When it comes to nicotine, it’s important to know how long it can remain in your blood system. Whether you’re a smoker or an ex-smoker, understanding the timeline for nicotine to stay in your bloodstream can help you make informed decisions about your health. In this article, we’ll look at the duration of nicotine in your blood system and the factors that can affect that timeline.
Nicotine can stay in your blood for 1-3 days after you have smoked a cigarette, although it will depend on your metabolism and how much you smoke. Nicotine can be detected in urine for up to 4 weeks after smoking. After this time it will be almost completely out of your system.
Contents
- How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your Blood System?
- How Nicotine is Detected in Your Blood System
- Testing for Nicotine in Your Blood System
- Risks of Nicotine in Your Blood System
- How to Reduce Nicotine in Your Blood System
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your Blood System?
- Q2: How Is Nicotine Detected in Your Blood System?
- Q3: What Are the Health Risks of Nicotine in the Blood System?
- Q4: Are There Any Natural Ways to Remove Nicotine from the Blood System?
- Q5: Does Nicotine Remain in Your Blood System Longer if You’re a Heavy Smoker?
- Q6: Can Nicotine Remain in Your Blood System After Quitting Smoking?
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your Blood System?
How Nicotine is Detected in Your Blood System
Nicotine is a chemical compound found in the leaves of tobacco plants, and it is the primary psychoactive ingredient in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. Nicotine is quickly absorbed into your bloodstream when you smoke or use one of these products. Nicotine can be detected in your blood system through a variety of tests, such as a blood test and a urine test. The amount of nicotine in your blood system can also be measured with a breath test.
How Long Nicotine Stays in Your Blood System
The amount of nicotine in your blood system will depend on how much and how often you smoke or use tobacco. Generally, nicotine can be detected in your blood for about two to three days after you last use it. However, the length of time that nicotine stays in your blood system can vary depending on several factors, such as your metabolism and how much you have smoked.
Factors That Affect Nicotine Clearance
There are several factors that can affect how long nicotine stays in your blood system. These factors include your age, gender, body weight, and the amount of nicotine you have been exposed to. For example, younger people tend to have faster metabolisms, which means that nicotine is cleared from their bodies more quickly. Additionally, people with higher body weights tend to have higher levels of nicotine in their system for longer periods of time.
Testing for Nicotine in Your Blood System
If you are concerned about nicotine in your blood system, you can have it tested by your doctor. Nicotine tests can be used to determine if you have been exposed to nicotine recently. The most common tests used to detect nicotine in your blood system are blood tests and urine tests. Blood tests are the most sensitive and accurate test for detecting nicotine, as they measure the amount of nicotine in your blood directly. Urine tests are less sensitive, but they can still be used to detect nicotine in your system.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can detect nicotine in your system up to two to three days after you have last used it. The test measures the amount of nicotine in your blood and can indicate if you have been exposed to nicotine recently. Your doctor will take a sample of your blood and send it to a laboratory for testing.
Urine Tests
Urine tests are also used to detect nicotine in your system. The test measures the amount of cotinine, a byproduct of nicotine, in your urine. Urine tests can detect nicotine in your system up to four days after you have last used it. Your doctor will take a sample of your urine and send it to a laboratory for testing.
Risks of Nicotine in Your Blood System
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance, and it can have long-term health effects. Smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products can increase your risk of developing lung cancer, heart disease, and other serious health conditions. Additionally, nicotine can increase your risk of developing addiction and dependence.
Nicotine Addiction
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance, and it can cause physical and psychological dependence. Smoking or using other tobacco products can increase your risk of developing an addiction. People who are addicted to nicotine may experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop using nicotine, such as cravings, irritability, and insomnia.
Nicotine Dependence
Nicotine dependence is a condition in which a person needs nicotine in order to function normally. People who are dependent on nicotine may experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop using nicotine, such as anxiety, depression, and difficulty concentrating. Long-term nicotine use can also lead to physical dependence, which can cause physical symptoms such as nausea, headaches, and fatigue.
How to Reduce Nicotine in Your Blood System
If you are concerned about the amount of nicotine in your blood system, there are several steps you can take to reduce it. Quitting smoking or using other tobacco products is the best way to reduce nicotine in your system. Additionally, if you are unable to quit, you can try using nicotine replacement therapy or other medications to help reduce your cravings.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy
Nicotine replacement therapy is a form of medication that helps reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Nicotine replacement therapy comes in a variety of forms, including patches, gums, lozenges, and inhalers. These products can help reduce your cravings for nicotine and make it easier to quit smoking.
