Opiate addiction is a serious problem that affects millions of people around the world. It can have a devastating impact on an individual’s physical, mental, and emotional health. Withdrawal from opiate use can be uncomfortable and often terrifying. Fortunately, there are a number of ways to help ease the symptoms of opiate withdrawal. In this article, we will discuss the various methods available to help those struggling with opiate withdrawal. We will look at lifestyle changes, medications, and therapies that can be used to help reduce the severity of withdrawal symptoms. With the right resources and support, it is possible to successfully manage opiate withdrawal and move towards a healthier future.
- Get plenty of rest. Taking time to relax and get enough rest can help support the body during opiate withdrawal.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Staying hydrated is essential for managing the physical symptoms of opiate withdrawal.
- Take over-the-counter medications. Nonprescription medications, such as ibuprofen, can help manage some of the side effects of opiate withdrawal.
- Gradually taper off opiate use. Tapering off the dose of opiates can help reduce the severity of withdrawal symptoms.
- Join a support group. Speaking with others who understand the struggles of opiate withdrawal can help alleviate feelings of isolation.
Contents
- What is Opiate Withdrawal?
- Managing Symptoms at Home
- Managing Cravings
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What is opiate withdrawal?
- What are the signs and symptoms of opiate withdrawal?
- What treatments are available for opiate withdrawal?
- What lifestyle changes can help with opiate withdrawal?
- What are the potential complications of opiate withdrawal?
- How can friends and family help someone going through opiate withdrawal?
- Opioid Withdrawal: What It’s Like to Detox from Opiates | MedCircle
What is Opiate Withdrawal?
Opiate withdrawal is the set of physical and psychological symptoms that occur when someone who has been habitually using opiates suddenly stops or significantly reduces their dose. Common symptoms of opiate withdrawal include sweating, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, and depression. Severe cases of opiate withdrawal can also include fever, anxiety, shaking, and even seizures.
Understanding Opiate Withdrawal
It is important to understand the severity of opiate withdrawal and the potential risks associated with it. One of the most serious risks is the potential for relapse. Without proper treatment and support, it is easy to become overwhelmed by cravings and succumb to the temptation of using opiates again. It is also important to understand that opiate withdrawal is not only a physical experience, but also a psychological one. The emotional toll of withdrawal can be just as difficult to manage as the physical symptoms.
Seeking Professional Help
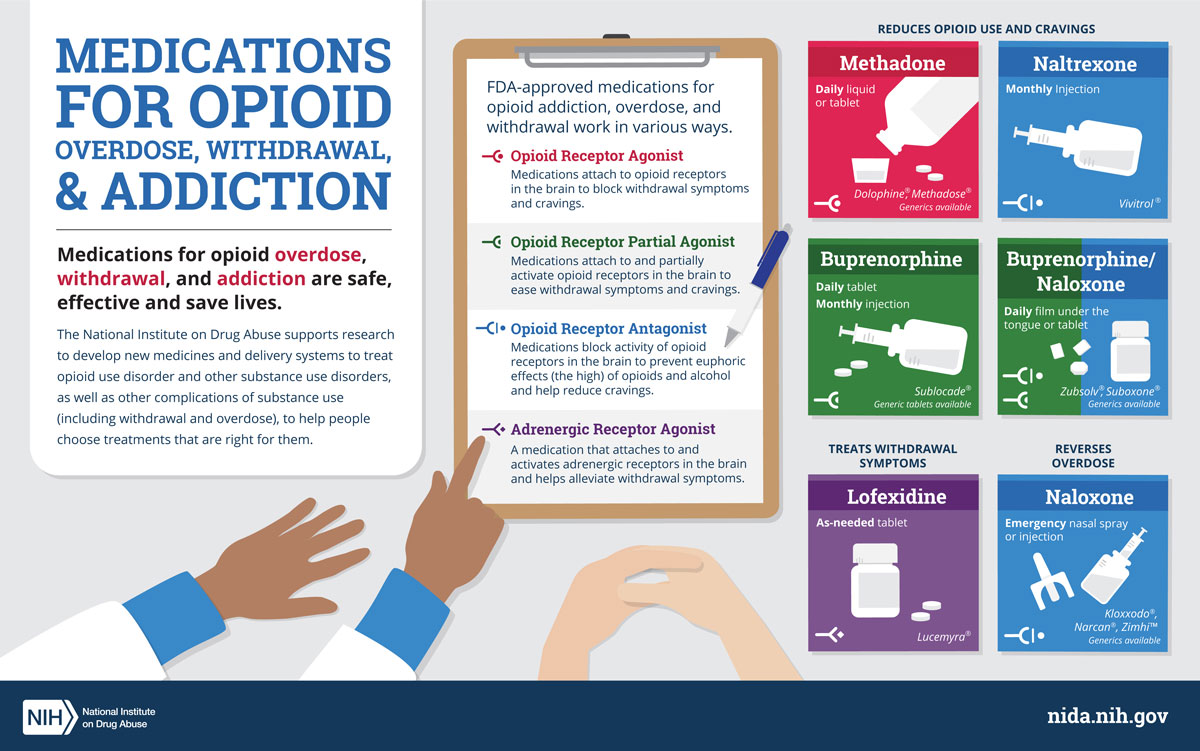
The best way to manage opiate withdrawal is to seek professional help. Medical professionals can provide medication-assisted treatment (MAT) that can significantly reduce the severity of withdrawal symptoms. This form of treatment usually involves prescribing medications such as buprenorphine or methadone, which act on the same brain receptors as opiates, but without the same euphoric effects. This can help to reduce the severity of withdrawal symptoms and make the process of withdrawal much more manageable.
