Drugs, both legal and illegal, can have a powerful and sometimes dangerous effect on the human brain. From prescription medication to recreational drug use, drugs can alter how the brain functions, leading to short-term or long-term changes in behavior, mood, and memory. This article explores how drugs affect the brain, the physiological and psychological impacts, and the potential for addiction.
Drugs have a wide range of effects on the brain, from temporary changes in brain chemistry to lasting damage. Common effects include altered awareness and perception, increased heart rate and blood pressure, and impaired judgment. Long-term drug use can cause changes in the brain that lead to addiction and other health problems, such as depression, anxiety, and memory loss.
Contents
- How Drug Abuse Impacts the Brain
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What Are the Different Ways Drugs Affect the Brain?
- What Areas of the Brain Are Affected by Drugs?
- What Are the Long-Term Effects of Drug Use on the Brain?
- What Are the Short-Term Effects of Drug Use on the Brain?
- How Can the Brain Recover from Drug Abuse?
- How Can People Reduce Their Risk of Drug Use?
- How Does Drug Use Affect Brain Development in Young People?
- How do drugs affect the brain? – Sara Garofalo
How Drug Abuse Impacts the Brain
Drug abuse has a range of adverse effects on the brain. Drugs of abuse affect the brain by altering neurotransmitter levels, disrupting communication between neurons, and altering the brain’s reward system. This leads to changes in mood, behavior, and cognition. Drug abuse can also lead to addiction, which is characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behaviors, despite the negative consequences.
Drugs of abuse act on the brain by altering levels of key neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin. These neurotransmitters are responsible for regulating mood, emotion, and behavior. When drug use increases the levels of these neurotransmitters, it can lead to feelings of euphoria and pleasure. However, these changes can become maladaptive, leading to changes in behavior, cognition, and mood.
Drug abuse can also disrupt communication between neurons in the brain. Drugs can block or activate certain receptors, which can lead to changes in neuronal communication. This can lead to changes in behavior, cognition, and emotion. Additionally, it can lead to changes in the brain’s reward system, which can cause compulsive drug-seeking behaviors, even in the face of negative consequences.
Effects on Cognition
Drug abuse can lead to changes in cognition, including deficits in attention, memory, and decision-making. These cognitive deficits can persist even after the individual has stopped using drugs. Additionally, some drugs, such as methamphetamine, can have neurotoxic effects, leading to long-term changes in the brain’s structure and function.
Drug abuse can also lead to changes in mood, such as depression and anxiety. These changes can be due to changes in neurotransmitter levels, as well as changes in the brain’s reward system. Additionally, drug abuse can lead to an increased risk of developing mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety disorders.
Effects on Behavior
Drug abuse can lead to changes in behavior, such as increased impulsivity and risk-taking. This can lead to dangerous and risky behaviors, such as driving while intoxicated, engaging in unprotected sex, or engaging in criminal activities. Additionally, drug abuse can lead to compulsive drug-seeking behaviors, even in the face of negative consequences.
Drug abuse can also lead to changes in social functioning and interpersonal relationships. Individuals who abuse drugs may become more isolated and withdrawn, leading to relationship problems with family and friends. Additionally, drug abuse can lead to legal problems, such as arrests for possession or use of drugs.
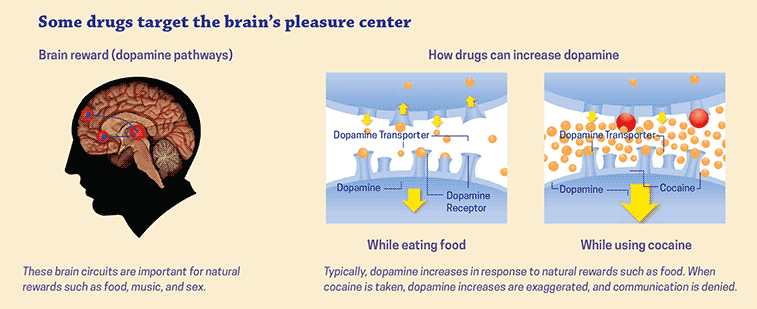
Effects on Brain Reward System
Drug abuse can lead to changes in the brain’s reward system. This system is responsible for regulating feelings of pleasure and motivation. When drugs are abused, they can activate this system, leading to feelings of euphoria and pleasure. However, with repeated use, the brain’s reward system can become desensitized to the drug, leading to tolerance and the need for higher doses to achieve the same effect.
