Drugs often have a powerful impact on the brain, influencing how the brain’s neurotransmitters work. Neurotransmitters are the brain’s chemical messengers, responsible for sending signals from one nerve cell to another, and play a major role in regulating our moods, memories, and behavior. In this article, we’ll examine how drugs can affect these neurotransmitters, and how this can have a wide range of effects on our mental and physical health. So let’s dive into the fascinating world of neurotransmitters and drugs and explore how they interact with one another.
Drugs affect neurotransmitters by altering the way in which they interact with receptors in the brain. Some drugs can act as agonists, which increase the activity of a neurotransmitter, while others can act as antagonists, which decrease the activity of a neurotransmitter. Drugs can also alter the amount of neurotransmitter available by either inhibiting its release or blocking its reuptake.
Contents
- What Are Neurotransmitters and How Do They Affect The Brain?
- How Do Drugs Affect Neurotransmitters In the Brain?
- How Do Different Types of Drugs Affect Neurotransmitters?
- How Can Neurotransmitter Levels Be Affected By Long-Term Drug Use?
- What Are The Risks Of Affecting Neurotransmitters With Drugs?
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What are neurotransmitters?
- 2. How do drugs affect neurotransmitters?
- 3. What are the long-term effects of drug use on neurotransmitters?
- 4. How are neurotransmitters affected by different drugs?
- 5. What are the potential dangers of drug use?
- 6. Is it possible to reverse the effects of drug use on neurotransmitters?
What Are Neurotransmitters and How Do They Affect The Brain?
Neurotransmitters are chemicals in the brain that transmit signals between neurons. They play an important role in the regulation of motor movement, emotions, learning and memory, and other cognitive processes. Neurotransmitters are responsible for the communication between neurons in the brain, and they can be affected by drugs. Drugs can either increase or decrease the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, which can lead to changes in behavior and cognition.
Neurotransmitters are produced by the brain in response to different stimuli and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they are picked up by the receptors of other neurons. The neurotransmitters then travel across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the receiving neuron, which can lead to an action potential. This action potential can then lead to the release of other neurotransmitters, creating a chain reaction in the brain.
Neurotransmitters can also be affected by drugs. Drugs can either increase or decrease the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, which can lead to changes in behavior and cognition. For example, some drugs can increase serotonin levels, which can lead to increased feelings of happiness and relaxation. Other drugs can decrease dopamine levels, which can lead to decreased motivation and pleasure.
How Do Drugs Affect Neurotransmitters In the Brain?
Drugs can affect neurotransmitters in the brain by either increasing or decreasing the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain. Drugs can increase neurotransmitter levels by either increasing the amount of neurotransmitter released from neurons or by blocking the reuptake of neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft. Drugs can also decrease neurotransmitter levels by blocking the release of neurotransmitter from neurons or by increasing the reuptake of neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft.
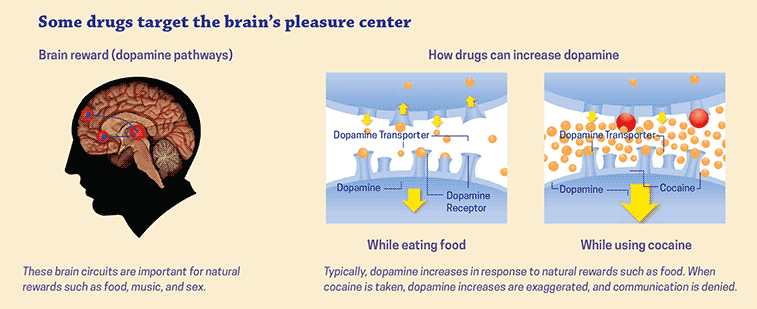
Drugs that increase neurotransmitter levels can lead to changes in behavior and cognition. For example, antidepressants increase the levels of serotonin in the brain, which can lead to increased feelings of happiness and relaxation. Stimulants, such as cocaine, increase the levels of dopamine in the brain, which can lead to increased feelings of alertness and pleasure.
Drugs that decrease neurotransmitter levels can also lead to changes in behavior and cognition. For example, antipsychotics decrease the levels of dopamine in the brain, which can lead to decreased symptoms of psychosis such as delusions and hallucinations. Sedatives decrease the levels of GABA in the brain, which can lead to decreased anxiety and increased relaxation.
How Do Different Types of Drugs Affect Neurotransmitters?
Different types of drugs can affect neurotransmitters in different ways. Stimulants, such as cocaine and amphetamines, increase the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to increased alertness and pleasure. Antidepressants, such as SSRIs, increase the levels of serotonin in the brain, which can lead to increased feelings of happiness and relaxation.
Antipsychotics decrease the levels of dopamine in the brain, which can lead to decreased symptoms of psychosis such as delusions and hallucinations. Sedatives decrease the levels of GABA in the brain, which can lead to decreased anxiety and increased relaxation. Opioids increase the levels of endorphins and enkephalins in the brain, which can lead to increased feelings of pleasure and pain relief.
