Smoking cigarettes has long been thought to have negative impacts on cardiovascular health. But does nicotine, the main active ingredient in cigarettes, actually constrict blood vessels? In this article, we will explore the evidence that suggests nicotine does, in fact, constrict blood vessels and what this could mean for those who smoke.
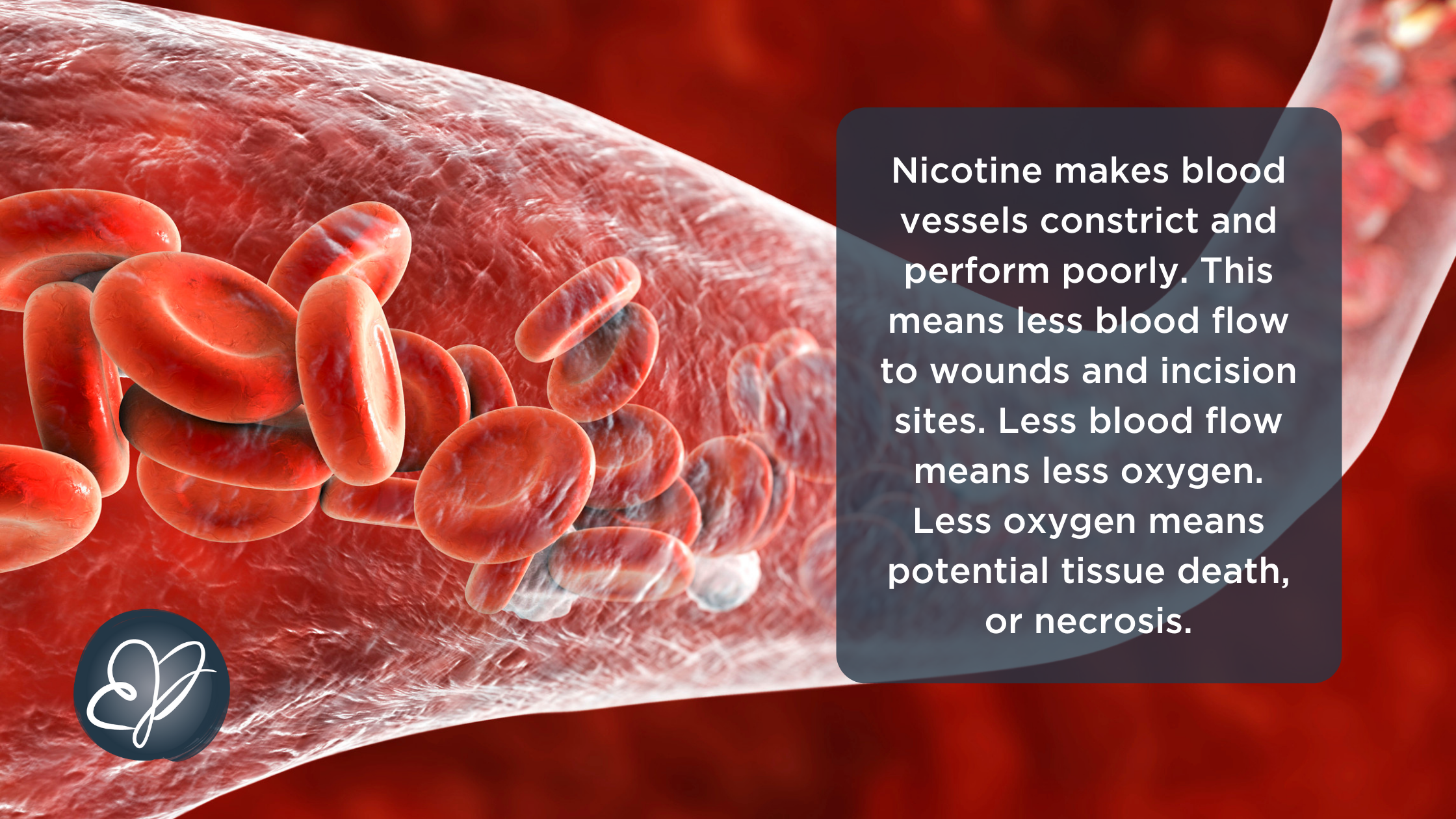
Yes, Nicotine constricts blood vessels, which can cause blood pressure to increase and reduce the amount of oxygen in the blood. Nicotine also increases adrenaline production, which can cause further narrowing of the blood vessels. Long-term use of nicotine can also damage the walls of the blood vessels, making them weaker and more prone to narrowing.
Contents
- Does Nicotine Consumption Result in Blood Vessel Constriction?
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- Question 1: Does nicotine constrict blood vessels?
- Question 2: How does nicotine constrict blood vessels?
- Question 3: What are the effects of nicotine constricting blood vessels?
- Question 4: How long does the effect of nicotine constricting blood vessels last?
- Question 5: Can nicotine constriction of blood vessels be reversed?
- Question 6: Are there any other effects of nicotine on the cardiovascular system?
Does Nicotine Consumption Result in Blood Vessel Constriction?
Nicotine is an addictive substance found in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. When ingested, nicotine can cause an array of physiological and psychological effects, including changes to the cardiovascular system. Many studies have been conducted to determine whether nicotine causes blood vessels to constrict.
The primary effect of nicotine on the cardiovascular system is to increase heart rate and blood pressure. Nicotine stimulates the release of adrenaline and other hormones, which can cause the heart to beat faster and harder, resulting in a spike in blood pressure. This can be dangerous for individuals with preexisting cardiovascular conditions, as it can put additional strain on the heart.
