Stimulants are substances that can increase energy and alertness, resulting in improved focus and enhanced performance. But how exactly do these substances work biochemically in the body? This article will explore the biochemical processes involved in the effects of stimulants and how they can be used to achieve various goals. From better cognitive performance to improved mood and energy levels, this article will provide an overview of how stimulants work biochemically to achieve these outcomes.
Stimulants work by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. This can help to increase alertness, focus, concentration, and energy. Stimulants also have an affect on the body’s metabolism by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. Stimulants can even help to reduce fatigue and make it easier to stay awake.
Contents
- What are Stimulants
- The Effects of Stimulants
- Risks of Stimulant Abuse
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What are Stimulants?
- How Do Stimulants Work Biochemically?
- What Side Effects Can Stimulants Cause?
- What Are the Potential Long-Term Effects of Stimulant Use?
- What Is the Difference Between Stimulants and Other Types of Drugs?
- What Are Some Common Stimulants?
- Stimulants (Ritalin and Adderall) Explained in 3 Minutes
What are Stimulants
Stimulants are a class of drugs that act on the central nervous system and produce a range of effects, including increased alertness and energy, improved concentration, and enhanced physical performance. Stimulants can be found in both prescription and non-prescription forms and are commonly used to treat conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. While stimulants can be beneficial in certain situations, they can also be highly addictive and have potentially dangerous side effects when abused.
Types of Stimulants
Stimulants are divided into two main categories: those that are prescribed and those that are not. Prescription stimulants, such as amphetamines, methylphenidate (Ritalin), and dextroamphetamine (Adderall), are used to treat conditions such as ADHD and narcolepsy. Non-prescription stimulants, such as caffeine and ephedrine, are widely available and are often used for recreational purposes.
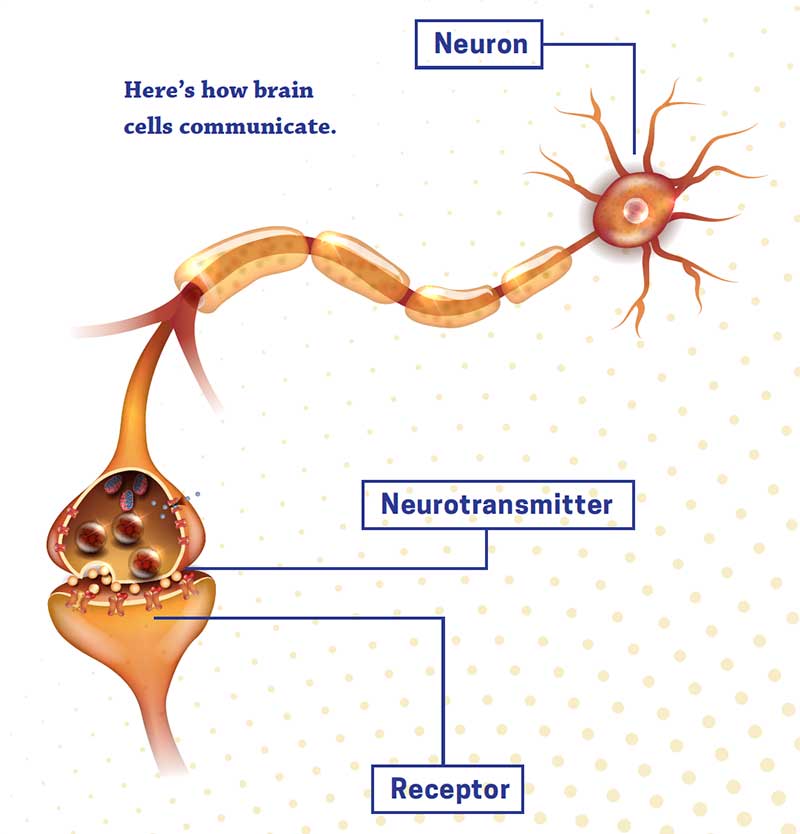
How Stimulants Work Biochemically
Stimulants work by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. For example, amphetamines increase the activity of dopamine and norepinephrine, while caffeine works by blocking the action of adenosine, a chemical that causes drowsiness. The effects of different stimulants can vary depending on how they interact with the brain’s chemistry.
