Opiate addiction is a serious issue that can have a devastating impact on an individual’s life. It can cause extreme physical and psychological distress, including withdrawal symptoms. If you or someone you know is struggling with opiate addiction, it’s important to understand how to stop opiate withdrawal. This article will provide an overview of the steps you can take to lessen the severity of the withdrawal symptoms and make the recovery process easier.
Steps to stop Opiate Withdrawal:
- Visit your doctor or a drug treatment center.
- Tell them about your opiate use and withdrawal symptoms.
- They will suggest medications to help with your withdrawal.
- They might also recommend counseling to help you stay clean.
- Take medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Eat nutritious foods to help your body heal.
- Exercise regularly to reduce stress and promote endorphins.
- Get plenty of rest and relaxation.
- Join a support group to help you stay motivated.
How to Manage Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms
Opiate withdrawal is a difficult process and can be both uncomfortable and dangerous. It is important to understand the signs and symptoms of opiate withdrawal and how to manage them. There are a variety of strategies that can help make the process easier, including medication, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. With the right treatment plan, opiate withdrawal can be made more manageable.
Talking to a Medical Professional
The first step in managing opiate withdrawal is talking to a medical professional. A doctor can provide information about the different treatments available and help to create a personalized plan. They can also provide medications to help ease withdrawal symptoms, such as anti-nausea drugs and painkillers. It is important to remember that medical professionals should be consulted before starting any type of treatment.
Making Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can also help to ease the symptoms of opiate withdrawal. Eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding substances such as alcohol can all be beneficial. It is also important to get plenty of rest and to practice relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing. These lifestyle changes can help to reduce stress and make the withdrawal process less uncomfortable.
Getting Emotional Support
It is also important to seek out emotional support during the opiate withdrawal process. This can include talking to family and friends, attending support groups, or seeing a therapist. Having a supportive network of people can help to make the process easier and provide much-needed encouragement.
Managing Withdrawal Symptoms with Medication
Medication can be an effective way to manage opiate withdrawal symptoms. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and anti-seizure drugs can all be used to ease withdrawal symptoms. It is important to talk to a doctor before starting any type of medication, as some medications can have dangerous side effects.
Using Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies can also be used to manage opiate withdrawal. Acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic treatments can all help to reduce withdrawal symptoms. Herbal supplements such as kratom and kava can also be used to help manage symptoms. It is important to talk to a doctor before starting any type of alternative therapy.
Managing Cravings
Managing cravings is an important part of the opiate withdrawal process. Cognitive behavioral therapy can be used to help identify triggers and develop strategies to cope with cravings. Avoiding people, places, and activities that can trigger cravings can also be helpful.
Staying Motivated
Staying motivated is key to managing opiate withdrawal. Setting small, achievable goals can help to keep motivation high. It is also important to remember that the process of withdrawal is not easy but that there is light at the end of the tunnel. With the right treatment plan and plenty of support, opiate withdrawal can be managed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Opiate Withdrawal?
Opiate withdrawal is a set of physical, psychological, and emotional symptoms caused by the sudden discontinuation of opiates after prolonged or excessive use. Common opiates include drugs like morphine, codeine, and heroin. Symptoms of opiate withdrawal include nausea, vomiting, sweating, and muscle aches. Other symptoms may include anxiety, insomnia, and diarrhea. Withdrawal can be an unpleasant and uncomfortable experience, and can even lead to serious health complications.
What Causes Opiate Withdrawal?
Opiate withdrawal is caused by the sudden discontinuation of opiates after prolonged or excessive use. When opiates are used repeatedly, the body becomes dependent on them and begins to rely on them to achieve a certain level of functioning. When the person suddenly stops taking opiates, the body must readjust and begin to function without them. This readjustment process is what causes the symptoms of opiate withdrawal.
What are the Symptoms of Opiate Withdrawal?
Common symptoms of opiate withdrawal include nausea, vomiting, sweating, muscle aches, anxiety, insomnia, and diarrhea. Other symptoms can include abdominal cramping, agitation, irritability, cravings for opiates, increased heart rate, and high blood pressure.
How can Opiate Withdrawal be Treated?
