Are you concerned about nicotine showing up in your blood test results? Are you a smoker, or have you been exposed to second-hand smoke recently? Knowing how long nicotine stays in your blood is important in understanding the effects of smoking on your body. In this article, we’ll explore the various factors that influence how long nicotine stays in your blood and provide tips for reducing nicotine levels.
Nicotine can stay in your blood for up to three days after you use it. It is quickly broken down by your body, so the levels of nicotine in your blood decrease over time. The amount of time it takes to clear nicotine from your system depends on how much and how often you use it. For example, if you smoke cigarettes every day, it may take up to two weeks for your body to clear the nicotine.
Contents
- How Long Does Nicotine Remain in the Blood?
- How Does Nicotine Reach the Bloodstream?
- What Are the Health Effects of Nicotine?
- Can Nicotine be Detected in Blood Tests?
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Blood?
- Q2: What Factors Affect How Long Nicotine Stays in the Blood?
- Q3: Are There Tests to Detect Nicotine in the Blood?
- Q4: Does Nicotine Stay in the Blood Longer if Someone Smokes More?
- Q5: Can Nicotine Be Detected in the Blood After Quitting Smoking?
- Q6: What Are the Health Benefits of Quitting Smoking?
How Long Does Nicotine Remain in the Blood?
Nicotine is a stimulant alkaloid found in tobacco products. It is a highly addictive substance and can have serious health effects. Nicotine is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and has a half-life of around two hours. This means that nicotine can stay in the bloodstream for up to four hours after being consumed.
The amount of time that nicotine stays in the bloodstream depends on several factors, including the type and amount of nicotine consumed and the person’s metabolism. For example, a person who smokes or chews tobacco or uses nicotine patches or gum may have a higher nicotine concentration in their blood than someone who only vapes. Some people may also be more sensitive to nicotine than others, meaning that it will take longer for it to be eliminated from their bloodstream.
It is important to note that nicotine can remain in the bloodstream for up to four hours after it has been consumed. This means that if a person has recently consumed nicotine, it is possible for them to still have a nicotine concentration in their blood even if they have not smoked, chewed, or vaped recently.
How Does Nicotine Reach the Bloodstream?
When nicotine is consumed, it is absorbed quickly into the bloodstream through the skin, lungs, and digestive system. From there, it travels to the liver, where it is broken down and metabolized. The metabolites of nicotine are then eliminated from the body through the urine.
The speed at which nicotine is absorbed into the bloodstream depends on the method of consumption. Smoking cigarettes or cigars results in a rapid absorption of nicotine into the bloodstream, while chewing tobacco or using nicotine patches or gum results in a slower absorption rate. Vaping is also a slower method of consuming nicotine, but it is still absorbed into the bloodstream faster than other methods.
What Are the Health Effects of Nicotine?
Nicotine has a range of health effects, both in the short and long term. In the short term, nicotine can have stimulant effects, resulting in increased alertness and focus, as well as elevated heart rate and blood pressure. In the long term, nicotine can increase the risk of developing cancer, heart disease, and other health problems.
It is also important to note that nicotine is highly addictive. This means that it can be difficult for someone to quit using nicotine products once they have become addicted. Quitting nicotine can cause withdrawal symptoms, such as irritability, cravings, and difficulty sleeping.
Can Nicotine be Detected in Blood Tests?
