Stimulant drugs are some of the most commonly prescribed medications in the world. From treating conditions like ADHD to improving alertness and concentration, stimulants can have a powerful and positive effect on those who use them. But how do they work? In this article, we will explore the science behind stimulant drugs and discuss how they work to provide relief from certain physical and mental ailments.
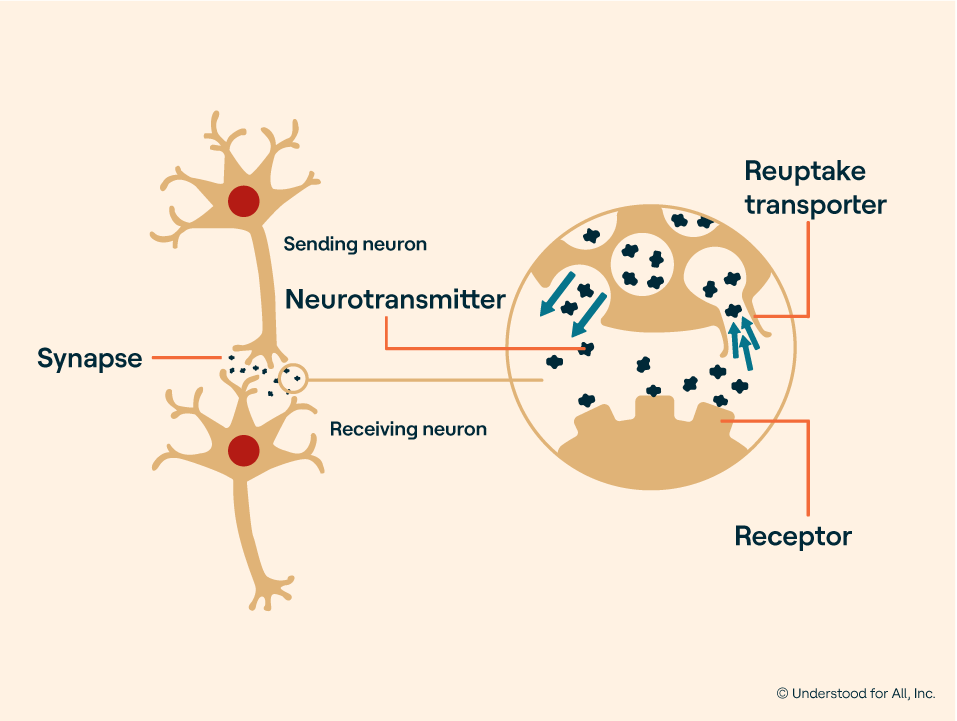
Stimulant drugs work by increasing levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These drugs increase alertness, attention, and energy, while decreasing fatigue and appetite. They also affect mood, concentration, and motivation. Common stimulant drugs include amphetamines, methylphenidate, cocaine, and caffeine.
Contents
What is a Stimulant Drug?
A stimulant drug is a type of medication that increases alertness, attention, and energy. Stimulants can be prescribed for people with certain medical conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and depression. Stimulants can also be taken recreationally, without a prescription, to increase energy and alertness.
Stimulants work by increasing the activity of certain chemicals in the brain, including dopamine and norepinephrine. This leads to increased energy, alertness, and focus. Stimulants can also have other effects, such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased breathing.
Types of Stimulants
There are several types of stimulant drugs available. Commonly used stimulants include amphetamines such as Adderall, Ritalin, and Vyvanse; methylphenidate, such as Concerta and Daytrana; and modafinil, such as Provigil and Nuvigil.
These drugs are generally taken orally, but some can be injected or smoked. Stimulants can also be found in some over-the-counter dietary supplements, such as caffeine and guarana.
Adderall, Ritalin, and Vyvanse
Adderall, Ritalin, and Vyvanse are all amphetamines. They increase the activity of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which leads to increased alertness and concentration. These drugs are prescribed for people with ADHD and narcolepsy, and can also be used recreationally to increase energy and focus.
