Opiates are a class of drugs prescribed to treat pain, but they can also lead to serious side effects. One of the most concerning side effects of opiate use is depression. While opiates can be beneficial in certain cases, they can also cause serious mental health issues if not used responsibly. In this article, we’ll explore the question: Do opiates cause depression? We’ll look at the research on this topic, the risks associated with opiate use, and strategies to help people manage depression if taking opiates.
Contents
Do Opiates Lead to Depressive Symptoms?
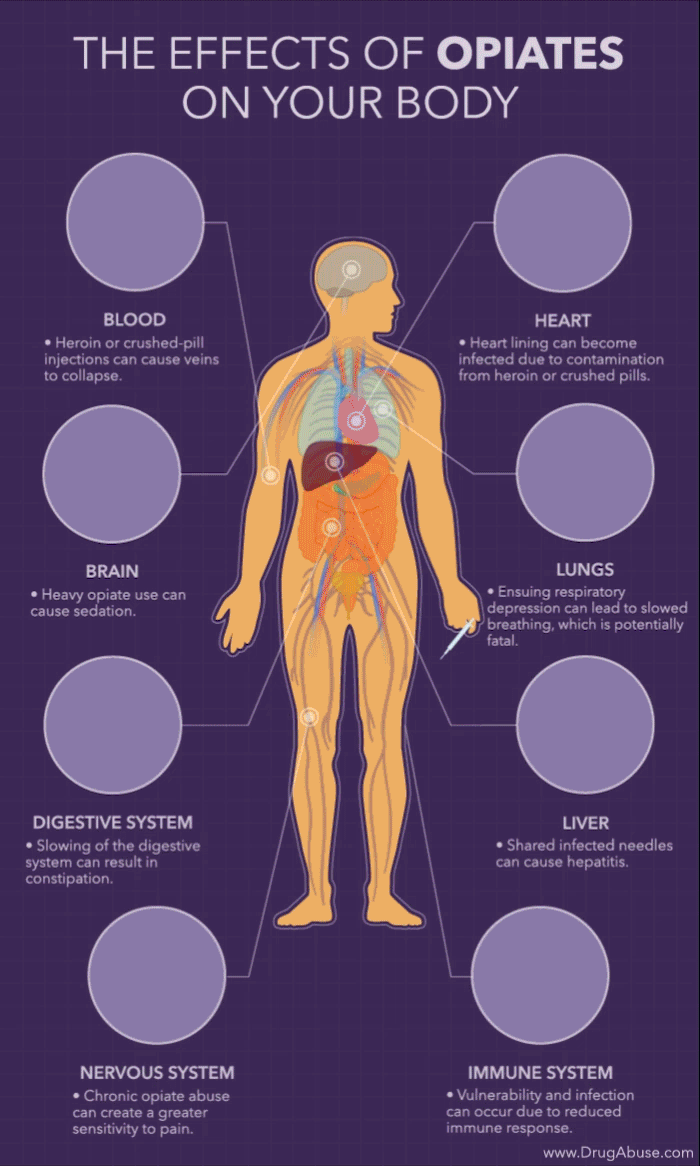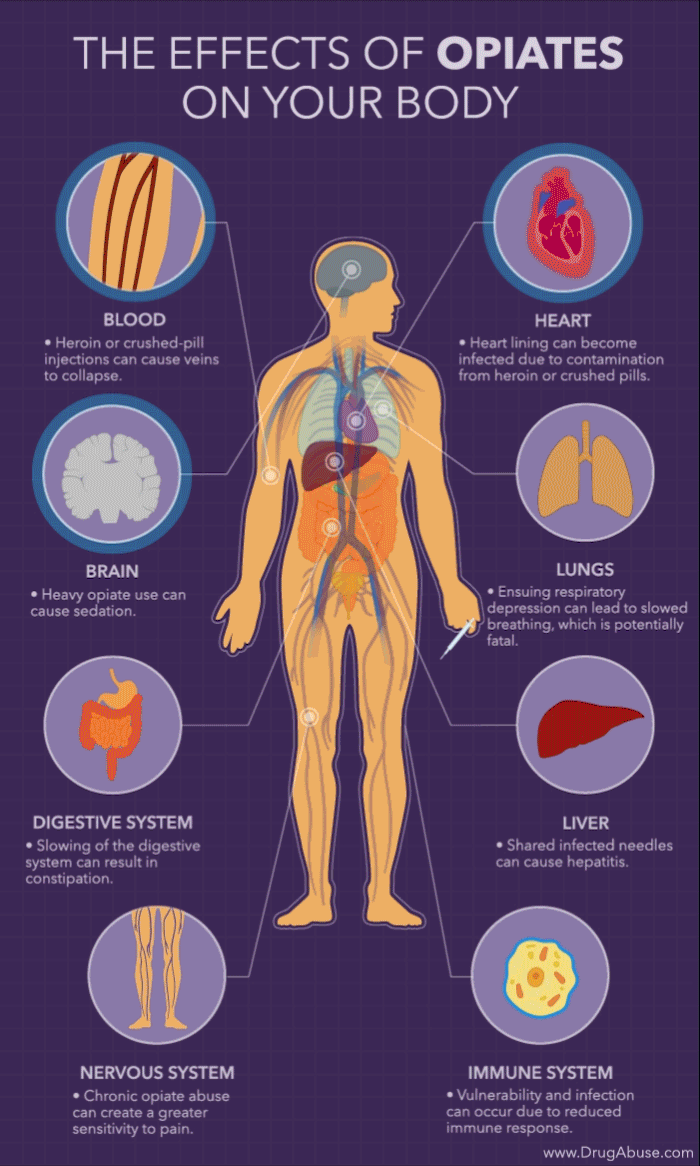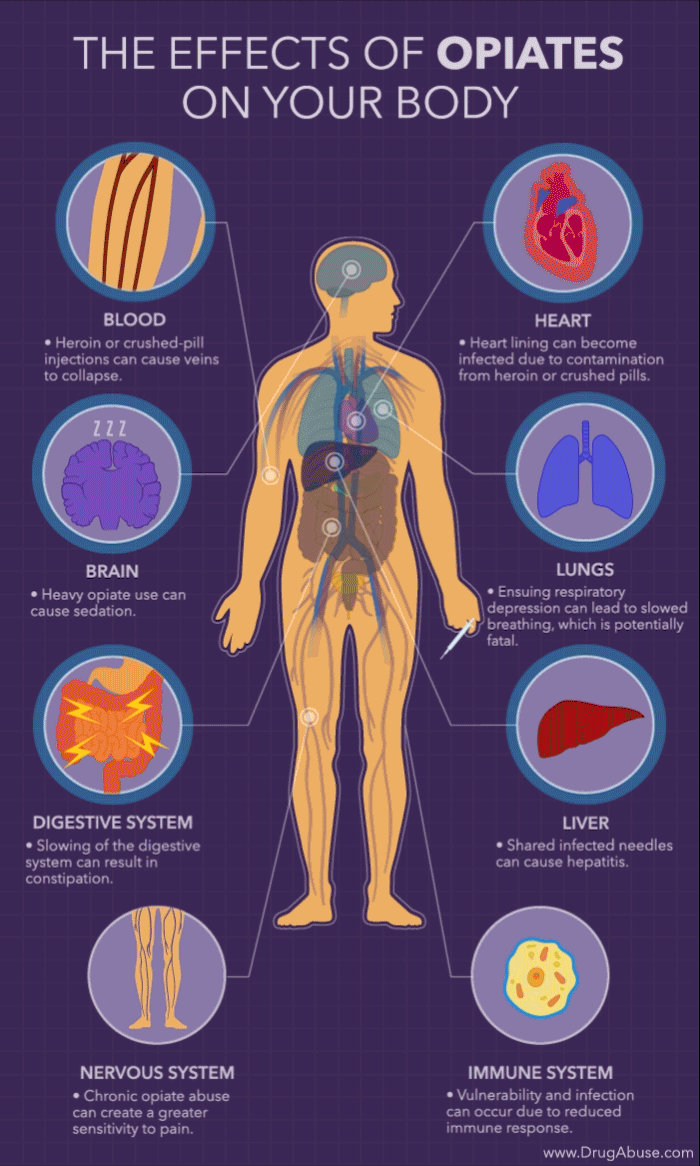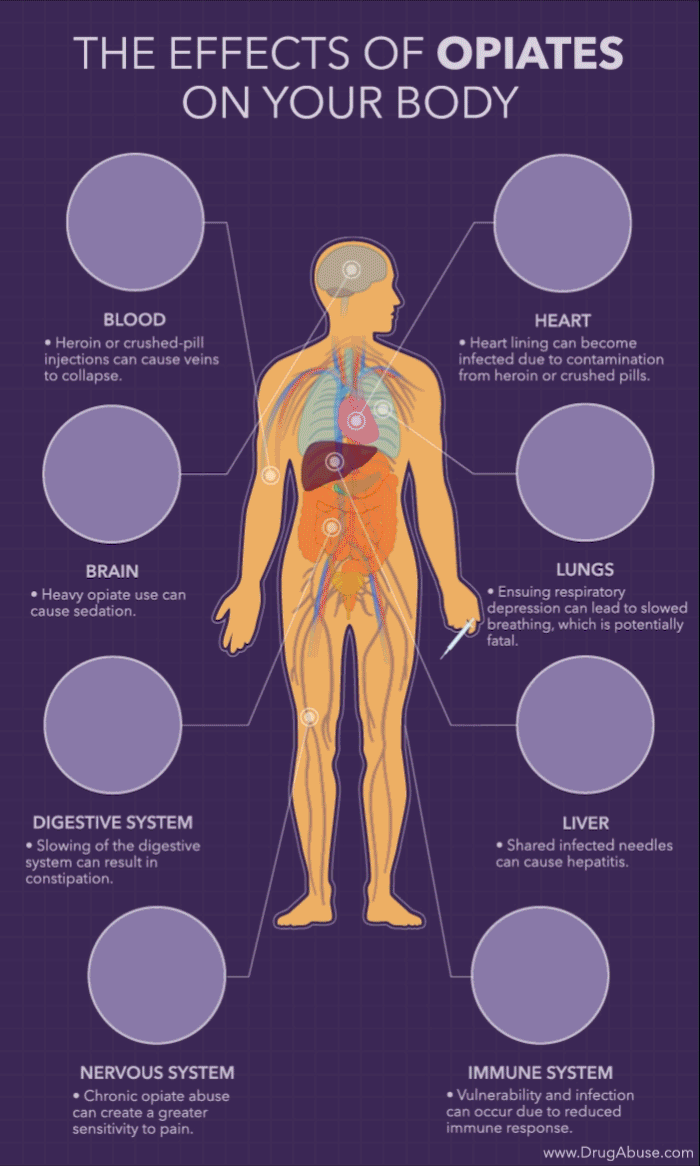
Opioids are a class of drugs commonly prescribed to treat pain, but they can have serious side effects. One of these is the potential to cause depression. Opioids can affect the brain in several ways, including altering levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which can lead to depression. Additionally, chronic opioid use can lead to physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms, which can also contribute to depressive symptoms.
How Opiates Alter Neurotransmitter Levels
Opioids work by attaching to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord. This alters the levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which can lead to depression. Serotonin and dopamine are neurotransmitters that help regulate mood, so when their levels are altered, it can lead to feelings of depression. Additionally, opioids can interfere with the natural production of these neurotransmitters, leading to further depression.
The Effects of Physical Dependence and Withdrawal
Chronic opioid use can lead to physical dependence, which can also lead to depression. When someone is physically dependent on opioids, they may experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking the drug. These symptoms can include feeling fatigued and having difficulty sleeping, which can lead to feelings of depression. Additionally, chronic opioid use often leads to tolerance, which means that the person needs to take higher doses of the drug in order to get the same effects. This can further contribute to feelings of depression.
Does Depression Lead to Opiate Use?
