Opiates are powerful drugs that have a wide range of uses in the medical field. They are often used to treat pain, anxiety, and even to induce sleep. But did you know that opiates can also have an effect on your blood pressure? In this article, we will explore how opiates can affect your blood pressure, including the potential risks and benefits. So, if you’re curious about the effects of opiates on your blood pressure, read on to learn more.
No, opiates do not lower blood pressure. In fact, high doses of opiates can cause high blood pressure. Opiates are a class of drugs derived from the opium poppy plant and are usually prescribed for pain relief. Common opiates include morphine, codeine, and oxycodone.
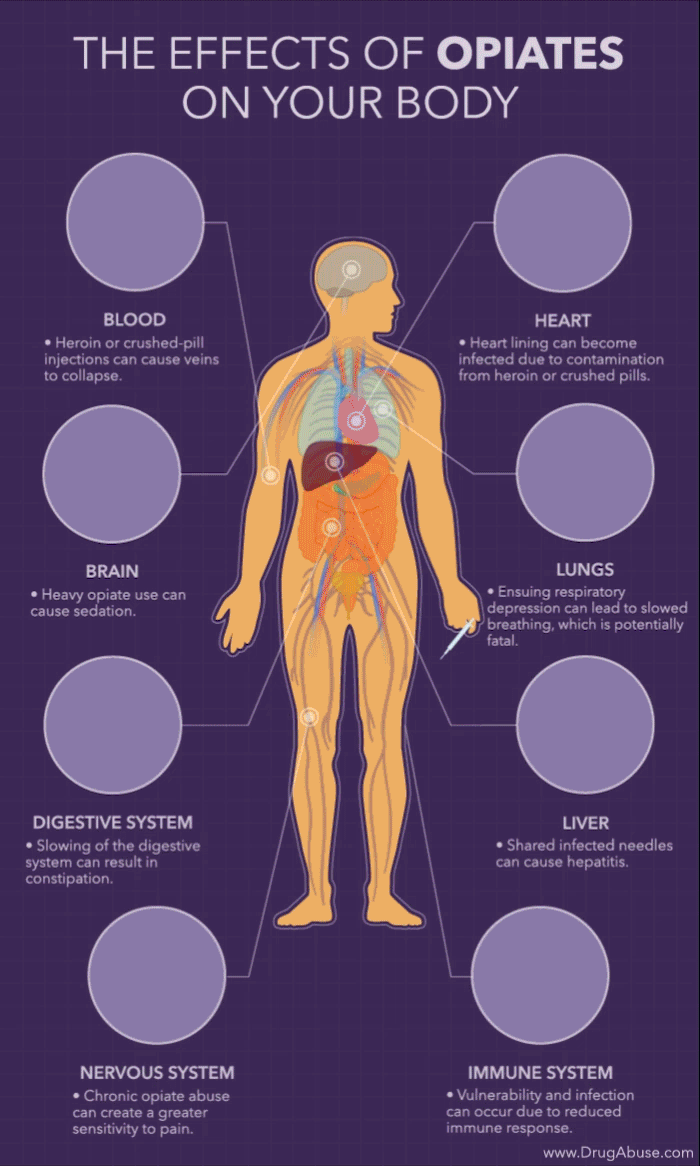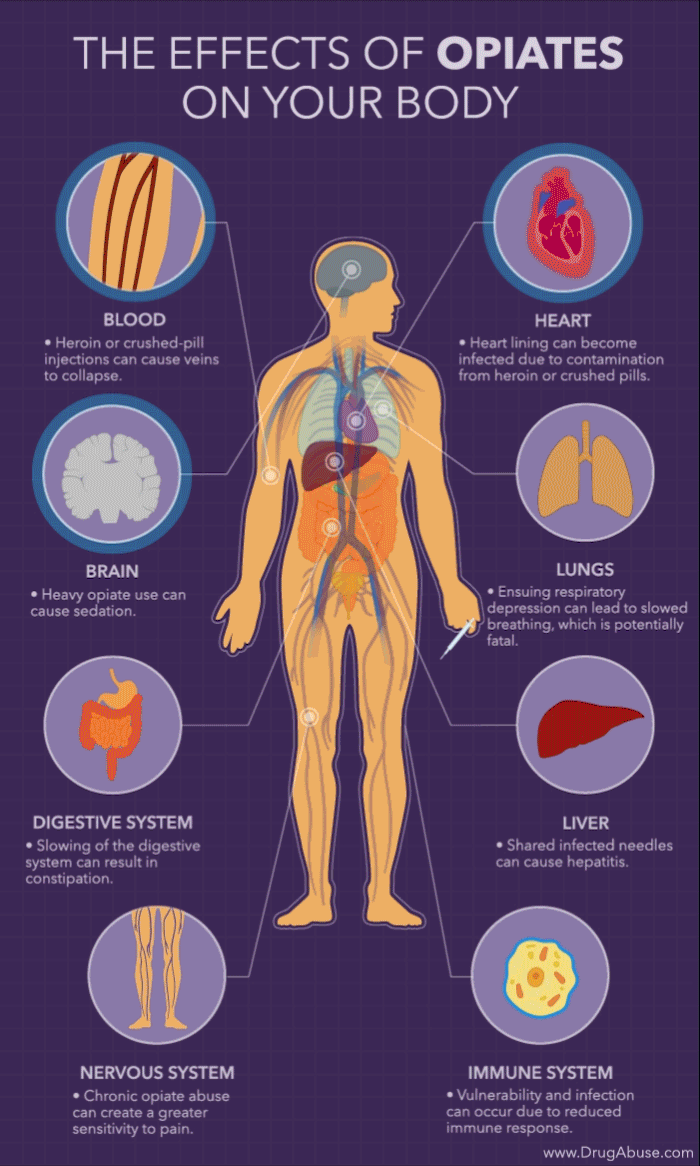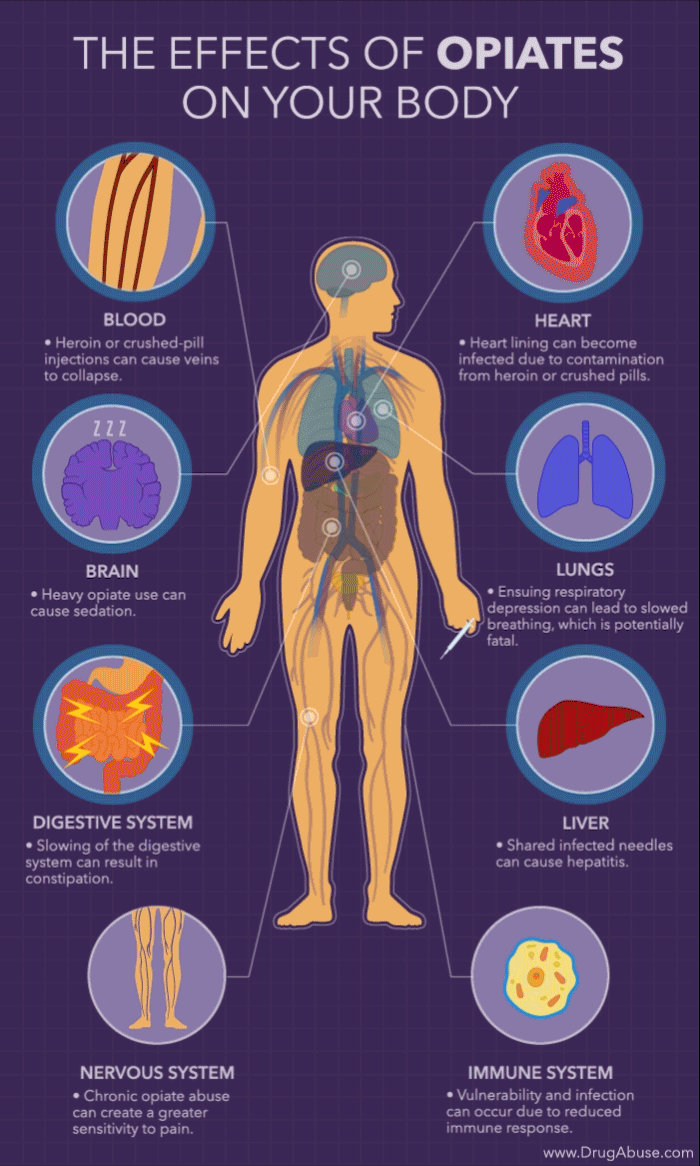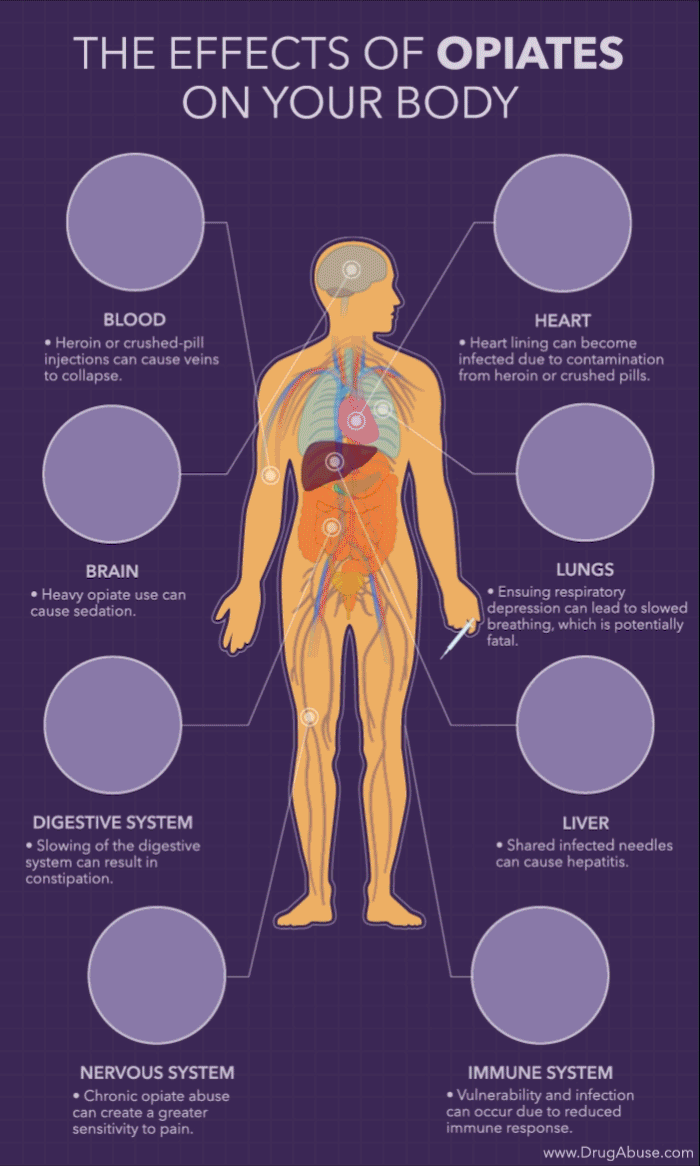
