Nicotine is a powerful stimulant found in tobacco products, but how exactly does it affect the body? From its impact on the central nervous system to the long-term health risks associated with its use, this article will explore the various ways in which nicotine affects the human body. We’ll also look at the potential benefits of nicotine use, as well as the potential for nicotine addiction. By the end, you should have a better understanding of the effects nicotine has on the body and how to limit or avoid them.
Nicotine affects the body by increasing the levels of adrenaline and noradrenaline hormones, stimulating the central nervous system, increasing blood pressure, heart rate and respiration, and causing alertness and a sense of well being. It also increases dopamine levels in the brain, leading to feelings of pleasure. Over time, however, the body becomes tolerant to the effects of nicotine and higher doses are needed to achieve the same effects. Long-term use of nicotine can lead to an increased risk of cancer, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
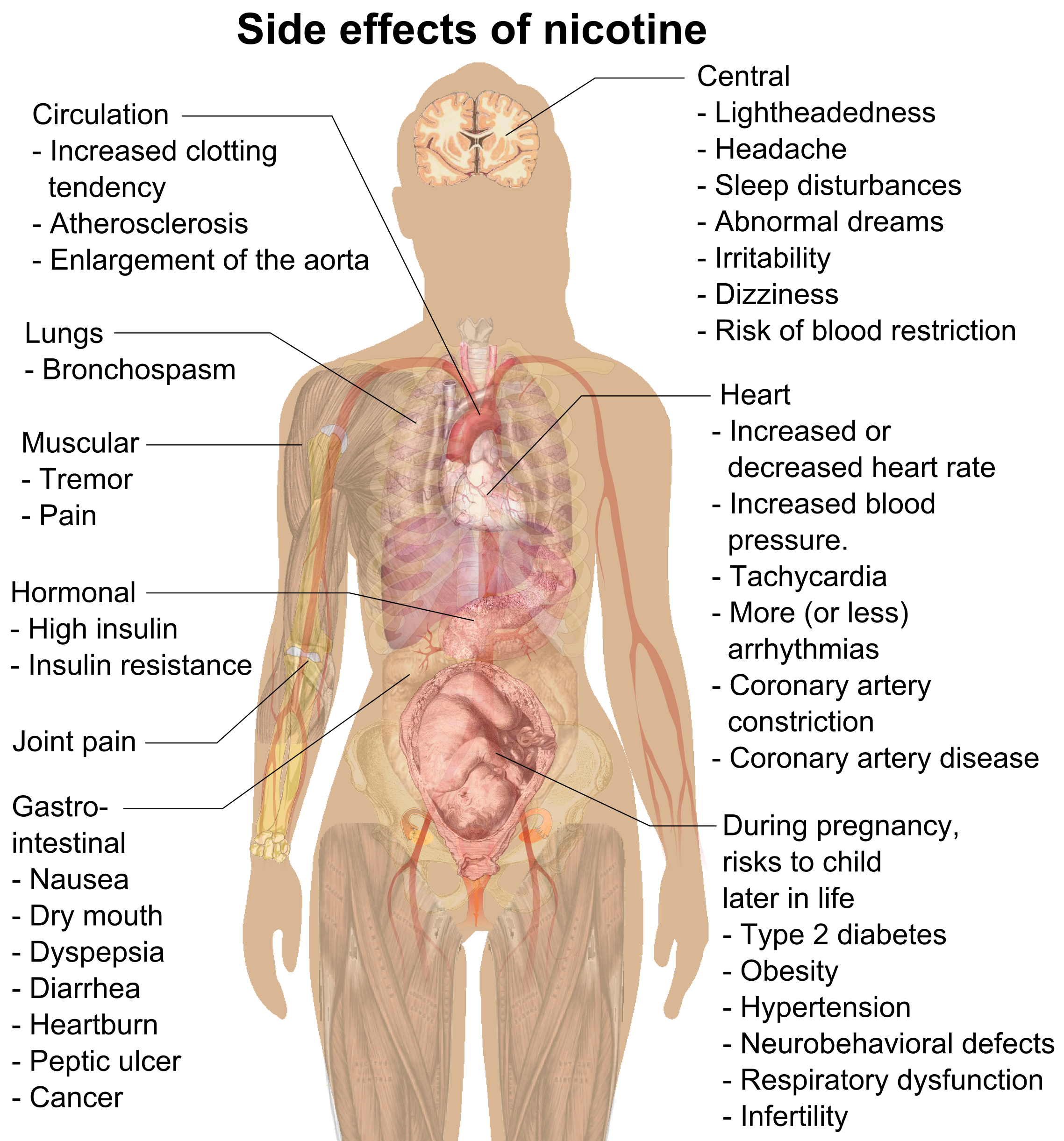
How Nicotine Affects the Body
Nicotine is a powerful stimulant found in tobacco products such as cigarettes, cigars, and e-cigarettes. It is highly addictive, and can have both short-term and long-term effects on the body. Nicotine affects the body’s central nervous system, heart rate, respiratory rate, digestion, and even the immune system. This article will explore the effects of nicotine on the body, both positive and negative.
