For many, nicotine is seen as an aide to help cope with stress and anxiety, but could it be that nicotine is actually contributing to anxiety levels? This question is one that has been debated for years and in this article, we will take a look at the connection between nicotine and anxiety to see if there is a causal relationship.
Can Nicotine Cause Anxiety?
Nicotine, the addictive chemical found in cigarettes, is known to affect the central nervous system and can increase a person’s risk of developing anxiety. While it is not known exactly how nicotine can cause anxiety, research suggests that nicotine can increase the release of chemicals in the brain that are associated with anxiety. This article will explore the evidence for nicotine’s role in anxiety and discuss the implications for those who use nicotine-containing products.
The Effects of Nicotine on the Brain
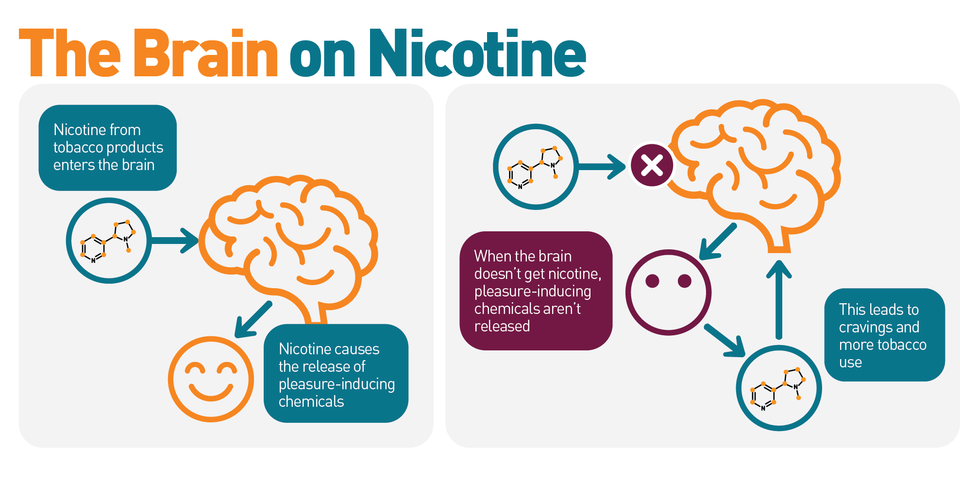
Nicotine is a stimulant drug that is found in cigarettes and other forms of tobacco. When nicotine is inhaled or ingested, it binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain. This binding triggers the release of neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, which are associated with mood regulation, reward, and motivation. These neurotransmitters can affect a person’s mood and behavior, which can lead to anxiety.
Research suggests that nicotine can also increase the release of cortisol, a hormone released in response to stress. High levels of cortisol can lead to feelings of fear and anxiety. Additionally, nicotine can lead to physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heart rate and shaking.
Nicotine and Anxiety Disorders
Studies have shown that people who use nicotine-containing products are more likely to suffer from anxiety disorders than those who do not use nicotine. In particular, those who suffer from panic disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder have been found to have higher rates of nicotine use than the general population.
Additionally, research suggests that nicotine use can exacerbate the symptoms of anxiety disorders. For example, one study found that nicotine use was associated with an increase in panic attacks among those with panic disorder. Other studies have found that nicotine can worsen the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety disorder.
Quitting Nicotine and Anxiety Symptoms
Although quitting nicotine can be difficult, it can also lead to improvements in anxiety symptoms. In one study, participants who quit smoking cigarettes experienced a decrease in anxiety symptoms after one month and a further decrease in symptoms after six months.
Additionally, research suggests that quitting nicotine can help reduce the risk of anxiety disorders. In one study, researchers found that former smokers had a lower risk of developing an anxiety disorder than those who continued to smoke.
Implications for Nicotine Users
The evidence suggests that nicotine can increase the risk of anxiety disorders and worsen the symptoms of existing anxiety disorders. For those who use nicotine-containing products, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and to consider quitting nicotine if they are experiencing symptoms of anxiety.
The Role of Vaping in Anxiety
Vaping is the use of electronic cigarettes, which contain nicotine and other chemicals. Research suggests that vaping can lead to an increase in anxiety symptoms. A study found that vaping was associated with an increase in anxiety symptoms in adolescents, and another study found that vaping was associated with increased anxiety in adults.
Therapies for Quitting Nicotine
Quitting nicotine can be difficult, and it is important to seek professional help if needed. There are a variety of therapies available to help those who are trying to quit nicotine. These therapies can include nicotine replacement therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and medication.
Conclusion
Nicotine can increase the risk of developing anxiety disorders and worsen the symptoms of existing anxiety disorders. Quitting nicotine can be difficult, but it can lead to improved anxiety symptoms and a reduced risk of anxiety disorders. Those who are using nicotine-containing products should be aware of the potential risks and consider quitting nicotine if they are experiencing symptoms of anxiety.
Related Faq
Can Nicotine Cause Anxiety?
Answer: Yes, nicotine can cause anxiety. Nicotine is a stimulant and it can increase your heart rate and blood pressure, which can lead to feelings of anxiety. Nicotine also increases the release of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can further increase feelings of anxiety. In addition, nicotine can affect the levels of certain brain chemicals, such as dopamine and serotonin, which can also contribute to anxiety.
What are the Symptoms of Nicotine-induced Anxiety?
Answer: Symptoms of nicotine-induced anxiety can include increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, sweaty palms, dizziness, trembling, difficulty sleeping, restlessness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Additionally, nicotine can cause panic attacks, which can be accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, and fear of dying.
Can Quitting Nicotine Help Reduce Anxiety?
Answer: Yes, quitting nicotine can help reduce anxiety. When you quit nicotine, your body slowly begins to adjust to being nicotine-free, and this can help reduce feelings of anxiety. Additionally, as you become more nicotine-free, your body chemistry can begin to return to normal, which can help reduce anxiety symptoms. Finally, quitting nicotine gives you the opportunity to engage in healthier activities and lifestyle habits, which can also help reduce anxiety.
What are Some Strategies to Quit Nicotine?
Answer: Some strategies to quit nicotine include setting a quit date, finding support from family and friends, using nicotine replacement therapies such as gums and patches, avoiding triggers and situations that may lead to nicotine cravings, and engaging in healthy activities to help cope with cravings. Additionally, counseling and behavior therapy can be helpful in developing strategies to cope with nicotine cravings and anxiety.
Are There Any Medications That Can Help Reduce Nicotine Cravings and Anxiety?
Answer: Yes, there are several medications that can help reduce nicotine cravings and anxiety. These include bupropion, varenicline, and nortriptyline. Additionally, other medications such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can be helpful in treating nicotine withdrawal symptoms and reducing anxiety. It is important to talk to your doctor before starting any medications.
What are Some Natural Ways to Reduce Anxiety?
Answer: There are several natural ways to reduce anxiety, including exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, avoiding caffeine and stimulants, practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation, and engaging in other activities that bring you joy. Additionally, talking to a mental health professional can be helpful in developing strategies to cope with anxiety.
In conclusion, nicotine is an addictive substance that can have an impact on mental health. While it is not always the cause of anxiety, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with nicotine consumption and to take the necessary precautions if you are a smoker. It is also important to remember that nicotine addiction is difficult to overcome and that seeking professional help may be beneficial if you are struggling with anxiety or other mental health issues.