Contents
- Does Opiate Use Lower Blood Pressure?
- Related Faq
- Do Opiates Lower Blood Pressure?
- What Are the Long-Term Effects of Opiates on Blood Pressure?
- Can Opiates Be Used to Treat High Blood Pressure?
- What Are the Side Effects of Opiates on Blood Pressure?
- How Can I Lower My Blood Pressure Without Opiates?
- What Should I Do If I Feel My Blood Pressure Rising After Taking an Opiate?
- How an opioid addiction can eat your heart alive
Does Opiate Use Lower Blood Pressure?
Opiate use is an increasingly common way to manage pain and other medical issues. As with any medication, there are potential side effects. One concern is whether opiate use can affect blood pressure. In this article, we will discuss the potential effects of opiate use on blood pressure, as well as other conditions it may influence.
What Are Opiates?
Opiates are a group of drugs derived from the opium poppy plant. They are used to relieve pain and can have calming, sedative effects. Common opiates include morphine and codeine, as well as synthetic opioids such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, and fentanyl. Opiates can be taken orally, injected, or smoked.
What Are the Effects of Opiate Use on Blood Pressure?
The effects of opiate use on blood pressure are not fully understood. Some studies have suggested that opiates can cause a decrease in blood pressure, while others have found no effect. Opiates can also cause a decrease in heart rate, and this can lead to a decrease in blood pressure. It is important to note that opiates can also cause an increase in blood pressure in some people.