The Effects of Stimulants
When taken in moderation, stimulants can have a range of beneficial effects, including increased alertness and concentration, improved physical performance, and increased energy. However, stimulants can also have negative side effects, including insomnia, irritability, anxiety, and increased blood pressure. In addition, stimulants can be highly addictive, and long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence.
Short-Term Effects of Stimulants
The short-term effects of stimulants can vary depending on the type and amount taken. Common short-term effects include increased alertness and energy, improved concentration, and enhanced physical performance. In addition, stimulants can also cause restlessness, irritability, and increased heart rate and blood pressure.
Long-Term Effects of Stimulants
When taken for extended periods of time, stimulants can become habit-forming and lead to physical and psychological dependence. Long-term use of stimulants can also lead to a range of health problems, including insomnia, anxiety, and high blood pressure. In addition, some stimulants can cause damage to the heart, liver, and kidneys if taken in large doses or over a long period of time.
Risks of Stimulant Abuse
Stimulants can be highly addictive, and abusing them can lead to a range of serious health problems. Stimulant abuse can also increase the risk of developing mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety. In addition, stimulant abuse can lead to an increased risk of accident or injury due to impaired judgment or coordination.
Physical Risks of Stimulant Abuse
The physical risks of stimulant abuse include increased heart rate and blood pressure, increased body temperature, and increased risk of stroke. In addition, stimulants can cause dehydration, nausea, vomiting, and restlessness. Long-term use of stimulants can also lead to organ damage, including damage to the heart, liver, and kidneys.
Psychological Risks of Stimulant Abuse
The psychological risks of stimulant abuse include increased anxiety, irritability, and aggression. In addition, stimulant abuse can lead to depression, paranoia, and difficulty concentrating. Stimulant abuse can also cause changes in behavior, such as increased risk-taking and impulsivity.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What are Stimulants?
Stimulants are substances that increase alertness and activity, boost energy, and heighten focus. Stimulants can be found naturally in coffee, tea, cocoa, and chocolate, or as manufactured drugs like Ritalin, Adderall, and Concerta. Stimulants work by increasing the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These chemicals help regulate alertness, attention, and movement.
How Do Stimulants Work Biochemically?
Stimulants work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. When these neurotransmitters are released, they bind to receptors on neurons and cause them to become more active. This increased activity increases alertness, attention, and energy. Stimulants also increase the release of other hormones such as adrenaline, which can further increase energy levels.
What Side Effects Can Stimulants Cause?
The most common side effects of stimulants are increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, headaches, restlessness, insomnia, and decreased appetite. Stimulants can also cause anxiety, irritability, and mood swings. Less common side effects can include irregular heartbeat, increased sweating, and increased risk of seizures.
What Are the Potential Long-Term Effects of Stimulant Use?
Long-term use of stimulants can lead to physical dependence, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms when the drug is stopped. Long-term use can also lead to tolerance, meaning the user will need to take larger amounts of the drug to get the same effect. Stimulants can also cause changes in the brain, including reduced motivation and impaired decision-making.
What Is the Difference Between Stimulants and Other Types of Drugs?
Stimulants are drugs that increase alertness, attention, and energy. These drugs are different from sedatives, which have the opposite effect and are used to reduce anxiety and induce sleep. Stimulants are also different from hallucinogens and other drugs that can cause changes in perception, mood, and behavior.
What Are Some Common Stimulants?
Some common stimulants include caffeine, amphetamines, methylphenidate, and modafinil. Caffeine is found naturally in coffee, tea, cocoa, and chocolate, while amphetamines and methylphenidate are prescription drugs used to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Modafinil is a prescription drug used to treat sleepiness and narcolepsy.
Stimulants (Ritalin and Adderall) Explained in 3 Minutes
In conclusion, stimulants work biochemically by stimulating the central nervous system and increasing the production of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Stimulants can have beneficial effects on the body, such as increased alertness, improved focus, and increased energy. However, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects and risks associated with the use of stimulants, and to use them responsibly. With careful consideration and monitoring of the potential risks, stimulants can be a valuable tool in achieving desired results.