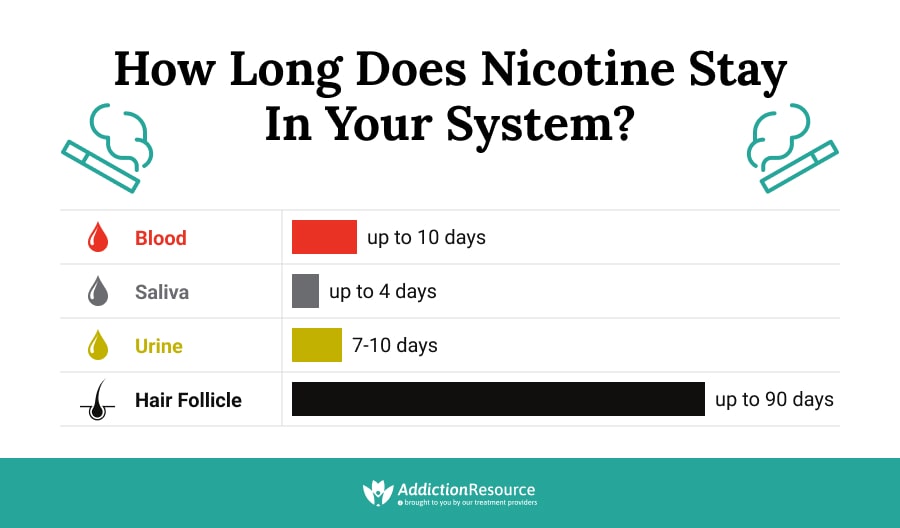
Yes, nicotine can be detected in blood tests. Nicotine can be detected in a blood sample for up to four hours after it has been consumed. Nicotine can also be detected in urine tests for up to three days after it has been consumed.
What Is the Purpose of Blood Testing for Nicotine?
Blood tests for nicotine are mainly used to determine if a person has recently consumed nicotine or if they are using nicotine products on a regular basis. Blood tests can also be used to detect nicotine in people who are trying to quit smoking or using other nicotine products.
What Are the Limitations of Blood Testing for Nicotine?
Blood tests for nicotine are not always accurate, as they do not always detect nicotine if it was consumed more than four hours before the test was taken. Blood tests also cannot determine how much nicotine was consumed, or how often it was consumed.
What Are the Alternatives to Blood Testing for Nicotine?
Urine tests are another option for detecting nicotine in the body. While urine tests are not as accurate as blood tests, they can detect nicotine in the body for up to three days after it has been consumed. Saliva tests can also be used to detect nicotine in the body, although they are not as accurate as blood or urine tests.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Blood?
Answer: Nicotine will typically stay in the blood for 1-3 days after the last use. However, this time frame can vary depending on how often someone smokes, how much nicotine is consumed, and the individual’s metabolism.
Q2: What Factors Affect How Long Nicotine Stays in the Blood?
Answer: Several factors affect how long nicotine stays in the blood. Frequency of smoking, the amount of nicotine consumed, and the individual’s metabolism all play a role in determining how long nicotine stays in the blood.
Q3: Are There Tests to Detect Nicotine in the Blood?
Answer: Yes, there are tests to detect nicotine in the blood. Nicotine can be detected in the blood through a urine or blood test. Urine testing is the most common method as it is less invasive and more accurate.
Q4: Does Nicotine Stay in the Blood Longer if Someone Smokes More?
Answer: Yes, nicotine will stay in the blood longer if someone smokes more. The more nicotine consumed, the longer it will stay in the blood. However, the amount of nicotine consumed and the individual’s metabolism will also affect the time frame.
Q5: Can Nicotine Be Detected in the Blood After Quitting Smoking?
Answer: Yes, nicotine can be detected in the blood after quitting smoking. Depending on how long someone has been smoking and how much nicotine was consumed, nicotine can stay in the blood for 1-3 days after quitting.
Q6: What Are the Health Benefits of Quitting Smoking?
Answer: Quitting smoking has many health benefits. The risk of developing lung cancer and other respiratory illnesses decreases, as well as the risk of developing coronary heart disease and stroke. Quitting smoking can also improve overall health, such as increasing energy levels, reducing stress and anxiety, and improving circulation.
In conclusion, it is important to understand how long nicotine stays in your blood as it relates to quitting smoking. Nicotine can be detected in the blood for up to 3 days after smoking, and can remain detectable for up to 4 weeks in the urine. However, it is important to note that the amount of nicotine in the blood decreases significantly after 1-3 days. By understanding how long nicotine stays in your blood, you can take proactive steps to reduce your cravings and help you quit smoking for good.