Additionally, the brain’s reward system can become dysregulated, leading to compulsive drug-seeking behaviors, even in the face of negative consequences. This dysregulation can also lead to cravings for the drug and difficulty abstaining from its use.
Long-term Effects
Long-term drug abuse can lead to lasting changes in the brain. This can include changes in the brain’s structure and function, as well as changes in neurotransmitter levels. Additionally, long-term drug abuse can increase the risk of developing physical and mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety disorders.
Finally, long-term drug abuse can lead to an increased risk of developing addiction. Addiction is characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behaviors, despite the negative consequences. Once an individual is addicted, they may struggle to stop using the drug, leading to further health and social problems.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Different Ways Drugs Affect the Brain?
Drugs affect the brain in a variety of ways. Stimulants like cocaine and amphetamines increase alertness and euphoria by rapidly increasing the release of certain neurotransmitters like dopamine. Depressants like alcohol and benzodiazepines slow down the activity of the central nervous system, causing relaxation and sedation. Hallucinogens like LSD and PCP alter mood and perception by affecting the release of serotonin and other neurotransmitters. Opioids like heroin and morphine act on the brain’s reward system, creating feelings of intense pleasure. Finally, some drugs like marijuana and nicotine can affect multiple neurotransmitters, leading to a variety of effects.
What Areas of the Brain Are Affected by Drugs?
The areas of the brain affected by drugs vary depending on the type of drug used. Stimulants primarily affect the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making and executive functions. Depressants act on the brain stem, which controls basic functions like breathing and heart rate. Hallucinogens affect the temporal and frontal lobes, which are involved in emotions and memory. Opioids act on the reward system, which is located in the limbic system. Finally, marijuana and nicotine can affect multiple areas of the brain, including the hippocampus, which is involved in learning and memory.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Drug Use on the Brain?
The long-term effects of drug use on the brain can be serious and vary depending on the type of drug used. Stimulants can lead to changes in the brain’s reward system and increased risk of addiction. Depressants can lead to disrupted sleep patterns, memory problems, and decreased motivation. Hallucinogens can cause persistent perceptual changes, flashbacks, and mood disturbances. Opioids can lead to decreased responsiveness to rewards and difficulty controlling impulses. Finally, marijuana has been linked to decreased motivation, memory problems, and decreased IQ.
What Are the Short-Term Effects of Drug Use on the Brain?
The short-term effects of drug use on the brain depend on the type of drug used. Stimulants can lead to alertness, increased energy, and euphoria. Depressants can lead to drowsiness, slowed reactions, and impaired judgment. Hallucinogens can cause disorientation, altered perception, and changes in mood. Opioids can lead to feelings of intense pleasure and relaxation. Finally, marijuana and nicotine can lead to impaired motor coordination and slowed reaction times.
How Can the Brain Recover from Drug Abuse?
The brain can recover from drug abuse, but the process can take time. It is important to stop using drugs and seek professional help to detoxify the body and begin the recovery process. After detox, a person should engage in therapy and other forms of treatment to help address any underlying mental health issues and develop healthy coping skills. While recovery is possible, the effects of drug use on the brain can be long-lasting, so it is important to seek help as soon as possible.
How Can People Reduce Their Risk of Drug Use?
There are several ways people can reduce their risk of drug use. Staying informed about the risks associated with drug use is important. Avoiding situations that could lead to drug use, such as parties and social gatherings where drugs are present, is also important. Finally, developing healthy coping skills, such as exercise and meditation, can help reduce the risk of drug use. Developing a strong support system of family and friends who can provide help and resources can also be beneficial.
How Does Drug Use Affect Brain Development in Young People?
Drug use can have a profound effect on the brain development of young people. Drugs, particularly stimulants like cocaine and amphetamines, can interfere with the development of the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making and executive functions. This can lead to impaired judgment and difficulty controlling impulses. Additionally, drugs can also interfere with the development of the hippocampus, which is involved in learning and memory. This can lead to problems with memory, concentration, and learning. Finally, drug use can lead to changes in brain chemistry, which can increase the risk of addiction and mental health issues.
How do drugs affect the brain? – Sara Garofalo
Drugs can have a devastating effect on the brain. They can disrupt the normal functioning of neurotransmitters, disrupt communication between neurons, and impair judgement and decision-making. Drugs can also damage the brain’s structure and chemistry, leading to long-term and even permanent changes. Ultimately, drugs can cause serious, long-term damage to the brain, resulting in a wide range of physical, mental, and emotional problems. For these reasons, it is essential to take the necessary measures to prevent drug abuse and addiction and to seek help for those already suffering from it.

