When it comes to opiate withdrawal, understanding the timeline of the process can be essential in getting the right treatment and support needed. Withdrawal can be an intense and uncomfortable experience, and if you or someone you know is dealing with an opioid addiction, knowing how long it takes for the withdrawal process to begin can help you prepare. In this article, we will explore the timeline and symptoms of opiate withdrawal, so that you can be better informed and ready for the journey ahead.
Contents
- What is Opiate Withdrawal?
- Factors Affecting the Duration of Withdrawal Symptoms
- How to Manage Opiate Withdrawal
- Risks of Untreated Opiate Withdrawal
- Conclusion
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- How Long Does Opiate Withdrawal Take to Start?
- Are Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms the Same for Everyone?
- What Can Help Ease Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms?
- How Long Does it Take to Overcome Opiate Withdrawal?
- What is the Risk of Relapse with Opiate Withdrawal?
- What is the Best Treatment Option for Opiate Withdrawal?
- How Long Does Opioid Withdrawal Last?
What is Opiate Withdrawal?
Opiate withdrawal is the physical and psychological symptoms that occur when someone who has been using opiates regularly stops taking them. It is caused by the sudden absence of the drugs that have been controlling the body’s opiate receptors. Symptoms of opiate withdrawal can range from mild to severe, and may last from a few days to several weeks.
Types of Symptoms
The most common symptoms of opiate withdrawal include anxiety, irritability, nausea, sweating, chills, insomnia, muscle aches and pains, diarrhea, vomiting, and an increased heart rate. Some people experience more severe symptoms such as depression, suicidal thoughts, and hallucinations.
Timing of Withdrawal Symptoms
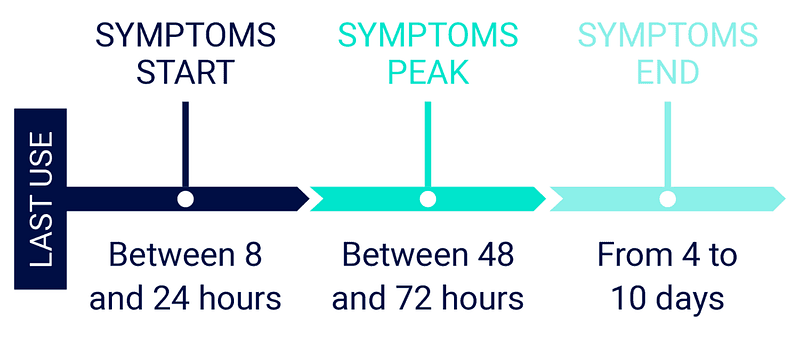
The timing of opiate withdrawal symptoms can vary depending on the type of opiate and the amount that was taken. Generally, withdrawal symptoms start within 6-12 hours after the last dose of opiate is taken and may peak between 24-72 hours. The symptoms usually begin to subside after 5-7 days, although some symptoms can last for weeks or longer.
Factors Affecting the Duration of Withdrawal Symptoms
The duration and severity of opiate withdrawal symptoms can be affected by a number of factors, including:
Type of Opiate Used
The type of opiate used can affect how long it takes for withdrawal symptoms to start. Generally, shorter-acting opiates such as heroin and oxycodone will cause withdrawal symptoms to start sooner than longer-acting opiates such as methadone and buprenorphine.
Amount of Opiate Taken
The amount of opiate taken can also affect the timing and severity of withdrawal symptoms. Generally, higher doses of opiates will cause more severe withdrawal symptoms and take longer to start.
How to Manage Opiate Withdrawal
Opiate withdrawal can be managed with the help of medications and other treatments. Medications such as buprenorphine and methadone can help to reduce the severity of withdrawal symptoms and make them more bearable. Other treatments such as counseling and support groups can also help to manage the physical and psychological symptoms of opiate withdrawal.
Risks of Untreated Opiate Withdrawal
Untreated opiate withdrawal can lead to serious health complications, including dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and even death. If you are experiencing withdrawal symptoms, it is important to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Conclusion
Opiate withdrawal can be a difficult and uncomfortable process, but it is possible to manage it with the help of medications and other treatments. The length and severity of withdrawal symptoms can vary depending on the type and amount of opiate used, but they typically start within 6-12 hours after the last dose and can last for up to several weeks. It is important to seek medical help if you are experiencing withdrawal symptoms, as untreated withdrawal can lead to serious health complications.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Opiate Withdrawal Take to Start?
Answer: The time it takes for opiate withdrawal to start can vary greatly depending on the individual and the type of opiate they have been using. Generally, symptoms begin to appear within 6-12 hours after the last dose, with peak intensity of symptoms occurring within 72-96 hours. The duration of withdrawal can range from a few days to several weeks.
Are Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms the Same for Everyone?
Answer: No, the severity of opiate withdrawal symptoms can depend on many factors, including the type of opiate used, the length and amount of time it was used, the individual’s metabolism, and any underlying medical conditions. Common opiate withdrawal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle aches, sweating, fatigue, anxiety, insomnia, and cravings for the drug.
What Can Help Ease Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms?
Answer: There are several medications that can help to ease the symptoms of opiate withdrawal. These include non-opioid medications, such as clonidine or buprenorphine, as well as opioid replacement therapy, such as methadone or buprenorphine. Additionally, the use of certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids and SAMe, can help to reduce the severity of opiate withdrawal symptoms.
How Long Does it Take to Overcome Opiate Withdrawal?
Answer: It can take anywhere from several days to several weeks to overcome opiate withdrawal, depending on the individual and the type of opiate they have been using. It is important to note that withdrawal symptoms can still persist even after the acute phase of withdrawal has passed. It is also important to seek professional treatment in order to ensure a successful recovery.
What is the Risk of Relapse with Opiate Withdrawal?
Answer: The risk of relapse with opiate withdrawal is very high, especially if the individual does not seek professional treatment. The relapse rate for individuals who do not receive treatment is approximately 95%. It is important to seek professional help in order to ensure a successful recovery.
What is the Best Treatment Option for Opiate Withdrawal?
Answer: The best treatment option for opiate withdrawal is to seek professional treatment. Treatment options can include both inpatient and outpatient programs, medications, or a combination of the two. Treatment should be tailored to the individual’s needs and should include strategies to reduce the risk of relapse. Additionally, ongoing support and counseling can help to ensure a successful recovery.
How Long Does Opioid Withdrawal Last?
The answer to the question “How long does opiate withdrawal take to start?” is variable depending on the individual. Generally, opiate withdrawal symptoms will begin within 6-12 hours of the last dose and peak within a few days. Withdrawal symptoms can last up to a month, but they will typically become less intense as time goes on. Withdrawal can be an uncomfortable process, but there are treatments and medications available to help ease the symptoms. If you or a loved one is experiencing opiate withdrawal, it is important to seek medical help and support.

