Drug withdrawal is a complex and often painful process. It is a physical reaction to the abrupt cessation of drug use that can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. From psychological cravings to physical changes, drug withdrawal can be a daunting experience, but understanding the process can help you better manage it. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what drug withdrawal is and what you can expect during the process.
Drug withdrawal is the physical and psychological symptoms that occur when someone who has been using drugs suddenly stops taking them. Symptoms of drug withdrawal can vary depending on the drug used, the amount used and the length of time it has been used. Common symptoms of drug withdrawal include cravings, fatigue, irritability, anxiety, agitation, sweating, confusion and difficulty sleeping. Severe withdrawal symptoms can include seizures, hallucinations and delirium. Treatment for drug withdrawal usually involves managing the symptoms and may include medications and lifestyle changes. Professional help is recommended for people suffering from drug addiction.
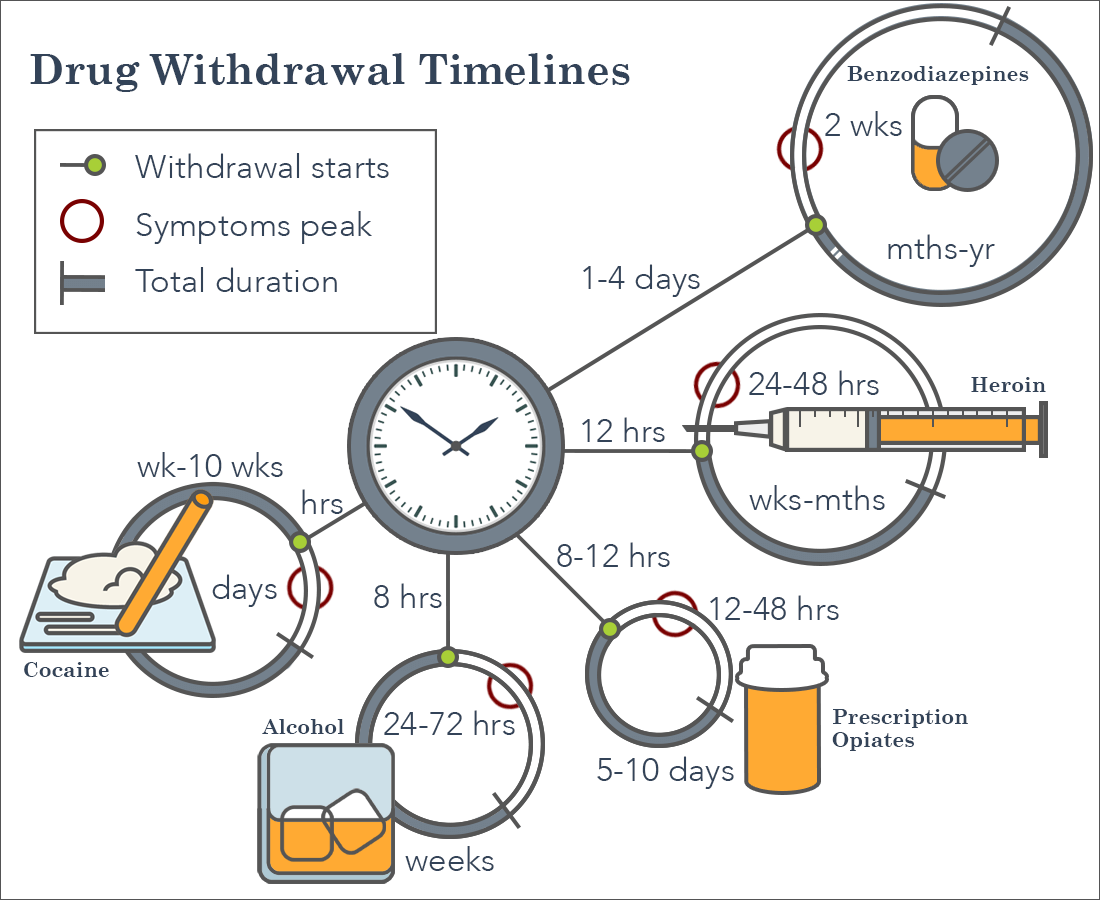
What is Drug Withdrawal?
