is caused by a combination of biological, environmental, social, and psychological factors. Biological factors include genetics, mental health, and the presence of other physical conditions. Environmental factors include home and family environments, peer influences, and access to substances. Social and psychological factors include trauma, stress, and mental health issues.
What Are the Symptoms of Addiction?
The symptoms of addiction vary depending on the type of substance and level of use. Common symptoms include impaired judgment, cravings, tolerance, withdrawal, and compulsive behaviors. Other symptoms include changes in sleep patterns, drastic changes in mood, and difficulty concentrating.
How is Addiction Treated?
Addiction is often treated with a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Psychotherapy can help an individual understand their addiction, recognize triggers, and learn healthy coping strategies. Medication can help manage cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Lifestyle changes may include avoiding triggers, engaging in physical activity and healthy hobbies, and developing healthy relationships.
What Is the Outlook for People with Addiction?
The long-term outlook for people with addiction is positive with the right treatment and support. Recovery is a long process and relapse is common, but with the right help, individuals can learn to manage their addiction and lead healthy, productive lives. It is important to remember that recovery is a journey, not a destination, and that relapse does not mean failure.
Addiction is a Brain Disorder
In conclusion, research and evidence supports the notion that addiction is a brain disease. It is not a matter of moral failing or lack of willpower, but rather a medical disorder that involves changes in the brain’s structure and function. While addiction is a serious problem that can have serious consequences, it is a treatable condition with the right support and resources. With the right approach, individuals can learn to manage their addiction and live productive, healthy lives.