Adderall, Ritalin, and Vyvanse all have the potential for abuse and addiction. They can have serious side effects, including anxiety, irritability, and insomnia.
Methylphenidate and Concerta
Methylphenidate and Concerta are two types of stimulants that work differently than amphetamines. They increase the activity of dopamine in the brain and also block the reuptake of dopamine, which leads to increased alertness and concentration. These drugs are prescribed for people with ADHD and can also be used recreationally to increase energy and focus.
Methylphenidate and Concerta can also have serious side effects, including anxiety, irritability, and insomnia.
How Do Stimulant Drugs Work?
Stimulant drugs work by increasing the activity of certain chemicals in the brain, including dopamine and norepinephrine. This leads to increased energy, alertness, and focus. Stimulants can also have other effects, such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased breathing.
Amphetamines
Amphetamines are a type of stimulant drug that increase the activity of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, leading to increased alertness and concentration. Amphetamines can be prescribed for people with ADHD and narcolepsy, and can also be used recreationally to increase energy and focus.
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate is a type of stimulant drug that increases the activity of dopamine in the brain and blocks the reuptake of dopamine, leading to increased alertness and concentration. Methylphenidate is often prescribed for people with ADHD and can also be used recreationally to increase energy and focus.
Side Effects of Stimulant Drugs
Stimulants can have a range of side effects, including increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased breathing. They can also cause anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and loss of appetite. Stimulants can also be addictive and have the potential for abuse.
Addiction and Abuse
Stimulants can be addictive, and they have the potential for abuse. People who abuse stimulants may experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking the drugs. These symptoms can include depression, irritability, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
Long-Term Effects
Long-term use of stimulants can lead to physical and psychological dependence. It can also lead to tolerance, meaning that higher doses are needed to get the same effects. Long-term use of stimulants can also lead to insomnia, weight loss, and anxiety.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Stimulant Drug?
A stimulant drug is a type of drug that produces an increased level of activity or alertness in the body. Stimulants can be either natural or synthetic, and they work by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain to increase energy, focus, and alertness. Common types of stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, and other prescription medications.
What are the Effects of Stimulant Drugs?
The effects of stimulant drugs vary depending on the type of drug, the dose, and the individual’s sensitivity. Generally, the effects of stimulants include increased alertness, energy, concentration, and motivation. In higher doses, stimulants can also cause increased heart rate and blood pressure, increased body temperature, restlessness, and anxiety.
How Does a Stimulant Drug Work?
Stimulant drugs work by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are responsible for regulating many aspects of the body, including mood, energy, motivation, and focus. When stimulated, these neurotransmitters are released in higher amounts, leading to increased alertness and energy.
What are the Side Effects of Stimulant Drugs?
The side effects of stimulant drugs vary depending on the type of drug and the dose taken. Common side effects include irritability, insomnia, headaches, loss of appetite, and increased heart rate and blood pressure. In some cases, stimulants can also lead to anxiety, restlessness, and dependence.
Are Stimulant Drugs Addictive?
Yes, many stimulant drugs can be addictive. Stimulants activate the brain’s reward system and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. When taken in large amounts or over a long period of time, stimulants can lead to addiction.
What are the Risks of Using Stimulant Drugs?
The risks of using stimulant drugs depend on the type of drug and the dose taken. Stimulants can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and sudden death. They can also lead to anxiety, insomnia, and restlessness. Stimulants can also be addictive and lead to physical and psychological dependence.
Why Stimulants Help ADHD
In conclusion, stimulant drugs work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. This increase in neurotransmitter levels leads to a heightened sense of alertness, focus, and energy. Stimulant drugs can be helpful in treating certain medical conditions, but they should always be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional. It is important to understand the potential side effects associated with stimulant drugs, including anxiety, insomnia, rapid heartbeat, and even addiction. By understanding how stimulant drugs work, we can better manage their use and ensure that they are used safely and responsibly.

