Nicotine is a substance found in tobacco products which is highly addictive and dangerous for our health. While it is widely known that smoking cigarettes is bad for our health, few people are aware of the numerous and wide-ranging effects that nicotine has on our bodies. In this article, we will explore the various effects of nicotine on our physical and mental health, as well as the ways in which nicotine addiction can negatively impact our lives.
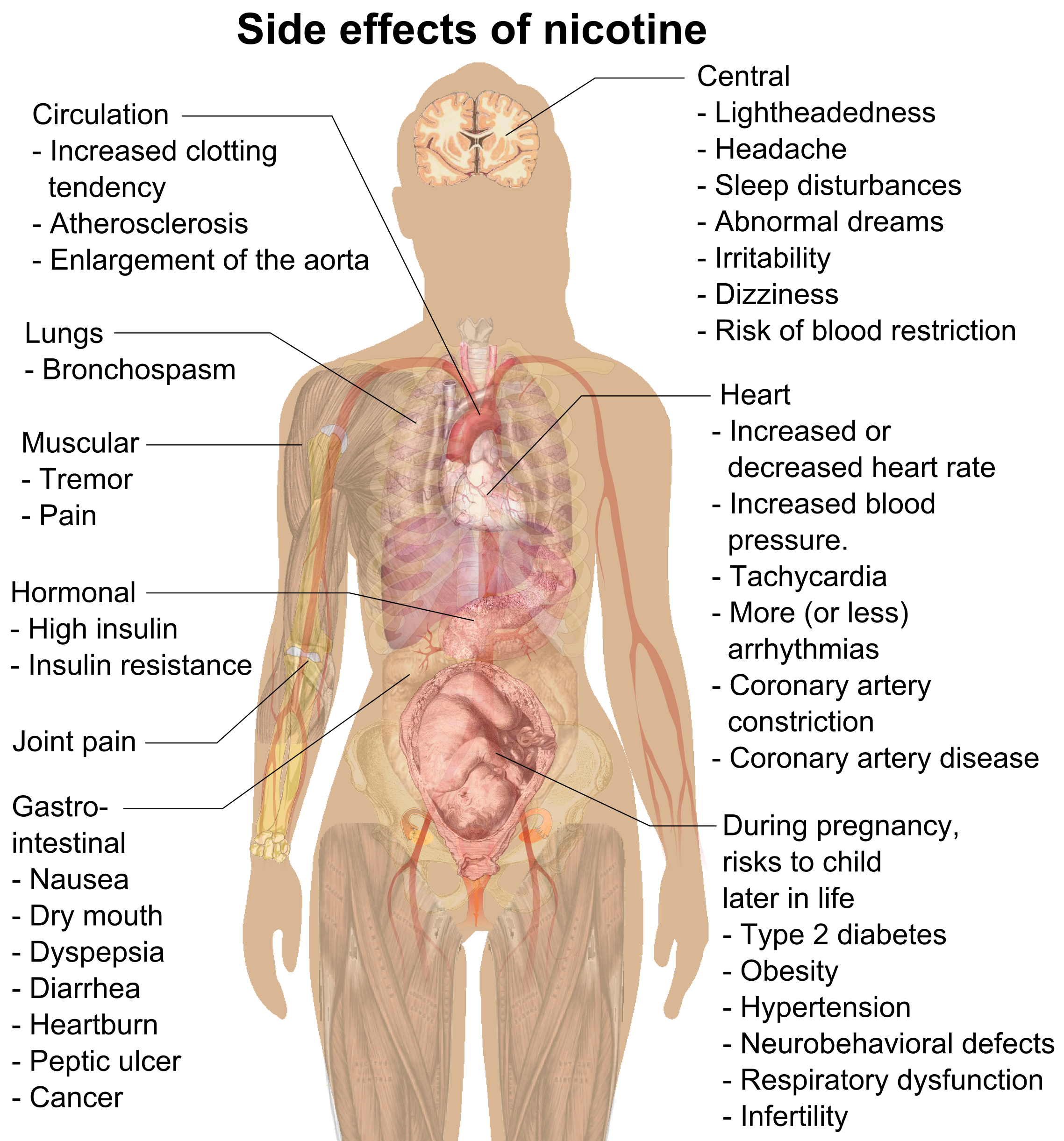
What are the Effects of Nicotine?
Nicotine is an addictive chemical found in tobacco products. It is mainly responsible for the physical and psychological addiction to smoking. People often overlook the effects of nicotine on their physical and mental health, and this can be dangerous. This article will discuss some of the effects of nicotine on the body and mind.
Physical Effects of Nicotine
The most obvious physical effect of nicotine is an increased heart rate. Nicotine stimulates the cardiovascular system, causing an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. This can lead to an increased risk of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular diseases. Nicotine also constricts blood vessels, which can reduce the amount of oxygen that is delivered to the heart. This can lead to an increased risk of high blood pressure and heart disease.