Effects on the Brain
Nicotine stimulates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of pleasure and reward. This makes nicotine highly addictive and causes users to seek out more nicotine to get the same feeling of pleasure. Long-term use of nicotine can also lead to changes in the brain, making it more difficult to feel pleasure from activities that don’t involve nicotine.
Nicotine also affects the brain’s ability to form memories and think critically. This can lead to trouble concentrating and making decisions. It also affects the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for impulse control and decision-making.
Effects on the Heart and Blood Vessels
Nicotine causes the heart to beat faster and increases the blood pressure. This can lead to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. Nicotine also narrows the arteries, which can lead to decreased blood flow and oxygen to the organs. This can lead to long-term damage to the heart, brain, and other organs.
Long-term use of nicotine can also increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Nicotine also affects the way the body processes carbohydrates and fats, which can lead to weight gain.
Effects on the Respiratory System
Nicotine has a direct effect on the lungs. It irritates the airways and increases mucus production. This can lead to difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing. It also increases the risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Long-term use of nicotine can also damage the cilia, which are small hairs in the lungs that help to filter out dust and other particles. This can lead to an increased risk of respiratory infections.
Effects on the Digestive System
Nicotine can cause the stomach to produce more acid, which can lead to heartburn, indigestion, and nausea. Long-term use of nicotine can also increase the risk of developing stomach ulcers.
Nicotine can also affect the way the body absorbs certain vitamins and minerals. This can lead to deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as vitamin B12 and iron.
Effects on the Immune System
Nicotine decreases the body’s ability to fight off infections, which can lead to an increased risk of developing certain illnesses. This can include colds, flu, and other respiratory infections. Long-term use of nicotine can also increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Conclusion
Nicotine is a powerful stimulant that can have both short-term and long-term effects on the body. Nicotine affects the brain, heart and blood vessels, respiratory system, digestive system, and immune system. It can lead to an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, cancer, and various infections. It is important to be aware of the risks associated with nicotine use and to take steps to reduce them.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is a chemical compound found in the tobacco plant, and is the primary ingredient responsible for the addictive properties of tobacco products. It is a colorless to pale yellow liquid that is volatile and has a pungent odor. Nicotine is an alkaloid that acts as a stimulant and is responsible for many of the physical and psychological effects of smoking. It is also used in some medications, including nicotine patches and gum, to help smokers quit.
What is the Chemical Structure of Nicotine?
Nicotine is a nitrogen-containing alkaloid compound found in the tobacco plant. Its chemical structure is C10H14N2, and it has a molecular weight of 162.23 g/mol. It is composed of a pyridine ring, an imidazole ring, and a pyrrolidine ring. Nicotine is a colorless to pale yellow liquid and is volatile, with a pungent odor.
What are the Effects of Nicotine on the Body?
Nicotine has both short-term and long-term effects on the body. In the short-term, nicotine stimulates the release of adrenaline, which increases heart rate and blood pressure. It also increases alertness and can improve concentration and reaction time. In the long-term, nicotine can lead to addiction and increases the risk of health problems, such as cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Brain?
Nicotine activates the reward system in the brain, releasing dopamine and other neurotransmitters that produce feelings of pleasure and reward. Over time, this can lead to addiction, as the brain develops a tolerance and needs more nicotine to achieve the same effects. Nicotine also affects the brain’s executive functions, such as decision-making and memory.
What are the Side Effects of Nicotine?
The side effects of nicotine can vary depending on the individual and the amount consumed. Common side effects include nausea, headaches, dizziness, increased heart rate and blood pressure, and difficulty sleeping. Other side effects include anxiety, depression, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Long-term use of nicotine can lead to addiction and increases the risk of health problems, such as cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
What is Nicotine Addiction?
Nicotine addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder in which a person is unable to stop using tobacco products despite the negative effects on their health and life. It is characterized by a strong urge to use nicotine, difficulty controlling the amount consumed, and withdrawal symptoms when not using nicotine. Over time, the brain develops a tolerance to nicotine and needs more to achieve the same effects. Nicotine addiction is a serious condition that requires professional treatment.
Nicotine has a wide range of effects on the body, some of which can be beneficial while others can be detrimental. Nicotine can improve cognitive function, reduce pain, and increase metabolic rate. However, it can also increase blood pressure, raise the risk of heart disease, and cause addiction and dependence. Therefore, it is important to understand the risks and benefits associated with nicotine and to use it responsibly. By recognizing the effects of nicotine and using it responsibly, individuals can enjoy its potential benefits while avoiding the potential harms associated with it.

