Stimulants are a type of drug that can provide a quick boost of energy, alertness, and focus. But what happens to our brains when we use them? In this article, we’ll explore how stimulants can affect the brain, both in the short and long term. We’ll look at the potential benefits and risks of stimulant use and how to best ensure our safety when using them. Read on to learn more about the stimulating effects of stimulants on the brain.
Stimulants can have various effects on the brain, including increased alertness, focus, and energy. However, too much of these substances can lead to serious health problems such as increased blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, and even stroke. Stimulants can also cause addiction and dependence, as well as other psychological issues. Long-term use of stimulants can lead to decreased appetite, insomnia, and even psychosis.
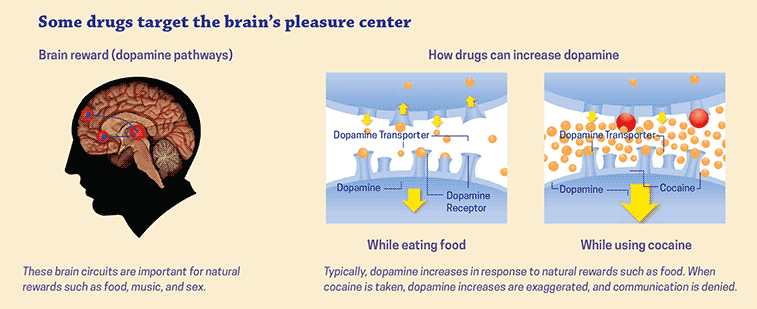
Contents
- What is a Stimulant?
- The Short-Term Effects of Stimulant Use
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a stimulant?
- How do stimulants affect the brain?
- What are the short-term effects of stimulants on the brain?
- What are the long-term effects of stimulants on the brain?
- What are the side effects of stimulants?
- What are some tips to help manage the effects of stimulants on the brain?
- How do drugs affect the brain? – Sara Garofalo
What is a Stimulant?
Stimulants are substances that increase alertness, attention, and energy. Commonly abused stimulants include cocaine, methamphetamine, amphetamines, caffeine, and nicotine. These drugs increase the activity of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
How Do Stimulants Affect the Brain?
Stimulants increase the activity of certain brain regions, leading to increased blood flow and increased neurotransmitter release. This leads to increased alertness and focus, as well as increased feelings of pleasure and reward. Stimulants also tend to increase the levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can lead to feelings of anxiety and restlessness.
The Long-Term Effects of Stimulant Use
Long-term use of stimulants can lead to changes in the brain. The brain can become tolerant to the effects of the drug, leading to an increase in the amount of the drug needed to achieve the same effect. Additionally, long-term use can lead to changes in the way the brain processes pleasure and reward, leading to difficulty feeling pleasure without using the drug.
The Short-Term Effects of Stimulant Use
Stimulants increase alertness and focus, and can also lead to increased energy, euphoria, and feelings of invincibility. Stimulants also tend to suppress appetite, leading to weight loss. However, these effects are short-lived and can be followed by a crash, where the user feels sluggish, irritable, and depressed.
The Risk of Addiction
Stimulants can be habit-forming, and users can quickly become addicted. Addiction to stimulants can lead to compulsive drug use and cravings, as well as physical and psychological dependence.
The Risk of Overdose
Overdose on stimulants can lead to serious health complications, including seizures, heart attack, stroke, and death. Overdose can also lead to extreme agitation and paranoia, which can lead to dangerous and violent behaviors.
Conclusion
Stimulants can have a variety of effects on the brain, both short-term and long-term. Stimulants can lead to increased alertness and focus, as well as feelings of euphoria, but they can also lead to addiction, overdose, and other serious health complications. It is important to be aware of the potential risks of stimulant use.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a stimulant?
A stimulant is a type of drug that can increase alertness, attention, and energy. Stimulants are typically used to treat conditions such as narcolepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and depression. They can be prescribed or bought without a prescription. Examples of stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine, and methylphenidate.
How do stimulants affect the brain?
Stimulants act on the brain by increasing the activity of certain chemicals, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is associated with pleasure and reward, while norepinephrine helps to regulate alertness, attention, and arousal. Stimulants increase the activity of these chemicals, which can lead to increased alertness, concentration, and energy. They can also cause a sense of euphoria and pleasure.
What are the short-term effects of stimulants on the brain?
The short-term effects of stimulants on the brain can include increased alertness and concentration, improved mood, and increased energy. Stimulants can also cause increased heart rate and blood pressure, increased body temperature, and increased breathing rate. Some people may also experience anxiety, irritability, and jitteriness.
What are the long-term effects of stimulants on the brain?
The long-term effects of stimulants on the brain can include changes in behavior, such as aggression or impulsivity. Stimulants can also affect the brain’s reward system, leading to addiction. Long-term use of stimulants can also increase the risk of mental health problems, such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis.
What are the side effects of stimulants?
The side effects of stimulants can include insomnia, headaches, nausea, and loss of appetite. Stimulants can also cause increased heart rate and blood pressure, increased body temperature, and increased breathing rate. In addition, long-term use of stimulants can lead to addiction, mental health issues, and changes in behavior.
What are some tips to help manage the effects of stimulants on the brain?
Some tips to help manage the effects of stimulants on the brain include avoiding overuse and taking regular breaks. It is also important to stay hydrated, get enough sleep, and stick to a healthy diet. If taking stimulants for a medical condition, it is important to follow the instructions of the doctor or pharmacist. It is also recommended to talk to a doctor if any side effects occur.
How do drugs affect the brain? – Sara Garofalo
In conclusion, the use of stimulants can have powerful effects on the brain, both positive and negative. It can increase alertness, focus, and energy, but it can also lead to addiction and long-term health consequences. It is important to be aware of the risks and seek professional medical advice before using stimulants. With responsible use, stimulants can be beneficial, but it is crucial to remember that too much of a good thing can be harmful.