Depression can also lead to opioid use. People with depression may turn to opioids in an attempt to self-medicate and temporarily relieve their symptoms. However, this can lead to a dangerous cycle, as opioid use can lead to further depression. Additionally, people with depression may be more likely to be prescribed opioids, which can also lead to physical dependence and further depression.
The Risk of Misuse and Addiction
The risk of misuse and addiction is another factor to consider when it comes to opioid use and depression. People with depression may be more likely to misuse opioids, which can lead to addiction. Addiction can further exacerbate depressive symptoms, as it can interfere with the person’s ability to function and lead to further feelings of hopelessness and despair.
The Risk of Overdose
The risk of overdose is also a concern when it comes to opioid use and depression. People with depression may be more likely to take larger doses of opioids in an attempt to self-medicate, which can lead to an overdose. Additionally, people with depression may be more likely to engage in risky behaviors, such as sharing needles or taking opioids with other drugs, which can also lead to an overdose.
Treatment for Opioid Abuse and Depression
The best way to treat opioid abuse and depression is to seek professional help. A healthcare provider can help the person develop an individualized treatment plan that takes into account their needs and goals. This may include medications, therapy, and lifestyle changes, such as exercise, healthy eating, and stress management. Additionally, support groups and other resources can be helpful in managing symptoms of depression and opioid abuse.
What Role Does Prevention Play?
Prevention is key when it comes to opioid abuse and depression. Healthcare providers should be aware of the potential risks of prescribing opioids, especially to people with a history of depression. Additionally, people who are taking opioids should be aware of the potential for depression and should seek help if they experience any depressive symptoms. Finally, it is important to educate people about the risks of opioid use and to provide resources for those who are struggling with addiction.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are Opiates?
Answer: Opiates are a class of drugs that are derived from the opium poppy plant. They include drugs such as morphine, codeine, and oxycodone. These drugs have powerful pain-relieving and sedative effects, and are commonly used to treat severe pain, and sometimes to help people with addiction. They can be taken orally, injected, or smoked.
Q2. Do Opiates Cause Depression?
Answer: Opiates can cause depression in some people. Studies have found that people who use opiates, particularly those who are taking them for a long period of time, are more likely to develop depression. This is likely due to the drugs’ effects on the brain’s reward system and their impact on neurotransmitter levels. Additionally, people who are taking opiates for pain relief may be more prone to depression due to the psychological effects of chronic pain.
Q3. What Are the Symptoms of Opiate-Induced Depression?
Answer: Symptoms of opiate-induced depression can include feelings of sadness, guilt, and hopelessness; fatigue; difficulty concentrating; changes in appetite; and thoughts of suicide. Other physical and psychological symptoms can also be present, such as sleep disturbances, difficulty relaxing, and irritability.
Q4. How Is Opiate-Induced Depression Treated?
Answer: Treatment for opiate-induced depression usually involves a combination of medications and psychotherapy. Antidepressant medications can be used to help reduce symptoms, as can psychotherapy. In some cases, a physician may also recommend lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity or reducing stress. In cases where the depression is severe, hospitalization may be necessary.
Q5. Are There Ways to Prevent Opiate-Induced Depression?
Answer: Yes, there are ways to help prevent opiate-induced depression. First, it is important to make sure that the dosage of opiates is appropriate for the individual’s needs. Additionally, it is important to monitor the individual’s mood and mental state, and to consult a doctor if any signs of depression are present. Finally, it is important to practice healthy habits, such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and getting enough sleep.
Q6. What Are the Long-Term Effects of Opiate Use?
Answer: The long-term effects of opiate use can vary depending on the individual and the type and amount of opiates used. In general, long-term use of opiates can lead to physical dependence, tolerance, and addiction. Additionally, it can lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Long-term use can also lead to liver and kidney damage, as well as an increased risk of overdose.
Does Opiate Abuse Cause Depression?
In conclusion, there is a clear link between opiates and depression. In many cases, the use of opiates can trigger depression or make an existing depressive disorder worse. It is important to be aware of this connection so that those suffering from depression can take the necessary steps to ensure their mental health. If you or someone you know is taking opiates and experiencing symptoms of depression, it is important to speak to a health professional about the potential risks and seek out appropriate treatment.