Another physical effect of nicotine is a decrease in the body’s ability to fight infections. Nicotine has been found to decrease the body’s immunity, making it more susceptible to illnesses and infections. Additionally, nicotine has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancers, such as lung, throat, and mouth cancer.
Mental Effects of Nicotine
Nicotine also has a number of mental effects on the body. Nicotine is known to increase alertness and focus, which can be beneficial in certain situations. However, nicotine can also increase anxiety and depression, which can lead to an increased risk of mental health problems.
Nicotine can also affect the brain’s ability to regulate emotions. Nicotine can increase stress levels, which can lead to a feeling of being overwhelmed or out of control. This can lead to irritability, anger, and mood swings.
Behavioral Effects of Nicotine
Nicotine can also have an effect on behavior. Nicotine can cause people to become more impulsive and aggressive. This can be dangerous if not controlled, as it can lead to reckless decisions and behaviors. Additionally, nicotine can make people more susceptible to peer pressure, which can lead to more dangerous behaviors.
Addiction to Nicotine
One of the most serious effects of nicotine is its addictive nature. Nicotine is highly addictive and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. People can become addicted to nicotine in as little as a few weeks of regular use. Once addicted, people can find it difficult to quit, as nicotine can cause intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Long-Term Effects of Nicotine
The long-term effects of nicotine are still being studied, but it is known that nicotine can lead to serious health problems. Long-term nicotine use can increase the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, long-term nicotine use can increase the risk of certain cancers, such as lung, throat, and mouth cancer.
Short-Term Effects of Nicotine
The short-term effects of nicotine are more widely known than the long-term effects. Nicotine can cause a number of short-term effects, such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and constricted blood vessels. Nicotine can also cause a decrease in the body’s ability to fight infections, as well as increased anxiety and depression.
The Health Risks of Nicotine
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance that can have both short-term and long-term effects on the body. Nicotine can increase the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, nicotine can increase the risk of certain types of cancers, such as lung, throat, and mouth cancer. Finally, nicotine can lead to addiction and withdrawal symptoms, which can be difficult to overcome.
Related Faq
What Is Nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine is a chemical compound found in tobacco, certain plants, and some other substances. It is a stimulant drug that affects the central nervous system, and it is the primary psychoactive ingredient in cigarettes and other tobacco products. It is also used as a recreational drug in some form, such as vaping and smokeless tobacco. Nicotine acts as a stimulant, and can cause feelings of euphoria and alertness.
What Are Some Short-Term Effects Of Nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine has many short-term effects. It can increase alertness, improve concentration, and reduce feelings of stress and anxiety. It can also increase heart rate and blood pressure, making it a risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Nicotine can also affect the digestive system, causing nausea, vomiting, and constipation. It can also lead to increased appetite and weight gain.
What Are Some Long-Term Effects Of Nicotine?
Answer: The long-term effects of nicotine can be very serious. It increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke. It can also worsen respiratory conditions, such as asthma and COPD. Nicotine can also increase the risk of developing cancer, and can cause damage to the lungs, brain, and other organs. Long-term nicotine use can also lead to addiction, and can cause withdrawal symptoms when quitting.
What Are The Effects Of Nicotine On The Brain?
Answer: Nicotine acts on the brain in several ways. It stimulates the release of dopamine, which is a neurotransmitter that is associated with feelings of pleasure. It can also affect certain areas of the brain that are associated with learning and memory. Long-term nicotine use can lead to changes in the brain, affecting cognitive function and decision-making. It can also lead to increased tolerance and dependence on nicotine.
What Are The Effects Of Nicotine On The Body?
Answer: Nicotine has many effects on the body. It increases heart rate and blood pressure, making it a risk factor for heart disease and stroke. It can also affect the digestive system, causing nausea, vomiting, and constipation. It can also cause changes in the body’s metabolism, leading to weight gain. Nicotine can also cause changes in mood, leading to irritability, depression, and anxiety.
What Are The Effects Of Nicotine On Pregnancy?
Answer: Nicotine use during pregnancy is highly dangerous for both the mother and the baby. Nicotine can cross the placenta, increasing the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, and preterm delivery. It can also cause birth defects, such as cleft lip and palate. In addition, nicotine can affect fetal development, leading to low birth weight and other health problems.
Nicotine, while often seen as a harmless substance, can have serious and long-term health effects. It can damage the lungs, increase the risk of heart disease, and lead to addiction. Furthermore, it can also have a negative effect on mental health, leading to depression and anxiety. While smoking or using nicotine in any form is not recommended, it is important to be aware of the potential health risks associated with it. Ultimately, the effects of nicotine can be far-reaching and should be taken seriously.