The effects of nicotine on the vascular system are more complex. While nicotine can cause an initial narrowing of arterial walls, long-term exposure to nicotine has been linked to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor, which can help counteract the narrowing effect. It is also worth noting that nicotine does not affect the veins in the same way that it affects the arteries.
Nicotine and its Impact on Blood Flow
Nicotine has been found to have both positive and negative effects on blood flow. In the short-term, nicotine can cause a decrease in blood flow by constricting arteries and veins. This decrease in blood flow can be beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure, as it can cause a drop in blood pressure. However, nicotine can also deprive the body of oxygen, which can be dangerous for individuals with preexisting cardiac issues.
Long-term exposure to nicotine can also have an effect on blood flow. Nicotine has been linked to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor, which can cause an increase in blood flow. This increase in blood flow can be beneficial for individuals with certain cardiovascular conditions, as it can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
The Effects of Nicotine on Blood Vessels
The effects of nicotine on blood vessels vary depending on the length of exposure. In the short-term, nicotine can cause a decrease in blood flow by constricting arteries and veins. This decrease in blood flow can be beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure, as it can cause a drop in blood pressure. However, nicotine can also deprive the body of oxygen, which can be dangerous for individuals with preexisting cardiac issues.
Long-term exposure to nicotine can also have an effect on blood vessels. Nicotine has been linked to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor, which can cause an increase in blood flow. This increase in blood flow can be beneficial for individuals with certain cardiovascular conditions, as it can help to reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
Nicotine and its Effects on the Endothelial System
The effects of nicotine on the endothelial system are complex. In the short-term, nicotine can cause a decrease in endothelial function, which can lead to a decrease in blood flow. Long-term exposure to nicotine has been linked to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor, which can help to counteract the decrease in endothelial function.
It is also worth noting that nicotine can cause changes in the chemical composition of the blood, which can have an effect on the endothelial system. Nicotine can cause an increase in the production of inflammatory cytokines, which can lead to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
The Effect of Nicotine on Other Systems
Nicotine can also have an effect on other systems in the body. Nicotine has been linked to an increased risk of cancer and other diseases, as well as an increased risk of mental health issues. Nicotine has also been linked to an increased risk of addiction, as it is highly addictive.
In addition, nicotine can cause changes in the chemical composition of the brain, which can affect cognition, memory, and emotions. Nicotine can also cause changes in the endocrine system, which can lead to an increased risk of diabetes and other metabolic diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nicotine can have both positive and negative effects on the cardiovascular system. In the short-term, nicotine can cause a decrease in blood flow by constricting arteries and veins. Long-term exposure to nicotine has been linked to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor, which can help to counteract the decrease in blood flow. Nicotine can also cause changes in the chemical composition of the blood, which can have an effect on the endothelial system. Finally, nicotine can have an effect on other systems in the body, such as the endocrine system and the brain.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: Does nicotine constrict blood vessels?
Answer: Yes, nicotine does constrict blood vessels. Studies have shown that nicotine causes the muscles in the walls of the blood vessels to contract, which results in a narrowing of the vessel and a decrease in blood flow. This constriction of the blood vessels is one of the primary mechanisms by which nicotine affects the cardiovascular system. The effects of nicotine on the blood vessels can be seen within minutes of exposure, and last for up to an hour after exposure.
Question 2: How does nicotine constrict blood vessels?
Answer: Nicotine causes constriction of the blood vessels by stimulating the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the smooth muscle cells in the walls of the blood vessels, causing the muscles to contract and resulting in a narrowing of the vessel and a decrease in blood flow. This constriction of the blood vessels is one of the primary mechanisms by which nicotine affects the cardiovascular system.
Question 3: What are the effects of nicotine constricting blood vessels?
Answer: Nicotine constriction of the blood vessels can have a variety of effects on the cardiovascular system. It can increase the risk of stroke and heart attack, as the reduced blood flow can result in a clot forming in the narrowed vessel. It can also increase the risk of high blood pressure, as the increased resistance to blood flow results in an elevation of pressure in the blood vessels. In addition, nicotine constriction of blood vessels can lead to reduced oxygen delivery to the tissues, as the oxygen-rich blood is unable to reach them.
Question 4: How long does the effect of nicotine constricting blood vessels last?
Answer: The effect of nicotine constricting blood vessels can last for up to an hour after exposure. However, the effects of nicotine on the cardiovascular system can be long-lasting and can increase the risk of stroke, heart attack, and high blood pressure.
Question 5: Can nicotine constriction of blood vessels be reversed?
Answer: Yes, the effects of nicotine constricting blood vessels can be reversed. This can be done through lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. It can also be done through medications such as ACE inhibitors, which can reduce the constriction of the blood vessels and improve blood flow.
Question 6: Are there any other effects of nicotine on the cardiovascular system?
Answer: Yes, nicotine has been shown to have a variety of other effects on the cardiovascular system. It can increase the risk of atherosclerosis by causing the accumulation of fatty deposits on the walls of the blood vessels. It can also cause an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, as well as an increase in the risk of arrhythmias. Finally, nicotine can also cause damage to the blood vessels, resulting in an increased risk of stroke and heart attack.
In conclusion, nicotine does have an effect on the human body, and it has been proven that nicotine does constrict blood vessels. Studies have shown that nicotine can have many negative effects on the body, such as increasing blood pressure and increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. It is important to be aware of the risks associated with nicotine use and to make sure that you are taking steps to reduce your chances of having any negative health effects associated with it.