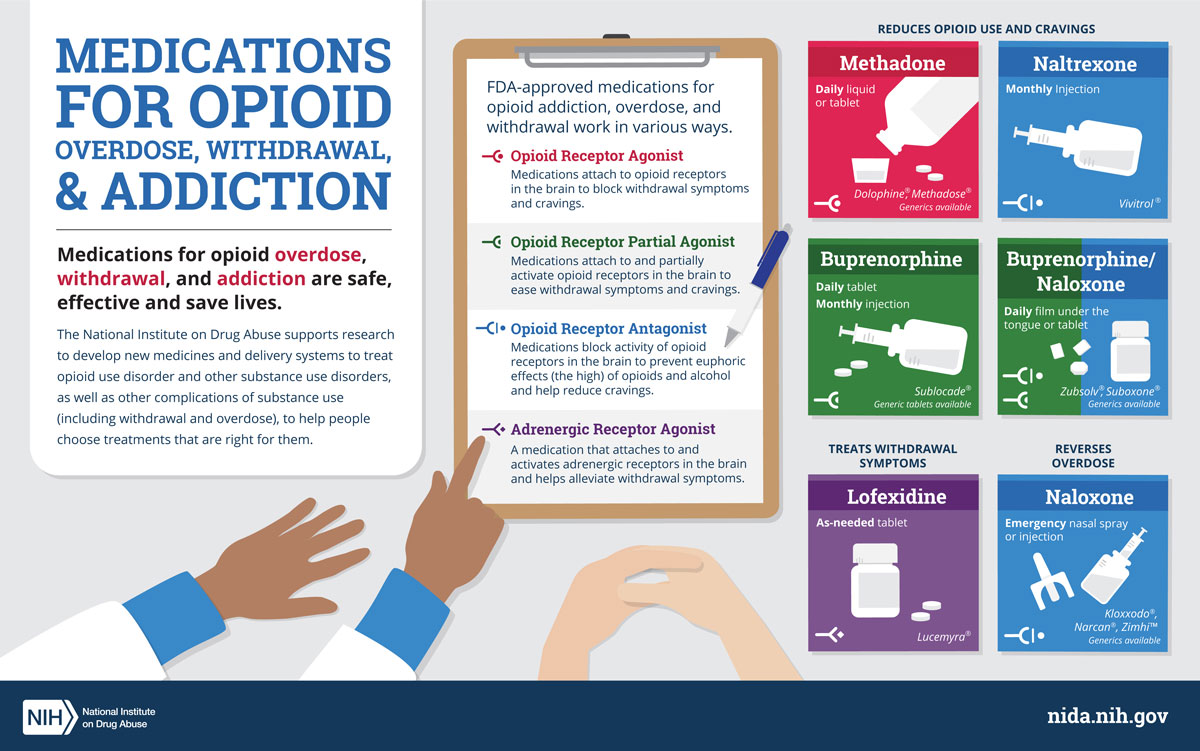
Opiate withdrawal can be treated with a variety of medications, including buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone. These medications can help reduce the severity of the withdrawal symptoms and make the process more manageable. In addition, counseling and behavioral therapy can help the person develop new coping strategies to manage their addiction.
What are the Long-term Effects of Opiate Withdrawal?
The long-term effects of opiate withdrawal can include depression, anxiety, insomnia, and changes in appetite. In some cases, the person may experience cravings for opiates for months or even years after discontinuing use. Additionally, the person may have difficulty concentrating and have impaired judgment.
How to Stop Opiate Withdrawal?
The best way to stop opiate withdrawal is to seek professional help. A doctor or addiction specialist can help the person identify the best treatment options for their individual situation. This may include medications, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Additionally, the person should avoid any further use of opiates, as this can worsen the withdrawal symptoms and lead to more serious health complications.
Opioid Withdrawal
Opiate withdrawal can be a difficult process to go through, but it is possible to manage the symptoms through a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. With the right support, you can safely and effectively manage the symptoms of opiate withdrawal and move forward with your life in a healthier and happier direction. Don’t give up hope; seek out the help you need to get through this tough time and come out stronger on the other side.

