Have you ever wondered what happens to your brain when you smoke cigarettes or use nicotine products? The answer might surprise you. Studies have shown that nicotine can have both short-term and long-term effects on the brain, including changes in brain chemistry and structure. In this article, we will discuss how nicotine affects the brain, both in the short-term and in the long-term, and explore the implications of this knowledge. So, if you want to know more about the dangers of nicotine, keep reading!
Nicotine affects the brain by eliciting a response from the central nervous system that results in increased heart rate, alertness, and concentration. Nicotine also increases levels of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, in the brain. This can lead to increased motivation, a feeling of relaxation, and even cravings for more nicotine. Over time, the body becomes used to the presence of nicotine, and the effects become less pronounced.
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is a substance found in the tobacco plant, which is used to make cigarettes and other tobacco products. It is a stimulant and is highly addictive. Nicotine acts on the central nervous system, producing a feeling of relaxation and pleasure. It also increases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration, and can increase alertness.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Brain?
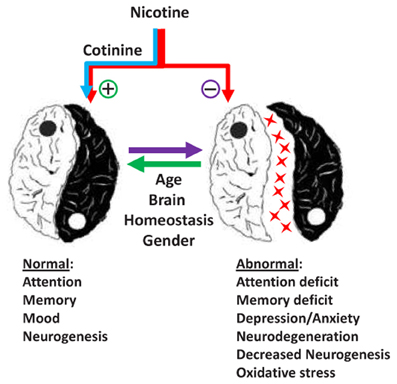
Nicotine affects the brain by producing a feeling of pleasure and satisfaction. It does this by increasing the amount of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is responsible for pleasure and reward. Nicotine also binds to acetylcholine receptors, which are involved in learning and memory. Nicotine also affects other parts of the brain, including the hypothalamus, which regulates hunger, thirst, and body temperature, and the hippocampus, which is involved in memory formation and recall.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Nicotine on the Brain?
Long-term exposure to nicotine can lead to an increased risk of developing certain neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, depression, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Furthermore, long-term nicotine use has been linked to an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, nicotine can affect the functioning of the brain, making it harder for an individual to concentrate and learn new information.
What are the Short-Term Effects of Nicotine on the Brain?
In the short-term, nicotine can produce a feeling of euphoria and a sense of alertness. This is due to the release of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which stimulate the reward centers of the brain. Additionally, nicotine can increase heart rate and respiration, leading to a feeling of relaxation and pleasure.
What Are the Risks of Short-Term Nicotine Use?
Short-term use of nicotine can have negative effects on the body, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, nicotine can cause dizziness, nausea, and headaches. Furthermore, nicotine can affect the functioning of the brain, making it harder for an individual to concentrate and learn new information.
What Are the Risks of Long-Term Nicotine Use?
Long-term use of nicotine can lead to an increased risk of developing certain neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, depression, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Furthermore, long-term nicotine use has been linked to an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, nicotine can affect the functioning of the brain, making it harder for an individual to concentrate and learn new information.
Related Faq
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is an alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants, which are native to North and South America, as well as in many other plants. It is an addictive stimulant and is the primary psychoactive component of tobacco. It is most commonly found in cigarettes, cigars, and other traditional forms of tobacco. Nicotine acts on the central nervous system and brain, and it can have both a short-term and long-term effect on the body.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Brain?
When nicotine is taken into the body, it quickly makes its way to the brain, where it binds to receptors and affects the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine. This can lead to an increase in alertness, concentration, and pleasure. In the short-term, nicotine can act as a stimulant, making people feel more alert and awake. In the long-term, nicotine can lead to addiction, as the body becomes increasingly dependent on nicotine and people need more and more of it to achieve the same effects. It can also lead to changes in the brain that can cause an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
What Are the Short-Term Effects of Nicotine?
The short-term effects of nicotine include increased alertness, concentration, and pleasure, as well as increased heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration rate. It can also lead to increased consumption of food and water, nausea, and dizziness. Short-term nicotine use can also cause irritability, insomnia, and restlessness.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Nicotine?
The long-term effects of nicotine include addiction, an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other health issues. It can also lead to changes in the brain that can cause an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Long-term nicotine use can also lead to an increased risk of developing respiratory problems, such as COPD and asthma.
What Are the Risks of Long-Term Nicotine Use?
The risks of long-term nicotine use include addiction, an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other health issues. It can also lead to changes in the brain that can cause an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Long-term nicotine use can also lead to an increased risk of developing respiratory problems, such as COPD and asthma. Additionally, long-term nicotine use can lead to an increased risk of developing gum disease and other dental issues.
Can Nicotine Have Positive Effects?
Despite its addictive nature, nicotine has been found to have some positive effects in certain cases. For example, it has been found to help people with ADHD focus better, and can help people with certain types of dementia and Parkinson’s disease improve their motor skills. Additionally, nicotine has been found to be helpful in treating certain types of pain, as well as depression and anxiety. However, it is important to note that nicotine is still an addictive substance, and its potential positive effects should be weighed against the potential risks.
Nicotine has a powerful and negative effect on the brain, and its consequences can be long-lasting. Not only does nicotine affect the brain in a variety of ways, but it also has the potential to be highly addictive. The consequences of nicotine addiction can have a devastating effect on one’s physical and mental health, resulting in a wide range of health problems. We must take the time to educate ourselves on the risks of nicotine and how it can affect our health and wellbeing. By understanding the dangers of nicotine, we can make informed decisions and take the necessary steps to protect our health and reduce the risks associated with nicotine.

