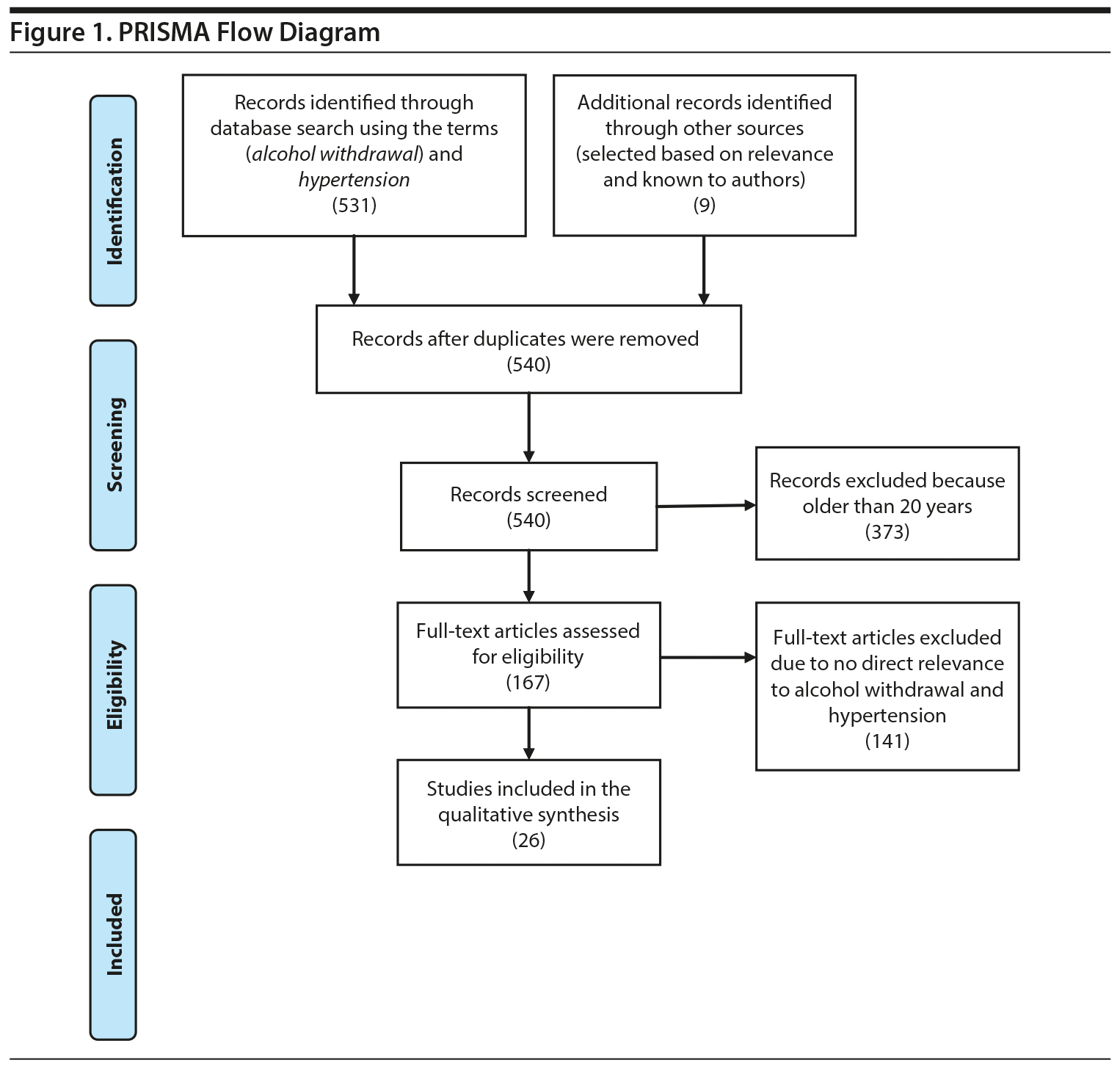
Alcohol has long been known to have an effect on our bodies, both physically and mentally. But what happens when someone who has been drinking heavily suddenly stops? Can alcohol withdrawal raise blood pressure? This question is important to understand, as it can help us determine the risks of drinking and abstaining from alcohol, as well as when and how to seek medical help if needed. In this article, we will explore the potential effects of alcohol withdrawal on blood pressure and what to do if you or a loved one experience a sudden change in their blood pressure.
Yes, alcohol withdrawal can raise blood pressure. This is due to the release of adrenaline and other hormones that increase heart rate and constrict blood vessels. Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, such as increased heart rate, sweating, anxiety, and restlessness, can all contribute to a rise in blood pressure.
Contents
- Can Abstinence from Alcohol Cause High Blood Pressure?
- Related Faq
- Question 1: What is alcohol withdrawal?
- Question 2: Can alcohol withdrawal raise blood pressure?
- Question 3: What other symptoms may occur with alcohol withdrawal?
- Question 4: Are there any long-term effects of alcohol withdrawal?
- Question 5: What are some ways to manage alcohol withdrawal?
- Question 6: What are the risks of alcohol withdrawal?
- What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Drinking Alcohol
Can Abstinence from Alcohol Cause High Blood Pressure?