How Can Neurotransmitter Levels Be Affected By Long-Term Drug Use?
Long-term drug use can have significant effects on neurotransmitter levels in the brain. Long-term use of stimulants, such as cocaine and amphetamines, can lead to decreased levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to decreased alertness and pleasure. Long-term use of antidepressants, such as SSRIs, can lead to decreased levels of serotonin in the brain, which can lead to decreased feelings of happiness and relaxation.
Long-term use of antipsychotics can lead to increased levels of dopamine in the brain, which can lead to increased symptoms of psychosis such as delusions and hallucinations. Long-term use of sedatives can lead to increased levels of GABA in the brain, which can lead to increased anxiety and decreased relaxation. Long-term use of opioids can lead to decreased levels of endorphins and enkephalins in the brain, which can lead to decreased feelings of pleasure and increased pain.
What Are The Risks Of Affecting Neurotransmitters With Drugs?
Affecting neurotransmitters with drugs can have significant risks. Long-term use of drugs can lead to decreased levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, which can lead to decreased cognitive function, increased risk of mental health problems, and increased risk of addiction. Additionally, drugs can have significant side effects, such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased risk of stroke.
Risk of Addiction
Drugs that affect the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain can have significant risks of addiction. Drugs that increase dopamine levels, such as stimulants, can lead to a reward pathway being created in the brain, which can lead to an increased risk of addiction. Additionally, drugs that decrease neurotransmitter levels, such as sedatives, can lead to a physical dependence on the drug, which can lead to an increased risk of addiction.
Risk of Mental Health Problems
Drugs that affect the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain can also have significant risks of mental health problems. Long-term use of drugs that increase dopamine levels, such as stimulants, can lead to increased risk of depression and anxiety. Long-term use of drugs that decrease neurotransmitter levels, such as sedatives, can lead to increased risk of psychosis and paranoia.
Risk of Decreased Cognitive Function
Long-term use of drugs that affect the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain can also lead to decreased cognitive function. Long-term use of drugs that increase dopamine levels, such as stimulants, can lead to decreased memory and concentration. Long-term use of drugs that decrease neurotransmitter levels, such as sedatives, can lead to decreased motor coordination and reaction time.
Risk of Physical Side Effects
Drugs that affect neurotransmitters in the brain can also have significant risks of physical side effects. Stimulants, such as cocaine and amphetamines, can lead to increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased risk of stroke. Sedatives, such as benzodiazepines, can lead to increased risk of dizziness, drowsiness, and respiratory depression.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are specialized chemical messengers that are released from nerve cells to send signals to other cells in the body. They are involved in a variety of functions, including memory, mood, sleep, and muscle control. Neurotransmitters are also involved in the reward pathways of the brain, which are responsible for the pleasurable feeling associated with drug use.
2. How do drugs affect neurotransmitters?
Drugs can alter the way neurotransmitters are released and received in the brain. For example, some drugs, such as opioids, can increase the amount of the neurotransmitter dopamine released in the brain, resulting in feelings of euphoria. Other drugs, such as alcohol, can block the receptors that normally receive neurotransmitters, resulting in changes in mood, behavior, and motor control.
3. What are the long-term effects of drug use on neurotransmitters?
Long-term use of drugs can have a significant effect on neurotransmitters, leading to significant changes in the brain’s reward pathways. This can lead to a decrease in the production and release of neurotransmitters, resulting in decreased pleasure and reward. It can also lead to increased tolerance to the drug, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect.
4. How are neurotransmitters affected by different drugs?
Different drugs can have different effects on neurotransmitters. For example, opioids can increase dopamine levels, resulting in feelings of euphoria, while alcohol can block the receptors that normally receive neurotransmitters, resulting in changes in mood, behavior, and motor control. Stimulants can also increase dopamine levels, while depressants can decrease them.
5. What are the potential dangers of drug use?
There are a number of potential dangers associated with drug use, including addiction, physical and psychological dependence, and increased risk of overdose. Chronic drug use can also lead to significant changes in the brain’s reward pathways, resulting in decreased pleasure and reward. In addition, drug use can also lead to increased risk of developing mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety.
6. Is it possible to reverse the effects of drug use on neurotransmitters?
In some cases, the effects of drug use on neurotransmitters can be reversed with time and abstinence from the drug. However, this is not always the case and the effects can be long-lasting. In addition, some drugs can cause irreversible damage to the brain, such as brain damage and neuronal death. Therefore, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible if drug use is suspected.
Drugs have a powerful effect on neurotransmitters, altering their activity and affecting the way messages are passed across the brain. These changes can cause serious health issues, from addiction to depression to psychotic behavior. It’s important to understand how drugs affect neurotransmitters so that you can make informed decisions about your own health. With the right knowledge and support, it is possible to make healthier decisions and reduce the risks of addiction and other drug-related problems.