Drug withdrawal is the process of discontinuing the use of a substance that has been used on a regular basis for an extended period. When someone stops using drugs or alcohol, their body begins to experience withdrawal symptoms as it adjusts to functioning without the drug. Drug withdrawal can involve physical and psychological symptoms, which can range from mild to severe in intensity.
Types of Drug Withdrawal Symptoms
Drug withdrawal symptoms vary depending on the type of drug that was used and the amount and duration of use. Some of the most common physical and psychological symptoms of drug withdrawal include agitation, anxiety, difficulty sleeping, nausea, sweating, tremors, and vomiting. These symptoms can last anywhere from a few hours to several weeks or even months.
Managing Drug Withdrawal Symptoms
The best way to manage drug withdrawal symptoms is to seek professional help from a medical or mental health professional. Detoxing from drugs or alcohol can be dangerous, and withdrawal symptoms can be severe. Medically supervised detox programs can help individuals manage their symptoms and make the process safer and more comfortable.
Treating Drug Withdrawal
In addition to medically supervised detox, there are several effective treatment options for drug withdrawal. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is a type of treatment that combines medications, counseling, and behavioral therapies to help individuals reduce or stop their drug use. MAT can also help individuals manage their withdrawal symptoms and cravings and prevent them from relapsing.
Long-Term Treatment for Drug Withdrawal
Once an individual has detoxed from drugs or alcohol, they may benefit from a longer-term treatment program. This could include residential treatment, partial hospitalization, or an intensive outpatient program. These types of programs provide individuals with the tools and support they need to maintain their sobriety and prevent relapse.
Preventing Drug Withdrawal
The best way to prevent drug withdrawal is to avoid using drugs or alcohol in the first place. If you or someone you know is struggling with substance use, seek help right away. Professional help can ensure that you have access to the resources and support you need to stay sober and prevent drug withdrawal.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Drug Withdrawal?
Answer: Drug withdrawal is the body’s reaction to having a drug removed or reduced, after a period of regular or prolonged use. It is the reaction of the body to the absence of a drug to which it has become accustomed. Symptoms of withdrawal can vary greatly depending on the drug used, the amount used, the frequency of use, and the length of time the drug has been used. Common symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, sweating, tremors, increased heart rate, and changes in appetite.
How Does Drug Withdrawal Manifest?
Answer: The symptoms of drug withdrawal vary depending on the drug used, the amount used, the frequency of use, and the length of time the drug has been used. Some common symptoms of drug withdrawal include insomnia, anxiety, tremors, nausea, sweating, changes in appetite, and increased heart rate. In extreme cases, withdrawal can also cause hallucinations, seizures, and delirium.
What Are the Possible Complications of Drug Withdrawal?
Answer: The complications of drug withdrawal depend on the drug being withdrawn from, the amount used, the frequency of use, and the length of time the drug has been used. Some potential complications include dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, hallucinations, seizures, and delirium. Withdrawal can also be associated with increased risk of relapse, increased risk of suicide and self-harm, and increased risk of overdose.
Who Is at Risk for Drug Withdrawal?
Answer: Anyone who has been using drugs regularly or for a prolonged period of time is at risk for drug withdrawal. Those who use drugs in high doses and/or more frequently are at an increased risk of more severe withdrawal symptoms. Additionally, those who have been using drugs for a longer period of time are also at an increased risk of more severe withdrawal symptoms.
How Is Drug Withdrawal Treated?
Answer: Drug withdrawal is typically treated with a combination of medications and supportive care. Medications used to treat the symptoms of withdrawal may include benzodiazepines, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. Additionally, supportive care may include psychological counseling, nutritional support, and physical exercise.
What Are Some Tips for Managing Drug Withdrawal?
Answer: There are several tips for managing drug withdrawal, including: getting enough rest, drinking plenty of fluids, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding triggers, seeking social support, and utilizing relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation. Additionally, it is important to seek medical help if symptoms become severe or unmanageable.
The science of opioid withdrawal
Drug withdrawal is a process that can be difficult and uncomfortable, but it is possible to manage and overcome it with the help of professional medical care. With the right support and resources, you can make the transition to a healthier and happier life, free from the effects of drugs. There is hope for those struggling with drug addiction, and with the right help, you can reclaim your life.