What Other Conditions Can Opiate Use Affect?
Opiates can also affect other conditions such as breathing, digestion, and mental health. Opiate use can cause respiratory depression, which can cause difficulty breathing. Opiates can also slow digestion, leading to constipation and other digestive issues. Additionally, opiate use can lead to depression and anxiety.
Are There Risks Associated with Opiate Use?
Yes, there are risks associated with opiate use. Opiate use can lead to addiction and dependence. It can also cause serious side effects, such as confusion, drowsiness, and nausea. Opiate use can also interfere with the body’s natural ability to regulate pain, leading to increased pain levels. Additionally, long-term opiate use can cause organ damage, including damage to the liver and kidneys.
Can Opiates Be Used Safely?
Yes, opiates can be used safely when taken as prescribed. It is important to talk to your doctor before taking any opiates, as they can interact with other medications and cause serious side effects. Additionally, it is important to use opiates only as directed and to use the lowest possible dose for the shortest amount of time.
What Are Alternative Treatments for Pain?
There are many alternative treatments for pain, including non-opioid medications, physical therapy, acupuncture, yoga, massage, and meditation. It is important to discuss all of your options with your doctor to determine the best treatment for your particular situation.
Can Opiates Be Taken with Other Medications?
Yes, opiates can be taken with other medications, but it is important to talk to your doctor before taking any medications together. Some medications can interact with opiates and cause adverse side effects. Additionally, some opiates can interact with other medications, so it is important to talk to your doctor about any potential interactions.
Related Faq
Do Opiates Lower Blood Pressure?
Answer: No, opiates do not lower blood pressure. In fact, opiates can have the opposite effect and raise blood pressure. Opiates are powerful pain relievers that can have a wide range of potential effects on the body, including an increase in blood pressure. This can be especially dangerous for those with a pre-existing heart condition as it can put them at risk of a heart attack or stroke. In addition, opiates can also cause constriction of the blood vessels, leading to elevated blood pressure.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Opiates on Blood Pressure?
Answer: The long-term effects of opiates on blood pressure can be serious. Prolonged use of opiates can lead to a number of different issues, including an increase in blood pressure. Over time, this can damage the heart, leading to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. In addition, long-term opiate use can also lead to other serious health issues such as liver and kidney damage, as well as an increased risk of addiction.
Can Opiates Be Used to Treat High Blood Pressure?
Answer: No, opiates should not be used to treat high blood pressure. While opiates can provide short-term relief from pain, they can have a number of other serious side effects including an increase in blood pressure. For this reason, opiates should not be used to treat high blood pressure. Instead, other medications such as beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be used to lower blood pressure.
What Are the Side Effects of Opiates on Blood Pressure?
Answer: Some of the side effects of opiates on blood pressure include an increased risk of heart attack or stroke, constriction of the blood vessels, and an increased risk of addiction. Opiates can also cause a decrease in blood pressure in some cases, which can be dangerous for those with pre-existing heart conditions. In addition, opiates can also lead to other serious health issues such as liver and kidney damage.
How Can I Lower My Blood Pressure Without Opiates?
Answer: There are a number of different ways to lower blood pressure without opiates. These include lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and reducing stress. In addition, certain medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and calcium channel blockers can also be used to lower blood pressure. It is important to speak to a doctor before taking any medications to lower blood pressure.
What Should I Do If I Feel My Blood Pressure Rising After Taking an Opiate?
Answer: If you feel your blood pressure rising after taking an opiate, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Opiates can have serious side effects, including an increase in blood pressure. If you experience any symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Additionally, if you are taking any other medications to lower your blood pressure, it is important to speak to your doctor about any potential interactions with the opiate.
How an opioid addiction can eat your heart alive
Overall, it is clear that opiates can have a significant effect on blood pressure. While opiates can lower blood pressure in the short-term, long-term use can have serious consequences and can lead to further complications. It is important to speak with a doctor before taking any opiate-based medications, as they can help determine the best course of action for managing blood pressure. Ultimately, it is clear that opiates can be beneficial in certain situations, and can be an effective treatment for lowering blood pressure.