Medications
There are also medications available that can help reduce nicotine cravings and withdrawal symptoms. These medications include varenicline (Chantix) and bupropion (Zyban). These medications can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, making it easier to quit smoking.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your Blood System?
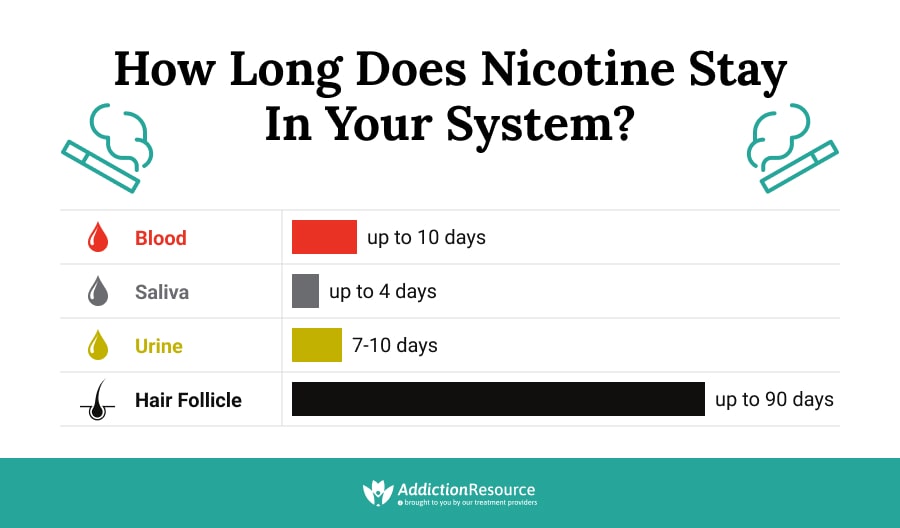
A1: Generally, nicotine is detectable in the bloodstream for 1-3 days, though it can remain in the body for up to 10 days. The amount of time nicotine stays in your blood depends on several factors, such as how much nicotine you were exposed to, how often you use it, and your metabolism. Generally, heavier smokers and those with slower metabolisms will have nicotine in their system for a longer period of time.
Q2: How Is Nicotine Detected in Your Blood System?
A2: Nicotine can be detected in the blood through a variety of methods, including blood tests, saliva tests, and urine tests. Blood tests are the most accurate way to detect nicotine, as they can detect minute amounts of the substance. Saliva tests are also accurate, but they can only detect nicotine that has been ingested or inhaled within the last few hours. Urine tests are less accurate than blood and saliva tests, but they can detect nicotine that has been ingested or inhaled in the last several days.
Q3: What Are the Health Risks of Nicotine in the Blood System?
A3: Nicotine is an addictive stimulant that can have adverse health effects when present in the bloodstream. Some of the potential health risks associated with nicotine include increased blood pressure and heart rate, an increased risk of stroke and heart disease, and an increased risk of developing cancer. Additionally, nicotine can interact with other substances and increase the risk of addiction to other substances.
Q4: Are There Any Natural Ways to Remove Nicotine from the Blood System?
A4: There are a few natural ways to remove nicotine from the bloodstream. The most effective way is to abstain from smoking and other forms of nicotine consumption. Additionally, drinking plenty of water and exercising regularly can help the body flush the nicotine out of the system. Eating certain fruits and vegetables, such as oranges, apples, and broccoli, can also help the body rid itself of nicotine.
Q5: Does Nicotine Remain in Your Blood System Longer if You’re a Heavy Smoker?
A5: Generally, yes. As mentioned above, the amount of time nicotine stays in your blood depends on several factors, such as how much nicotine you were exposed to, how often you use it, and your metabolism. Generally, heavier smokers and those with slower metabolisms will have nicotine in their system for a longer period of time.
Q6: Can Nicotine Remain in Your Blood System After Quitting Smoking?
A6: Yes, nicotine can remain in your blood system for up to 10 days after quitting smoking. After quitting smoking, the amount of nicotine in your system will gradually decrease over time. However, it may take several weeks or even months for nicotine to completely leave your bloodstream. Additionally, if you start smoking again, the nicotine will return to your bloodstream.
The answer to the question of how long nicotine stays in your blood system is not a simple one. Depending on many factors, such as how often you smoke and the amount of nicotine you consume, it can last anywhere from two to three days to several weeks. It is important to be aware of the long-term effects of nicotine on your body. Nicotine not only affects your cardiovascular system, but it has also been linked to other health conditions, including cancer and lung disease. Quitting smoking is the best way to reduce the amount of nicotine in your body and improve your overall health.

