Opiates have become a growing problem across the world, as they can be highly addictive and have a range of adverse side effects. While people may not immediately associate dopamine with opiates, it is worth exploring the potential link between these two substances. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter found in the brain that plays a key role in regulating emotions and pleasure. In this article, we will discuss whether dopamine can be considered an opiate, and what effects this could have on the body.
Contents
What is Dopamine and Is it an Opiate?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger found in the brain that is involved in the reward system and regulating emotion. Its primary function is to act as a reward for certain behaviors, helping to create a feeling of pleasure. Dopamine is also involved in movement, cognition, learning, and attention. It is often referred to as the “happy hormone” because it is associated with feelings of pleasure and motivation. So, is dopamine an opiate? The answer is no; dopamine is not an opiate.
What is an Opiate?
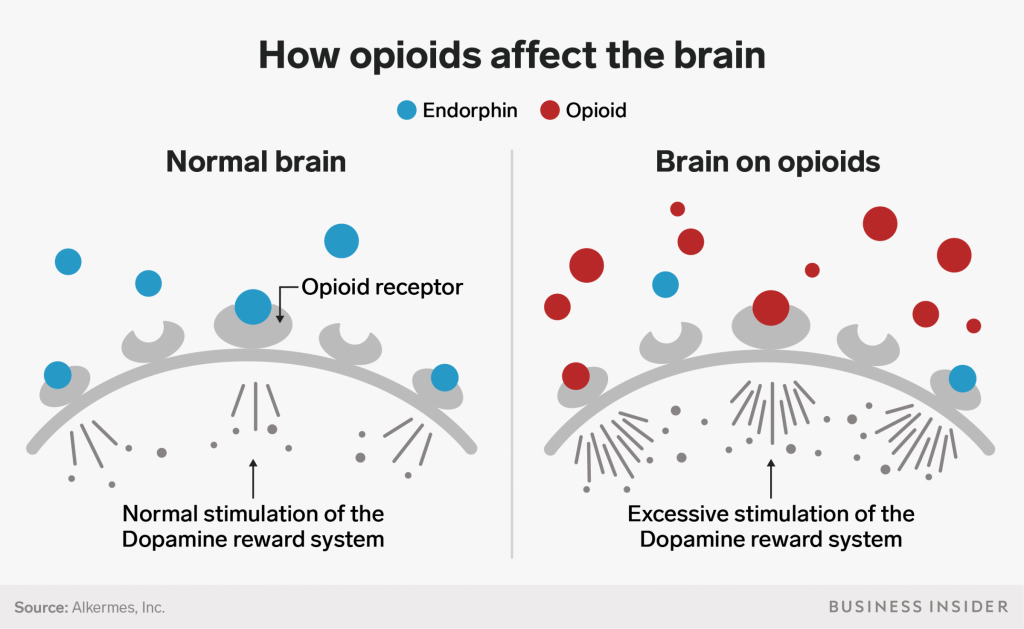
An opiate is a type of drug derived from the opium poppy plant. Opiates work by binding to specific receptors in the brain, which can lead to feelings of pleasure, relaxation, and sedation. The most common opiates are morphine and codeine, which are used to treat pain but can also be abused. Other opiates include heroin, hydrocodone, fentanyl, and oxycodone. While opiates can produce feelings of pleasure, they also carry the risk of addiction and other serious side effects.
What are the Effects of Opiates?
Opiate use can lead to physical dependence, which means that the body becomes accustomed to the drug and requires higher doses to achieve the same effects. This can lead to a cycle of abuse in which the user needs more and more of the drug to experience the desired effects. In addition, opiates can have severe side effects such as nausea, constipation, and respiratory depression. Long-term opiate use can also lead to addiction, which is a chronic and debilitating condition characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behavior and relapse.
What are the Benefits of Dopamine?
Unlike opiates, dopamine does not produce feelings of pleasure or relaxation. Instead, it helps to regulate mood, attention, and reward-seeking behavior. As a result, dopamine plays a key role in motivation and can help people stay focused on tasks and overcome challenges. It is also involved in the reward system, which helps people recognize and repeat behaviors that are beneficial. Additionally, dopamine has been linked to improved memory, learning, and decision-making.
Are There Any Risks Associated with Dopamine?
Although dopamine does not carry the same risks as opiates, there are still some potential risks associated with its use. For example, dopamine levels that are too high or too low can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and depression. Additionally, excessive dopamine release can lead to behavioral problems such as aggression, addiction, and impulsivity.
How is Dopamine Regulated?
The brain regulates dopamine levels through a series of complex processes. The first step is the release of dopamine from neurons, which is regulated by the brain’s reward system. This system helps to reward behaviors that are beneficial, such as eating and exercising. The release of dopamine is also regulated by other neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine.
Can Dopamine be Manipulated?
Yes, dopamine levels can be manipulated through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly can help to maintain healthy levels of dopamine in the brain. Additionally, certain supplements such as L-tyrosine and dopamine precursors can be taken to increase dopamine levels. However, it is important to speak to a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, or chemical messenger, that plays an important role in how we think, feel and move. It is involved in reward-motivated behavior, regulating emotions, and controlling movement. Dopamine is released in response to pleasurable activities like eating and sex, as well as when we accomplish goals or receive recognition. Low dopamine levels have been linked to depression, ADHD, Parkinson’s disease, and other conditions.
Where is Dopamine found in the body?
Dopamine is found in the brain, where it is produced by nerve cells located in the brainstem and in certain areas of the cortex. It is also found in other parts of the body, including the heart, kidneys, and pancreas.
Is Dopamine an Opiate?
No, dopamine is not an opiate. Opiates are drugs derived from the opium poppy plant, such as morphine and codeine, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain and produce pain relief. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that acts on dopamine receptors, and is not an opiate.
What are the effects of Dopamine?
The effects of dopamine depend on its location in the brain. In the nucleus accumbens, dopamine is involved in reward-motivated behavior and is released in response to pleasurable activities like eating and sex. In the prefrontal cortex, dopamine is involved in decision-making and regulating emotions. In the basal ganglia, dopamine is involved in the control of movement.
What are the symptoms of low Dopamine?
Low dopamine levels can result in symptoms such as fatigue, depression, poor concentration, lack of motivation, and lack of pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable. Low dopamine levels have also been linked to a number of conditions, including ADHD, Parkinson’s disease, and schizophrenia.
How is Dopamine regulated?
Dopamine is regulated by a number of factors, including hormones, neurotransmitters, and drugs. Hormones such as cortisol, estrogen, and testosterone can influence dopamine levels, as can certain neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine. Drugs such as antidepressants and antipsychotics can also affect dopamine levels.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, dopamine is not an opiate. It is a neurotransmitter found in the brain and is responsible for regulating motivation and pleasure. Studies have shown that dopamine can be released when people experience positive emotions, such as joy and excitement, as well as when they experience pain. While dopamine does not have the same effects as opiates, it can affect our moods and motivation in a similar way. Therefore, understanding dopamine is important in order to better understand our behavior and the way we respond to various stimuli.