Abstaining from alcohol can have a dramatic effect on a person’s blood pressure. In some cases, alcohol withdrawal can lead to a sudden and significant increase in blood pressure. People with a history of alcohol abuse or alcoholism may be at greater risk. Understanding the potential health effects of alcohol withdrawal can help individuals make informed decisions and reduce their risk of developing high blood pressure.
When a person stops drinking alcohol, the body must adjust to the sudden decrease in alcohol levels in the blood. This can cause a range of physical and emotional symptoms, such as anxiety, headaches, nausea, and irritability. Some of these symptoms may activate the body’s “fight or flight” response, which can cause a sudden spike in blood pressure. This spike in blood pressure is known as alcohol withdrawal hypertension.
In some cases, alcohol withdrawal can cause a sustained increase in a person’s blood pressure. This can be dangerous and can put a person at risk of developing more serious health problems, such as heart attack and stroke. People with a history of alcohol abuse or alcoholism may be especially vulnerable to developing high blood pressure as a result of alcohol withdrawal.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Alcohol Withdrawal?
Alcohol withdrawal can cause a range of physical and psychological symptoms, such as:
• Nausea
• Headaches
• Sweating
• Anxiety
• Irritability
• Insomnia
• Muscle aches
• Rapid heart rate
• High blood pressure
• Delirium tremens (DTs)
• Seizures
• Hallucinations
• Depression
These symptoms can be mild or severe, depending on the individual and the amount of alcohol they were consuming before they stopped drinking.
How Can I Lower My Blood Pressure After Alcohol Withdrawal?
If you experience an increase in your blood pressure after quitting drinking, there are several things you can do to help lower it.
• Exercise regularly: Exercise can help lower your blood pressure and keep it in a healthy range.
• Eat a balanced diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower your blood pressure.
• Reduce stress: Stress can cause a sudden spike in your blood pressure. Finding ways to reduce stress, such as yoga, mindfulness, and deep breathing, can help keep your blood pressure in check.
• Get enough sleep: Getting enough sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy blood pressure.
• Avoid alcohol: Avoiding alcohol can help keep your blood pressure in a healthy range.
What are the Long-Term Health Effects of High Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure can have serious long-term health effects if left untreated. It can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. It can also damage the walls of the blood vessels, leading to aneurysms and arteriosclerosis.
Heart Attack
High blood pressure can lead to hardening and narrowing of the arteries, which can reduce the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart. This can cause a heart attack.
Stroke
High blood pressure can also lead to a stroke. When the arteries become narrowed and hardened, it can cause a clot to form in the blood vessels, which can lead to a stroke.
Kidney Disease
High blood pressure can also lead to kidney disease. When the arteries become narrowed and hardened, it can reduce the flow of blood and oxygen to the kidneys, which can lead to kidney damage.
Aneurysms and Arteriosclerosis
High blood pressure can also lead to aneurysms and arteriosclerosis. Aneurysms are bulges in the walls of the arteries, and arteriosclerosis is the hardening and narrowing of the arteries. Both of these conditions can lead to serious health problems.
Related Faq
Question 1: What is alcohol withdrawal?
Answer: Alcohol withdrawal is the set of physical, psychological, and emotional symptoms that occur when a person who has been drinking heavily suddenly stops. Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal vary from person to person, but can include anxiety, shakes, sweating, nausea, and increased heart rate and blood pressure. In some cases, alcohol withdrawal can be serious and require medical attention.
Question 2: Can alcohol withdrawal raise blood pressure?
Answer: Yes, alcohol withdrawal can raise blood pressure. When someone consumes alcohol for an extended period, their body becomes used to the presence of alcohol and the blood pressure can drop as a result. When a person stops drinking suddenly, their body has to adjust to the absence of alcohol and, as a result, their blood pressure can rise.
Question 3: What other symptoms may occur with alcohol withdrawal?
Answer: Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal can vary from person to person, but generally include anxiety, tremors, headaches, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, and a rapid heart rate. In more severe cases, seizures, hallucinations, and delirium tremens (DTs) can occur. It is important to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur.
Question 4: Are there any long-term effects of alcohol withdrawal?
Answer: Yes, there can be long-term effects of alcohol withdrawal. These can include changes in mood, decreased appetite, and difficulty sleeping. In addition, some people can experience cognitive impairments, such as difficulty with memory and concentration. Long-term use of alcohol can also lead to organ damage, including liver and kidney damage.
Question 5: What are some ways to manage alcohol withdrawal?
Answer: The best way to manage alcohol withdrawal is to seek medical help. Medical professionals can assess the severity of the withdrawal and provide medications, such as benzodiazepines, to help manage the symptoms. In addition, lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly can help manage withdrawal symptoms.
Question 6: What are the risks of alcohol withdrawal?
Answer: The risks of alcohol withdrawal can be serious and include seizures, delirium tremens (DTs), and death. It is important to seek medical attention if any of the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal occur. In addition, continued heavy drinking can lead to further health complications, including liver and kidney damage, an increased risk of stroke, and heart disease.
What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Drinking Alcohol
Alcohol withdrawal can be a serious medical condition that can cause a variety of physical and mental health risks, including an increase in blood pressure. While medical professionals are best equipped to treat alcohol withdrawal, it is important to understand the potential risks associated with it, and to make sure that any treatment is done safely and responsibly. With the right care and support, you can make sure that you are able to manage your alcohol withdrawal and live a healthy life.