Managing Symptoms at Home
Although professional help is the best way to manage opiate withdrawal, there are also some home remedies that can help to alleviate some of the symptoms.
Healthy Diet and Exercise
It is important to eat a healthy diet and stay as physically active as possible during withdrawal. A balanced diet of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help to reduce some of the symptoms associated with opiate withdrawal, such as nausea, fatigue, and muscle cramps. Regular exercise can also help to reduce symptoms such as anxiety and depression.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques can be helpful in managing the psychological symptoms of withdrawal. Practicing deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help to reduce stress and anxiety, as well as promote a sense of calm and wellbeing.
Managing Cravings
Managing cravings is one of the most difficult aspects of opiate withdrawal. It can be easy to succumb to the temptation of using opiates again, especially during times of stress and anxiety.
Distraction Techniques
It is important to find ways to distract yourself when cravings become too strong. Listening to music, reading, or engaging in hobbies can help to take your mind off the cravings and make them easier to manage.
Support Groups
Support groups are also a great way to manage cravings. Connecting with others who are going through the same experience can help to provide comfort and understanding. Additionally, support groups can provide a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and receive advice and encouragement.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is opiate withdrawal?
Opiates are a group of drugs that are used to treat pain. They are highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence in those who use them. Opiate withdrawal is the process of reducing or discontinuing the use of opiate drugs, which can lead to physical and psychological symptoms, such as nausea, abdominal pain, anxiety, insomnia, and depression.
What are the signs and symptoms of opiate withdrawal?
The signs and symptoms of opiate withdrawal can vary depending on the type of opiate being used and the duration of use. Common symptoms include agitation, irritability, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, chills, insomnia, muscle aches, and cravings.
What treatments are available for opiate withdrawal?
There are a variety of treatments available for opiate withdrawal, including medication-assisted treatment (MAT), behavioral therapies, and lifestyle changes. MAT is the most common form of treatment, and involves the use of medications such as buprenorphine, methadone, and naloxone to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Behavioral therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and contingency management can also be used to help individuals cope with withdrawal and other related issues.
What lifestyle changes can help with opiate withdrawal?
Making lifestyle changes can be an important part of managing opiate withdrawal and preventing relapse. These changes include exercising regularly, avoiding triggers, eating a healthy diet, getting adequate sleep, avoiding drug use, and participating in support groups. Additionally, engaging in activities such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress and anxiety.
What are the potential complications of opiate withdrawal?
The potential complications of opiate withdrawal can be severe and include dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, malnutrition, and even death. It is important to seek medical attention if any of these complications are suspected or if the individual is experiencing severe withdrawal symptoms.
How can friends and family help someone going through opiate withdrawal?
Friends and family can be a great source of support for someone going through opiate withdrawal. They can provide emotional support, motivate the individual to stick with their treatment plan, and help identify and avoid triggers. Additionally, they can help with practical tasks such as grocery shopping, meal preparation, and transportation. Lastly, they can provide encouragement to participate in activities and help find activities that the individual enjoys.
Opioid Withdrawal: What It’s Like to Detox from Opiates | MedCircle
The truth is, opiate withdrawal is a difficult process to go through. However, with the right help, support, and guidance, it is possible to make it through recovery and live a healthier, substance-free life. With the right strategies to help manage withdrawal symptoms, resources to assist with the psychological aspects of addiction, and support from family and friends, recovery is a real possibility. It is never too late to get the help you need and begin the journey towards a better life.

