The opioid crisis has been a hot topic for some time now, and it’s an issue that continues to plague our nation. From the deadly toll of opioid overdoses to the impact on families and communities, the opioid crisis has left an indelible mark on countless lives. But what about the individual people addicted to opioids? How many people are actually impacted by the opioid crisis? In this article, we’ll explore the scope of the opioid crisis and find out how many people are addicted to opioids.
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, an estimated 2.1 million people in the United States had an opioid use disorder in 2018. This number is based on the misuse of prescription opioids and the use of illegal opioids, such as heroin.
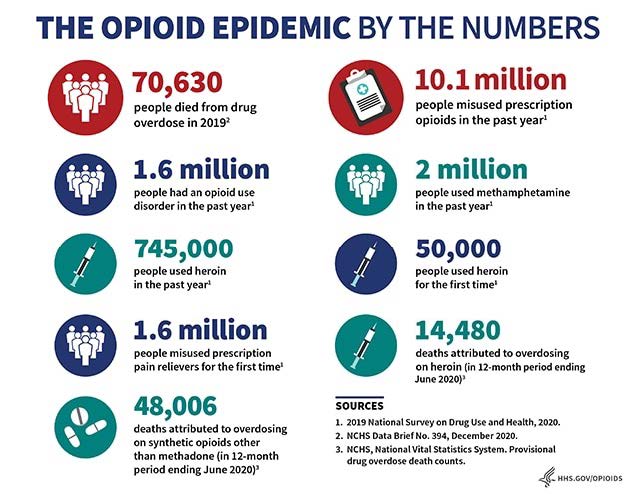
Contents
Overview of Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction has become an epidemic in many countries around the world, with millions of people suffering from the potentially fatal consequences of substance abuse. Opioids are a class of drugs derived from opium, which are prescribed to relieve moderate to severe pain. These drugs act on the brain and can create a sense of euphoria and relaxation, leading to addiction and physical dependence. Opioid addiction is a serious problem, with a wide range of physical and psychological effects, including an increased risk of overdose.
Opioid addiction is also linked to a wide range of social, psychological and physical problems. Long-term use of opioids can lead to a decrease in physical and cognitive functioning, an increase in mental health issues, and an increase in the risk of developing an infectious disease. The most serious consequence of opioid addiction is an increased risk of death due to overdose.
Number of People Addicted to Opioids
The number of people addicted to opioids is difficult to estimate due to the difficulty in defining what constitutes addiction. However, a number of studies have attempted to estimate the prevalence of opioid addiction in different countries. According to the World Health Organization, the global prevalence of opioid use disorder is estimated to be between 0.2% and 1.5%.
In the United States, the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) estimates that over 2 million people aged 12 or older were addicted to opioids in 2019. This figure represents 0.7% of the population, a 30% increase from the previous year. It is estimated that the number of people addicted to opioids has increased by over 200% since 2000.
Risk Factors for Opioid Addiction
There are a number of risk factors that can increase a person’s likelihood of developing an opioid addiction. These include a personal or family history of substance abuse, a history of mental health problems, and a history of trauma. Other risk factors include poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and a lack of access to treatment for opioid addiction.
Genetic Factors
Research suggests that genetic factors can play a role in the development of opioid addiction. Studies have found that those with a family history of substance abuse are more likely to develop an opioid addiction.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also increase the risk of opioid addiction. People who live in poverty or have limited access to healthcare are more likely to become addicted to opioids. Additionally, those who have experienced trauma, such as physical or sexual abuse, are more likely to develop an opioid addiction.
Treatment of Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction is a complex condition that requires comprehensive treatment. Treatment plans typically involve a combination of medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. The goal of treatment is to help individuals stop using opioids and to cope with their addiction in a healthy way.
Medications for Opioid Addiction
There are a number of medications that can be used to treat opioid addiction. These include buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone. These medications act on the brain and can reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, making it easier for individuals to quit using opioids.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy can be an important part of the treatment process for opioid addiction. This type of therapy focuses on helping individuals identify and address the underlying causes of their addiction. It can involve individual, group, and family therapy, as well as relapse prevention strategies.
Prevention of Opioid Addiction
Preventing opioid addiction is a key part of tackling the opioid epidemic. Strategies for prevention include promoting responsible opioid prescribing practices, increasing access to treatment, and educating individuals about the risks associated with opioid use. It is also important to ensure that those at risk of opioid addiction are identified and provided with the necessary support.
Responsible Prescribing Practices
One of the most important steps in preventing opioid addiction is to promote responsible opioid prescribing practices. This includes using the lowest possible dose of opioids and avoiding long-term opioid use, whenever possible. It is also important to ensure that individuals are regularly monitored for signs of addiction.
Access to Treatment
Increasing access to treatment is essential for preventing and treating opioid addiction. This includes making sure that treatment is available to those who need it, regardless of their ability to pay. It is also important to ensure that treatment is provided in a safe and supportive environment.
Conclusion
Opioid addiction is a serious problem, with millions of people around the world affected. It is important to understand the risk factors for opioid addiction and to take steps to prevent and treat the condition. This includes promoting responsible opioid prescribing practices, increasing access to treatment, and educating individuals about the risks associated with opioid use.
Related Faq
What is an Opioid?
An opioid is a type of drug that is used to relieve pain. It is derived from the opium poppy plant and works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain to reduce the sensation of pain. Opioids can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including chronic pain and opioid use disorder. However, they have a high potential for misuse and addiction, and can have serious side effects.
What Causes Opioid Addiction?
Opioid addiction is caused primarily by misuse or abuse of opioids. People become addicted to opioids when they take them in higher doses or more frequently than prescribed, or when they take them without a prescription. Other risk factors for opioid addiction include mental illness, substance use disorders, certain medical conditions, and social and environmental factors.
How Many People Are Addicted to Opioids?
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, an estimated 2.1 million people had an opioid use disorder in 2018. This figure includes those who were addicted to prescription opioids, such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, and codeine, as well as those who were addicted to illicit opioids, such as heroin and fentanyl.
What Are the Signs of Opioid Addiction?
The signs of opioid addiction can vary, but some common signs include craving the drug, taking higher doses or more frequent doses than prescribed, and engaging in risky behaviors, such as doctor shopping or stealing, to obtain the drug. Other signs of opioid addiction may include changes in mood or behavior, such as increased aggression or irritability, and physical changes, such as lack of energy or poor coordination.
What Are the Treatment Options for Opioid Addiction?
The most effective treatment for opioid addiction is an evidence-based approach that includes medication-assisted treatment (MAT), counseling, and support groups. MAT is a combination of medications, such as buprenorphine, naltrexone, and methadone, which can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Counseling and support groups provide individuals with the tools and resources they need to overcome their addiction.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Opioid Addiction?
The long-term effects of opioid addiction can be severe and include an increased risk of overdose, organ damage, mental health issues, and social problems. Overdose can be fatal, and organ damage can include liver and kidney damage, as well as damage to the heart and lungs. Mental health issues can include depression and anxiety, and social problems can include financial difficulties, legal issues, and strained relationships.
Descent into opioid addiction captured on video
The opioid crisis is an epidemic that affects millions of people in the United States and around the world. While addiction is a complex issue and hard to quantify, the overall number of people addicted to opioids is staggering. With the right combination of education, prevention, and treatment, we can help reduce the number of people struggling with opioid addiction and provide a brighter future for those affected by this devastating problem.

