Opiates are a class of drugs that are naturally derived from the opium poppy plant. They are widely used to treat pain, as well as other conditions such as anxiety and insomnia. In recent years, there has been an increase in their misuse, leading to the development of a variety of dangerous and potentially deadly side effects. In this article, we will explore what exactly opiates are, the potential risks they pose, and why they should be used with caution. We will also discuss the treatments available to those suffering from opiate addiction.
The Meaning of Opiate
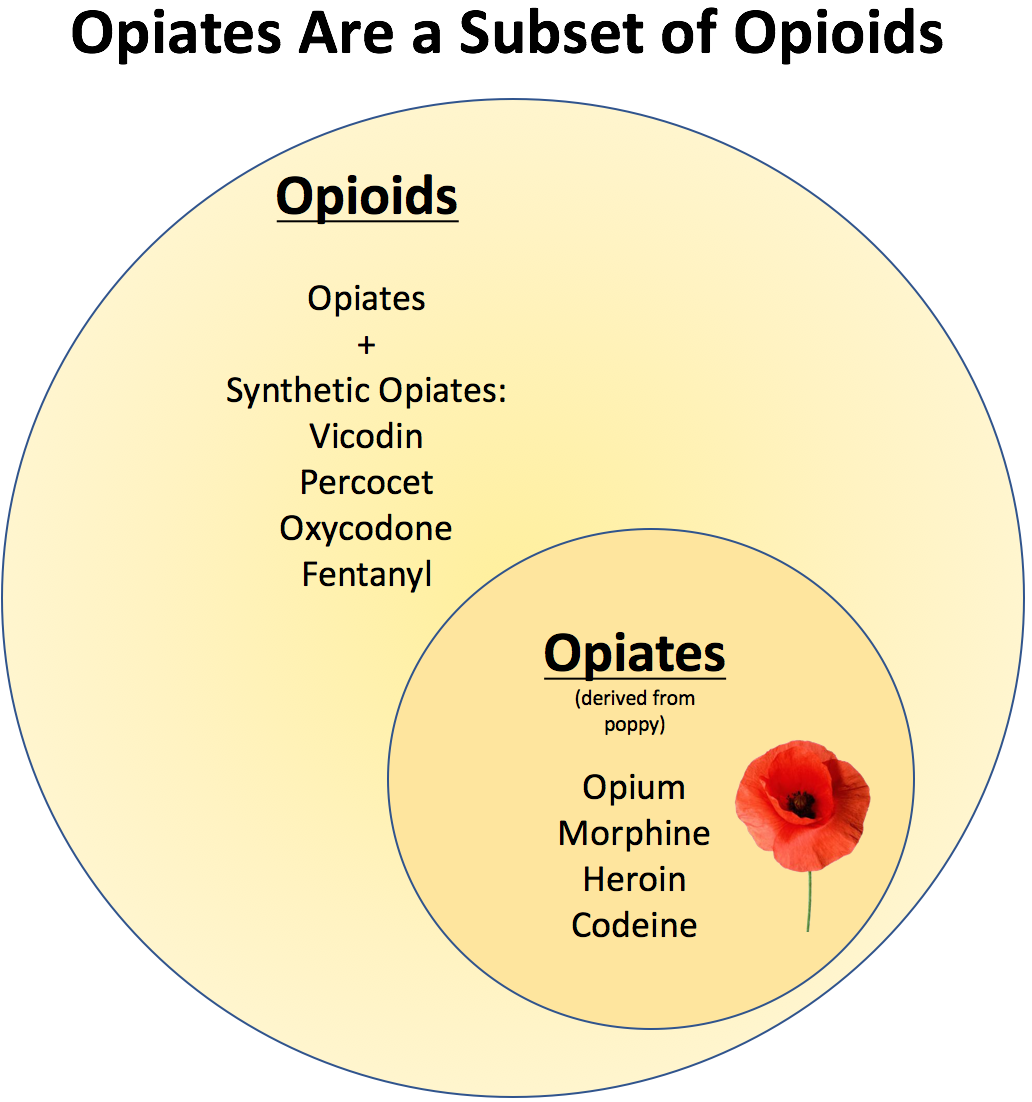
Opiate is an umbrella term used to describe a class of drugs that are derived from the opium poppy plant. This includes both natural and synthetic drugs, and they work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and body. Opiates can produce a variety of effects, including pain relief, relaxation, sedation, and euphoria. The effects of opiates depend on the dose, route of administration, and individual characteristics of the person taking the drug.
Opiate drugs are highly addictive and can have serious and potentially life-threatening side effects. These drugs are prescribed by doctors to treat moderate to severe pain, but they are often abused for their pleasurable effects. Long-term use of opiates can lead to tolerance, dependence, and addiction.
Types of Opiates
Opiate drugs can be divided into two main categories: natural and synthetic. Natural opiates are derived from the opium poppy plant and include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. These drugs are used to treat moderate to severe pain and are available in both oral and intravenous forms. Synthetic opiates are man-made drugs and include oxycodone, hydrocodone, and fentanyl. These drugs are often used to treat chronic pain, but they can also be abused for their pleasurable effects.
Opiate drugs can also be divided into two categories based on their action in the body. Short-acting opiates, such as morphine, act quickly but their effects last for a short period of time. Long-acting opiates, such as fentanyl, act more slowly but their effects last longer.
Effects of Opiates
Opiate drugs produce a range of effects, including pain relief, relaxation, sedation, and euphoria. The effects of opiates depend on the dose, route of administration, and individual characteristics of the person taking the drug. The desired effects of opiates can quickly become addictive, and long-term use of opiates can lead to tolerance, dependence, and addiction.
Opiate drugs can also have serious side effects, including nausea, vomiting, constipation, respiratory depression, and slowed heart rate. These drugs can also interfere with the brain’s ability to regulate emotions and can cause depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Treatment for Opiate Addiction
Treatment for opiate addiction typically involves a combination of medication and psychotherapy. Medications such as buprenorphine and methadone can be used to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms and to help people maintain abstinence. Psychotherapy can help people identify and address the underlying causes of their addiction and can provide support during the recovery process.
Inpatient and outpatient treatment programs may also be beneficial for people recovering from opiate addiction. These programs can provide a safe, structured environment where people can focus on their recovery and get the support they need.
Prevention of Opiate Abuse
The best way to prevent opiate abuse is to avoid taking opiate drugs. If you are prescribed an opiate drug, it is important to take the medication only as directed by your doctor. It is also important to talk to your doctor about any concerns or questions you have about the medication.
It is also important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of opiate abuse. If you notice any changes in a loved one’s behavior, such as increased secrecy, mood swings, or changes in sleeping patterns, it is important to talk to them about it.
Risks Associated With Opiate Use
Opiate use carries a number of risks, including addiction, overdose, and death. Long-term use of opiates can also lead to physical and psychological dependence, which can be difficult to break. Opiate abuse can also lead to serious health problems, including liver damage, kidney damage, and respiratory depression.
In addition, opiate use can have serious legal consequences. Possession of opiates without a prescription is illegal, and people can face severe penalties, including jail time, if they are caught with the drugs.
Conclusion
Opiate is an umbrella term used to describe a class of drugs derived from the opium poppy plant. These drugs can produce a variety of effects, including pain relief, relaxation, sedation, and euphoria. Opiate drugs are highly addictive and can have serious side effects, including nausea, vomiting, constipation, and respiratory depression. Treatment for opiate addiction typically involves a combination of medication and psychotherapy, and prevention involves avoiding opiate drugs and being aware of the signs and symptoms of abuse. Opiate use carries a number of risks, including addiction, overdose, and death.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Opiate Mean?
Answer: Opiate is a term used to describe a class of drugs that are derived from the opium poppy plant. These drugs are highly addictive, and they have powerful effects on the brain and body. They are used to relieve pain, treat addiction, and induce sleep. Common opiates include morphine, codeine, oxycodone, heroin, and fentanyl.
What Are the Effects of Opiates?
Answer: When taken, opiates can cause an intense feeling of euphoria and relaxation. They can also reduce pain, anxiety, and stress. Other effects of opiates include constipation, slowed breathing, and slowed heart rate. Long-term use of opiates can lead to physical dependence and addiction.
How Are Opiates Used?
Answer: Opiates are most commonly used as a pain reliever. They can be taken orally, injected, or inhaled. Opiates are also sometimes used to treat opioid addiction and to help people sleep.
Are Opiates Legal?
Answer: Opiates are usually only available with a prescription from a doctor, and they are tightly regulated by the government. In some cases, they are used in research or for medical purposes. However, some opiates, such as heroin, are illegal.
What Are the Risks of Taking Opiates?
Answer: Taking opiates can be risky, even when taken as prescribed. Overdosing on opiates can be fatal, and long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Other risks of taking opiates include slowed breathing, constipation, and slowed heart rate.
What Are the Alternatives to Opiates?
Answer: There are several alternatives to opiates for treating pain, such as over-the-counter medications, physical therapy, acupuncture, and yoga. Non-opioid medications, such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and naproxen, can also be used for pain relief. For treating opioid addiction, medications such as buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone can be used.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates are a group of drugs derived from the poppy plant which have powerful pain-relieving and sedative effects. These drugs may provide short-term relief from pain and anxiety, but they can also be extremely addictive and even deadly when misused. It is important to understand the risks associated with opiates before using them. With proper education, appropriate medical advice, and a commitment to safety, those who need opiates can use them responsibly and benefit from the relief they provide.